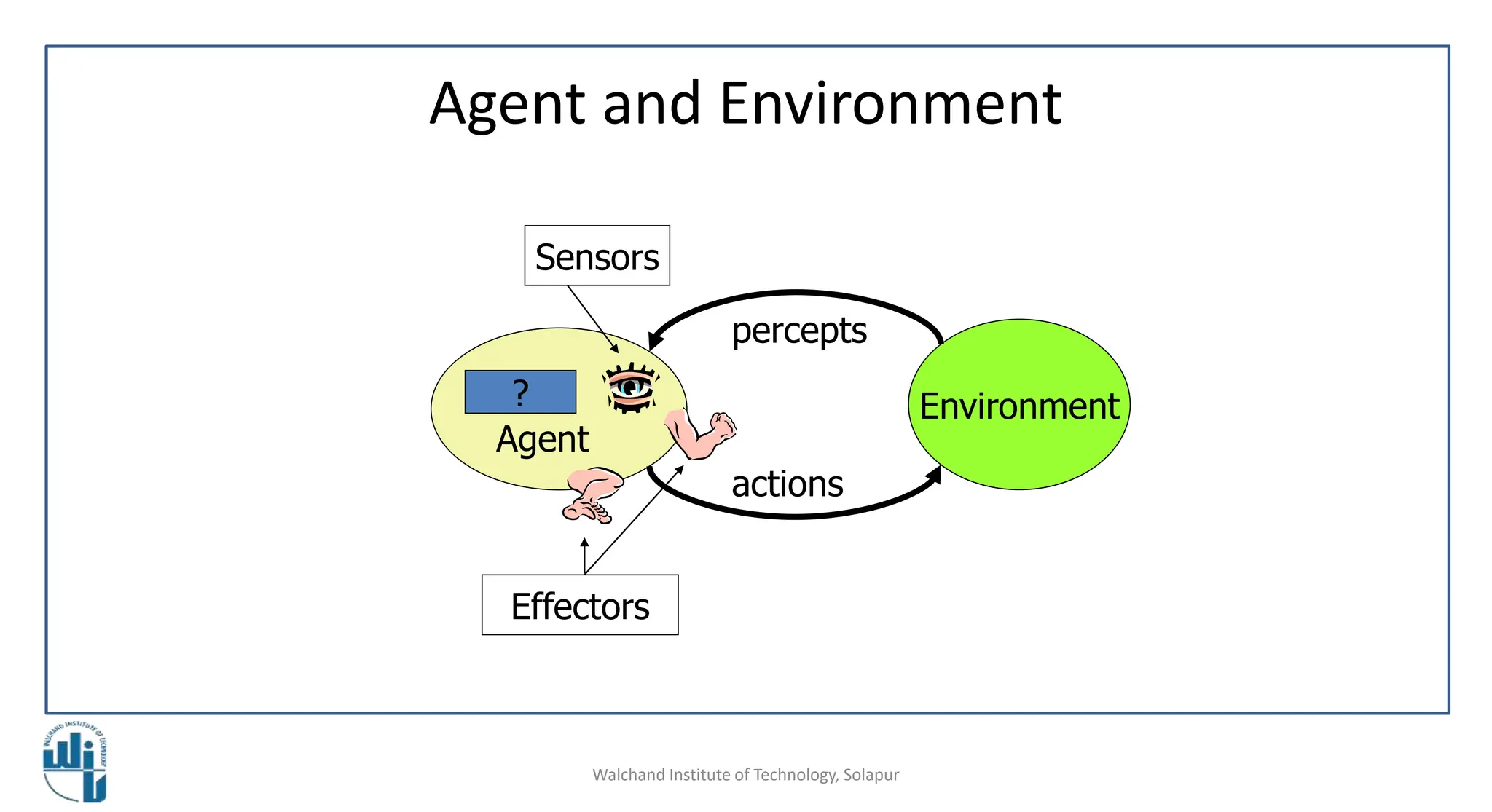
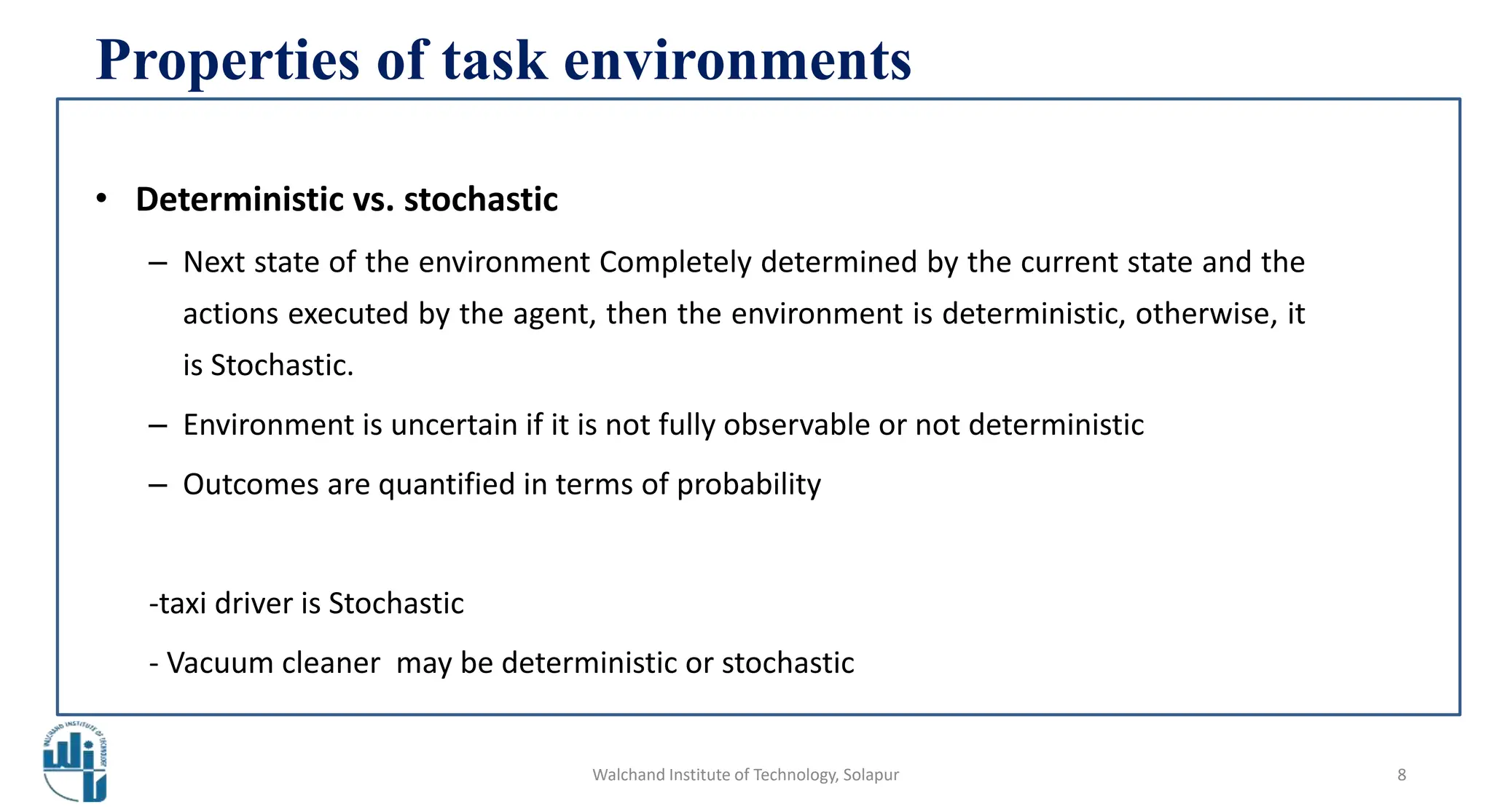
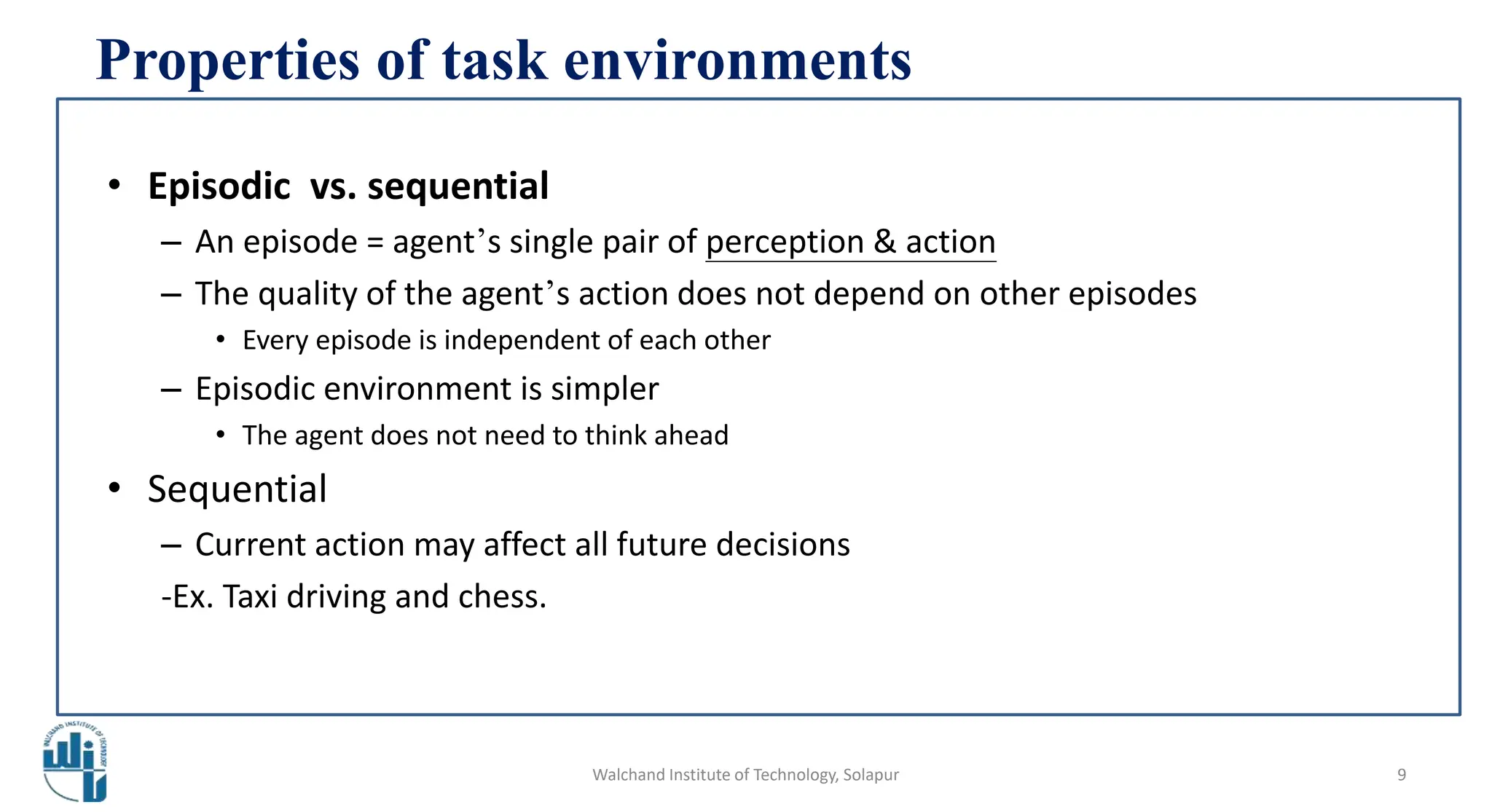
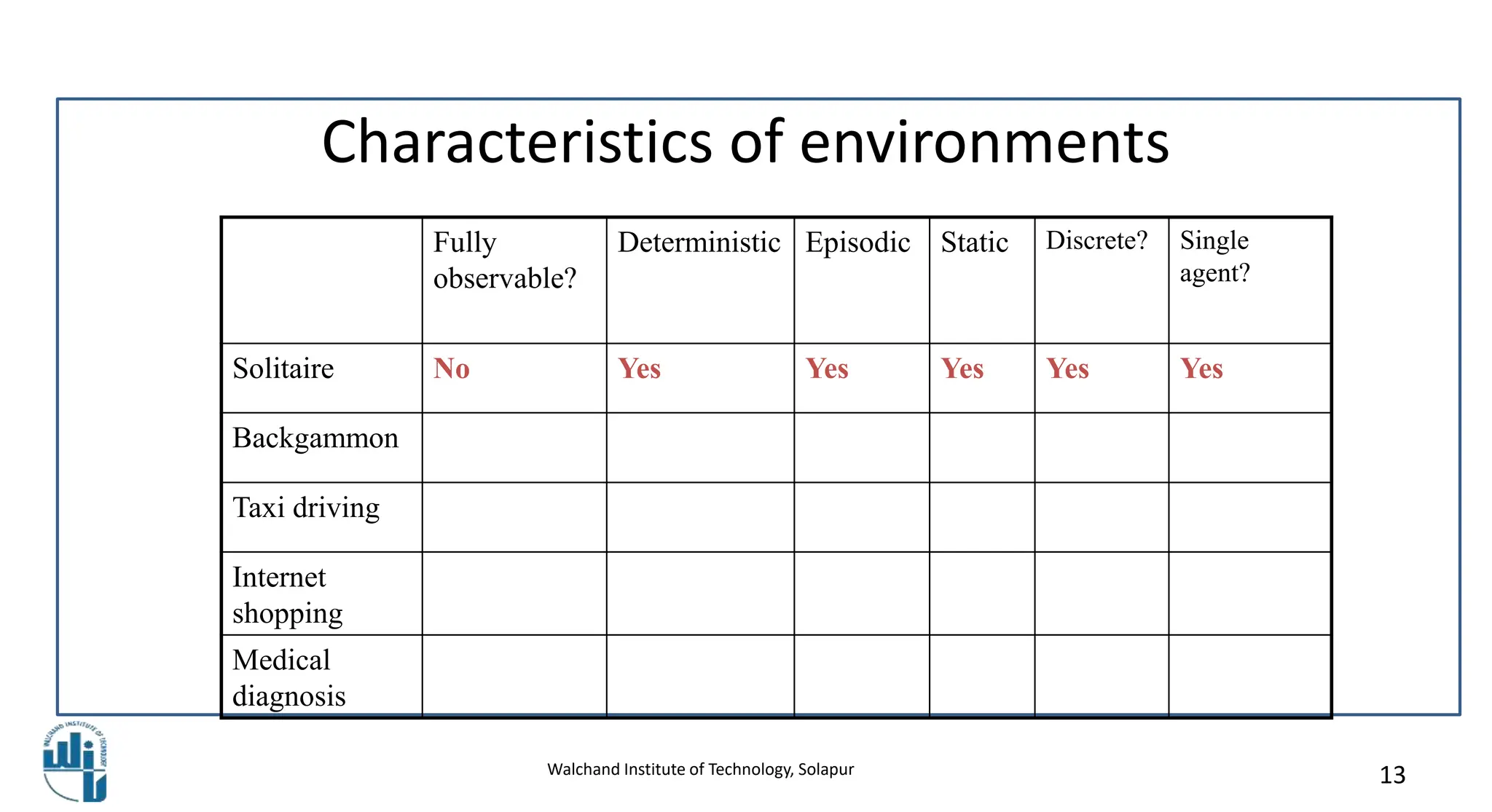
