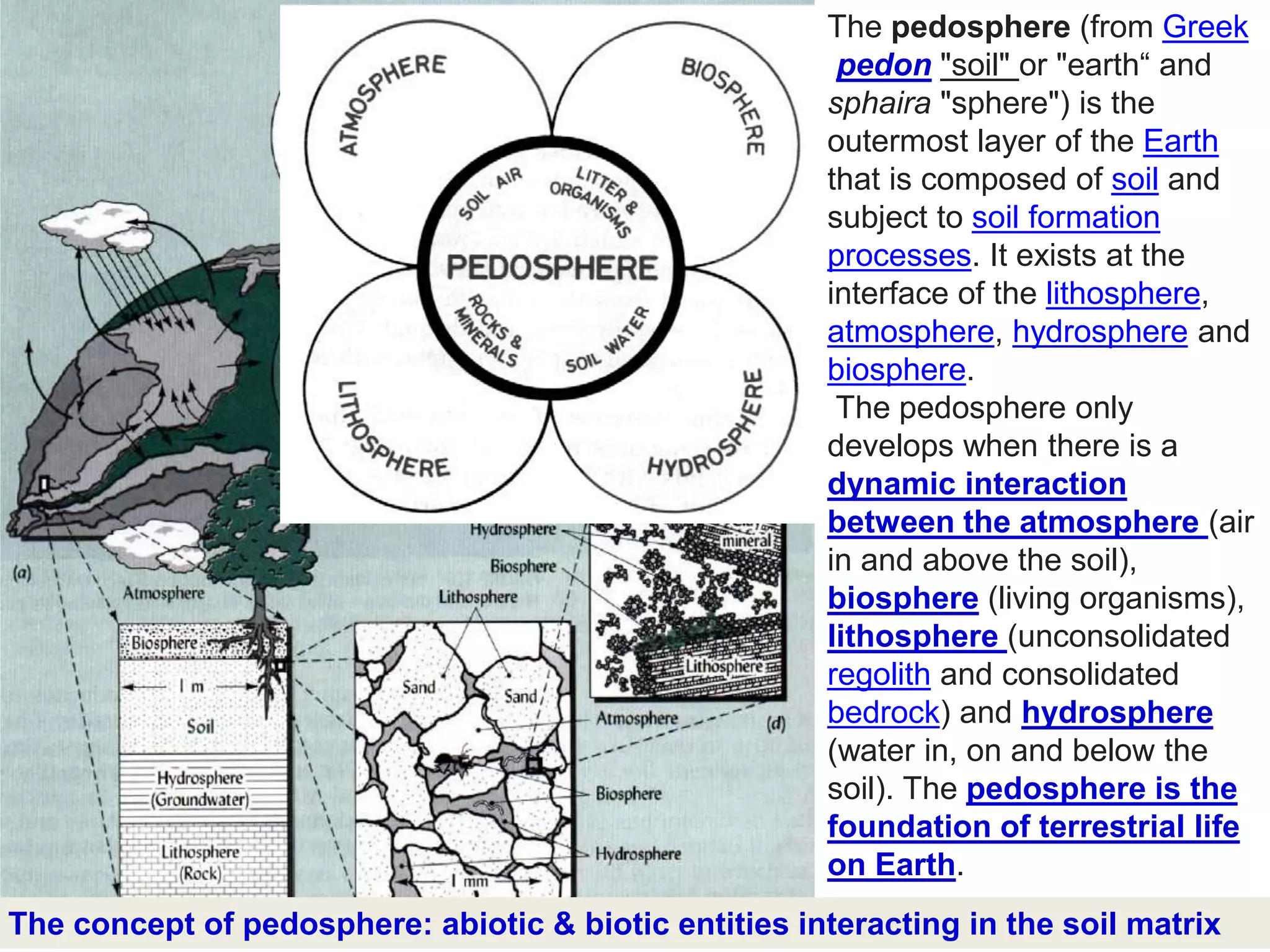
