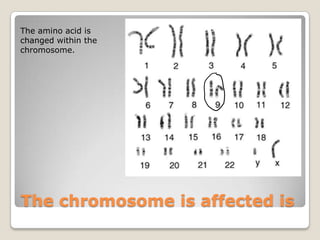
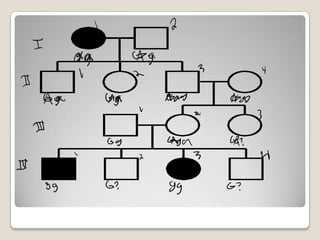
Galactosemia is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation in the GALT gene that results in the inability to break down the sugar galactose. It primarily affects babies and can cause failure to thrive, jaundice, infections, and cataracts if not treated by removing galactose from the diet. People with Romani descent have a higher risk of carrying the autosomal recessive mutation. The mutation changes an amino acid in the GALT enzyme needed to break down galactose, leading to its buildup in the blood if untreated.