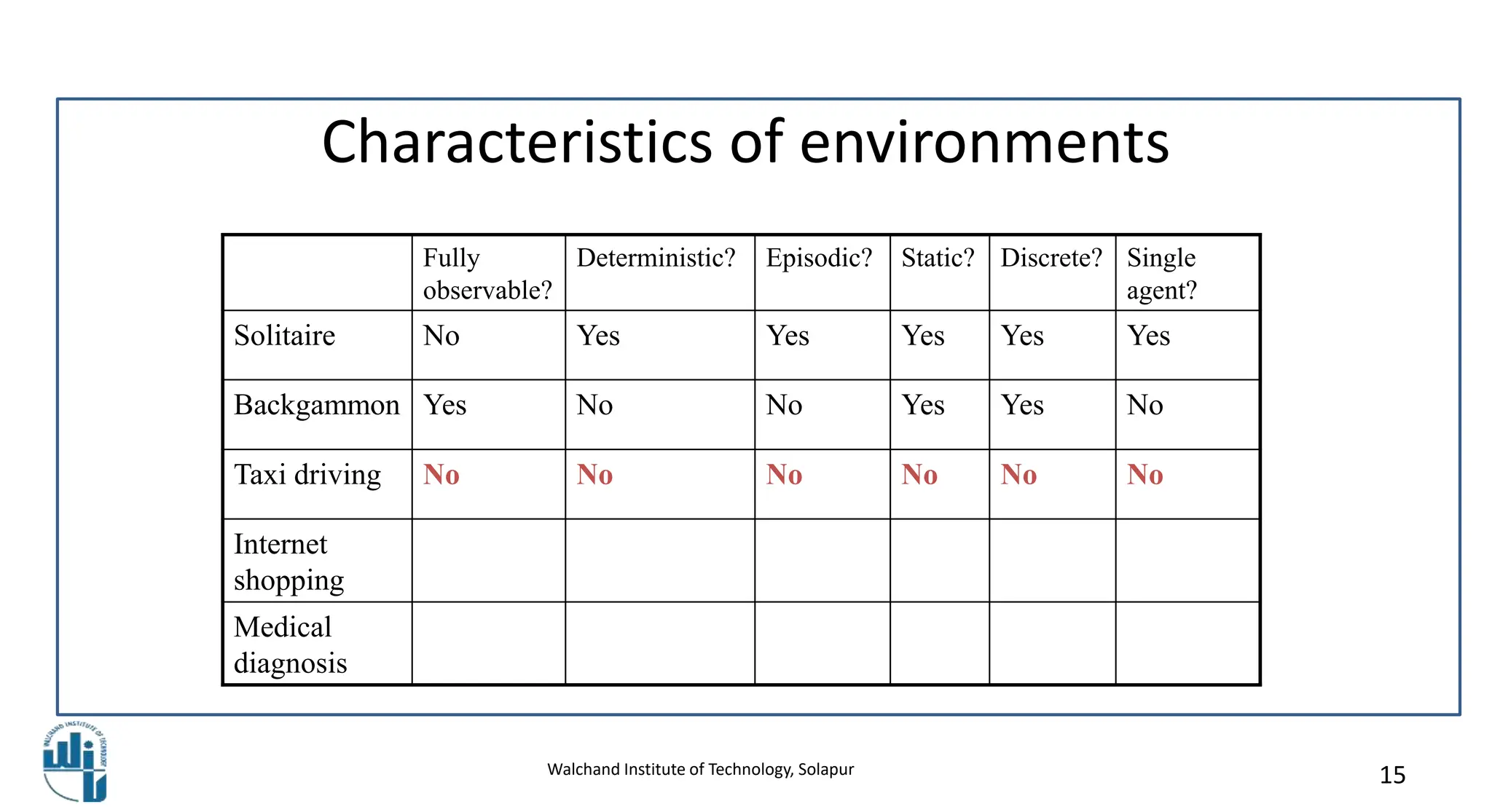
This document discusses properties of task environments in artificial intelligence. It begins with learning outcomes which are to differentiate task environments based on properties and identify those properties. It then lists and describes several key properties of task environments: fully observable vs partially observable, single agent vs multiagent, deterministic vs stochastic, episodic vs sequential, static vs dynamic, discrete vs continuous, and known vs unknown. Examples are provided for each property, such as taxi driving being stochastic and non-deterministic. A table compares example environments based on these properties. The document concludes with references for further reading.