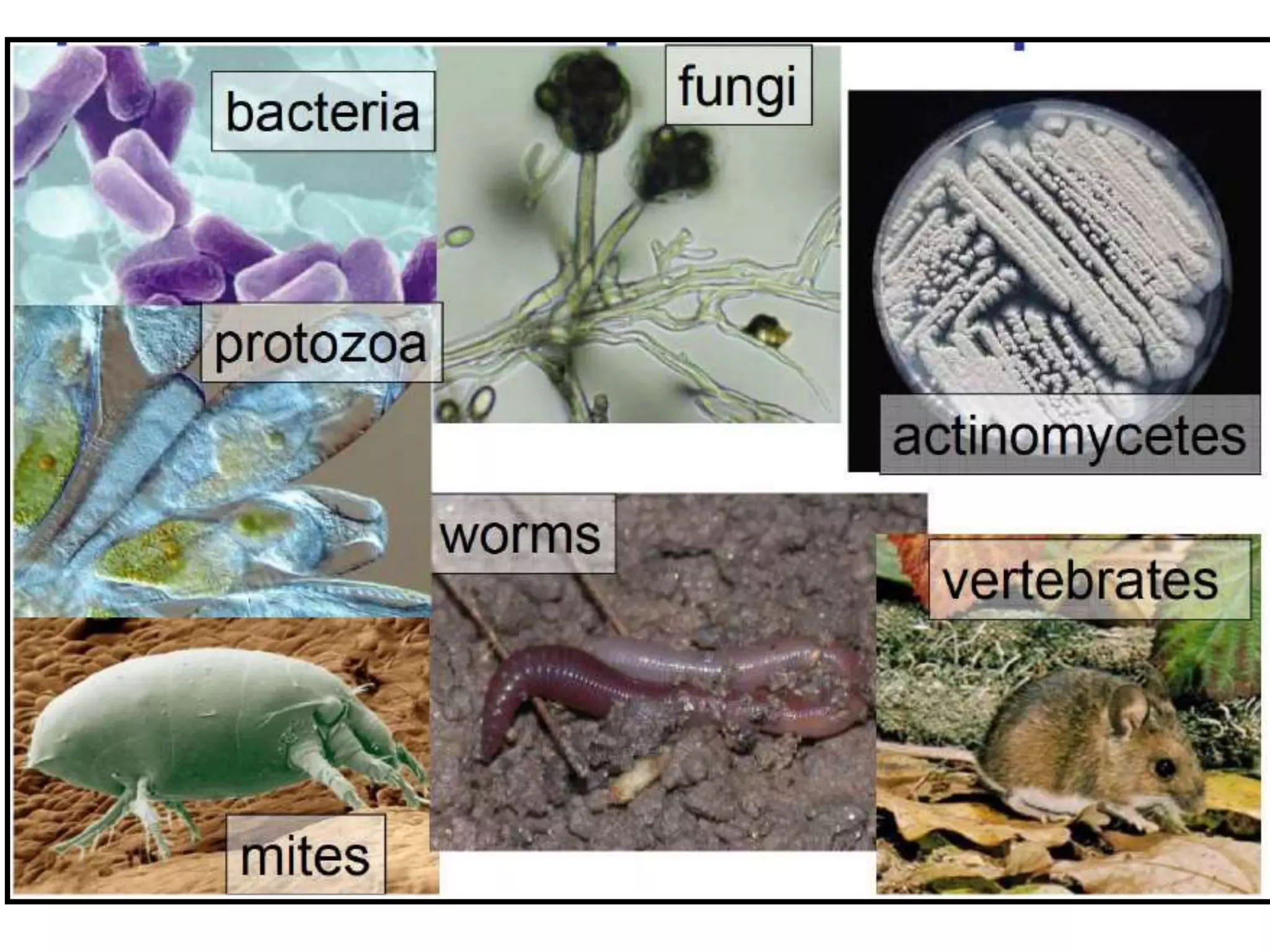
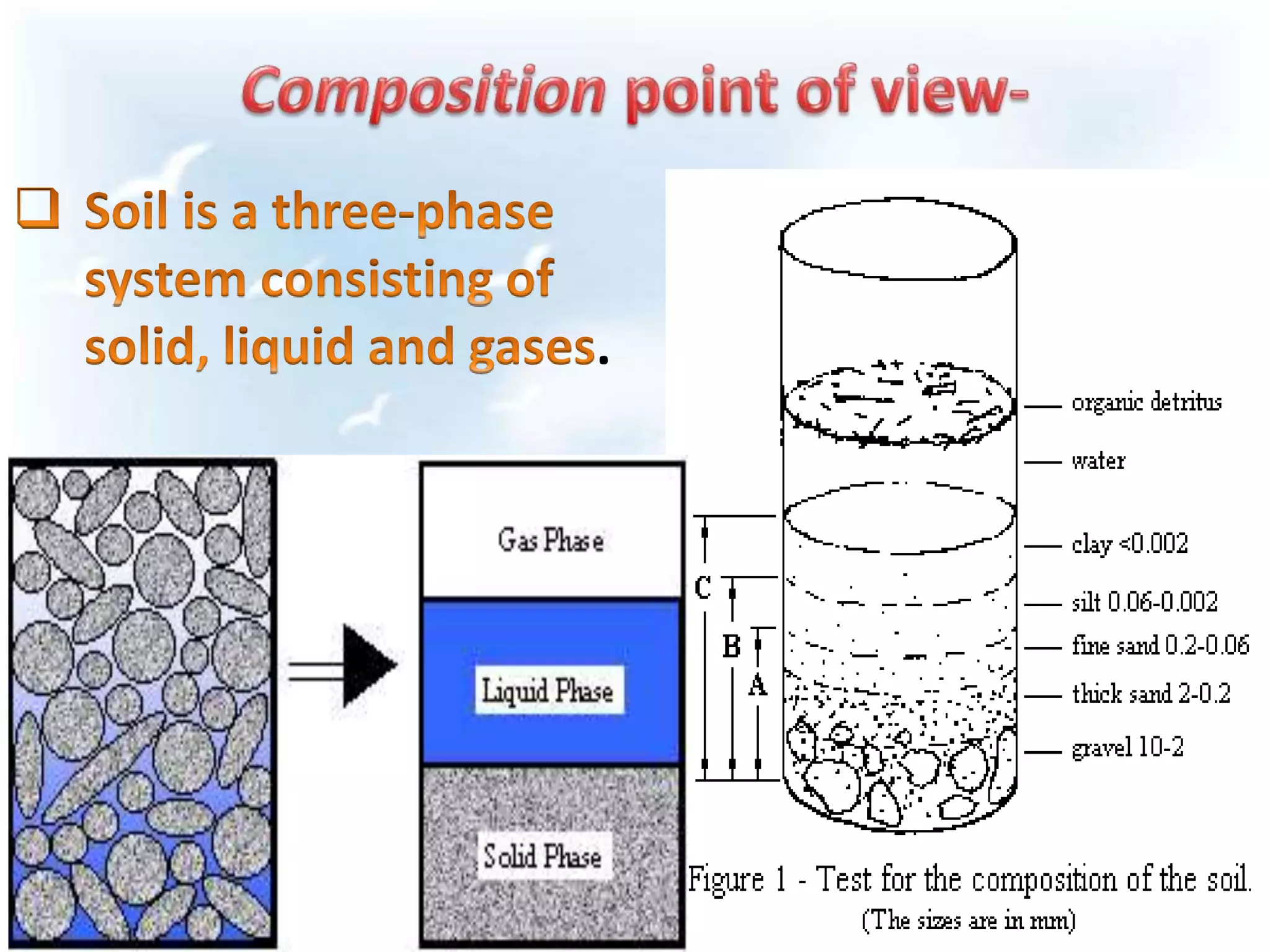
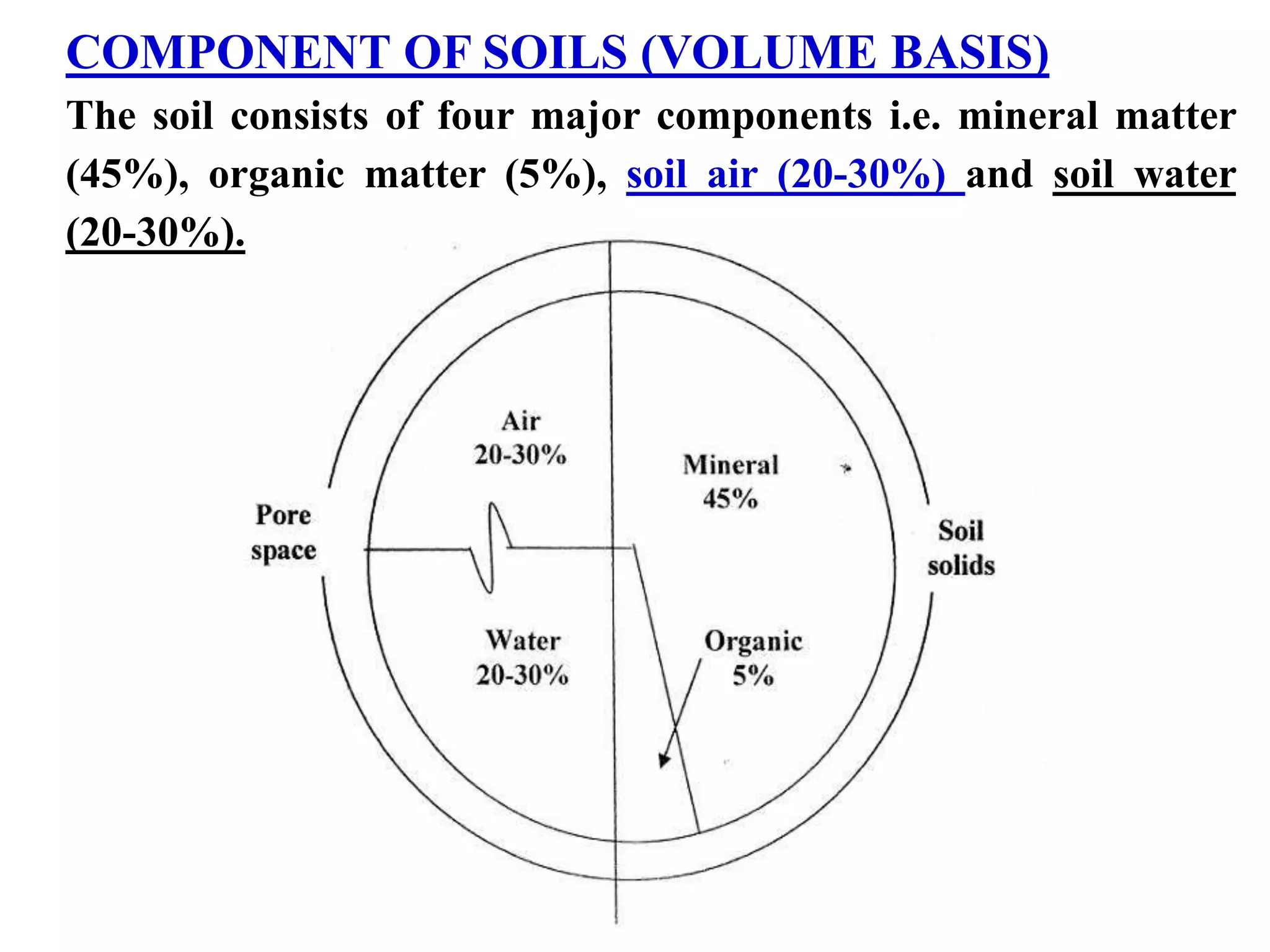
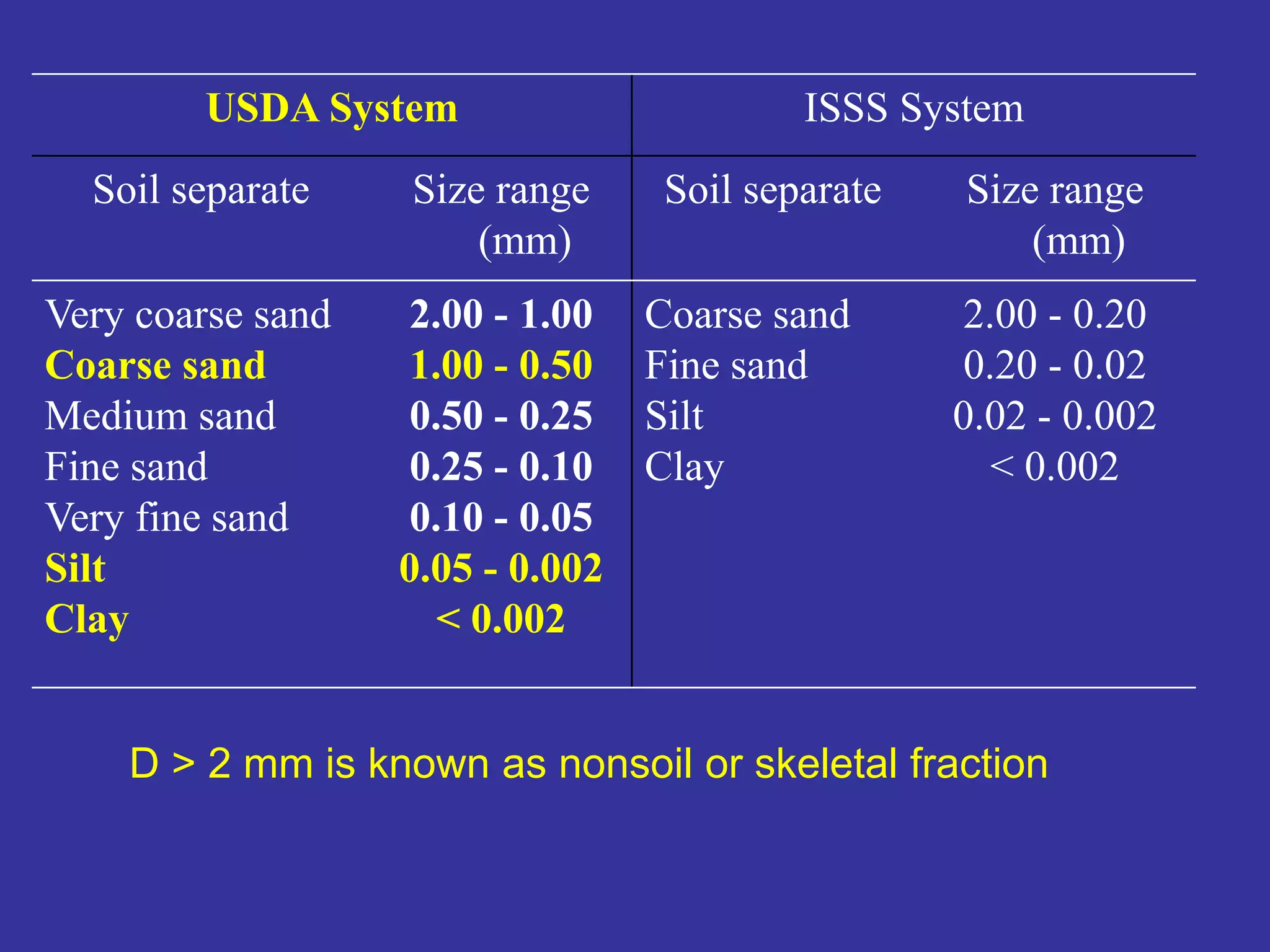
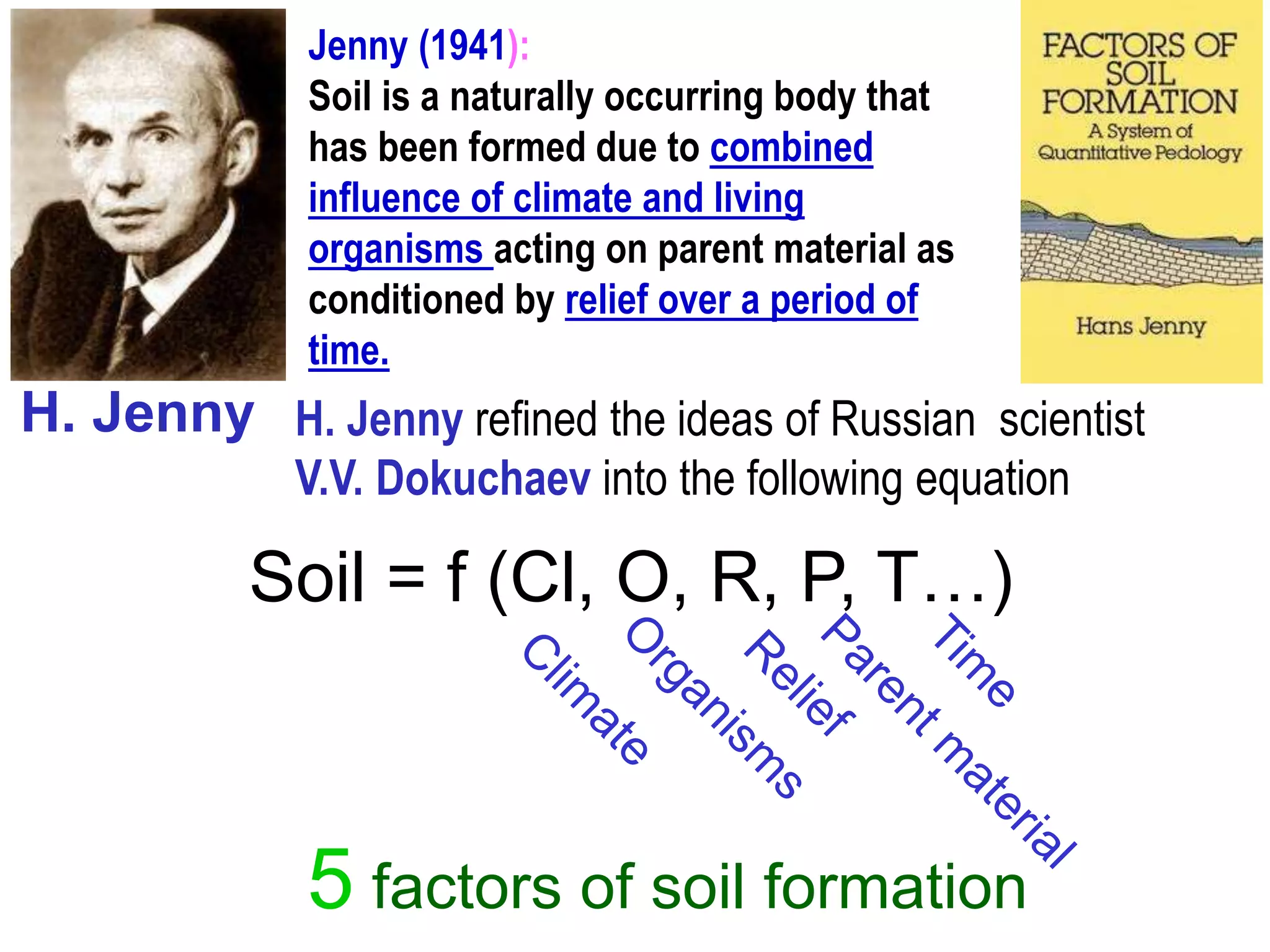
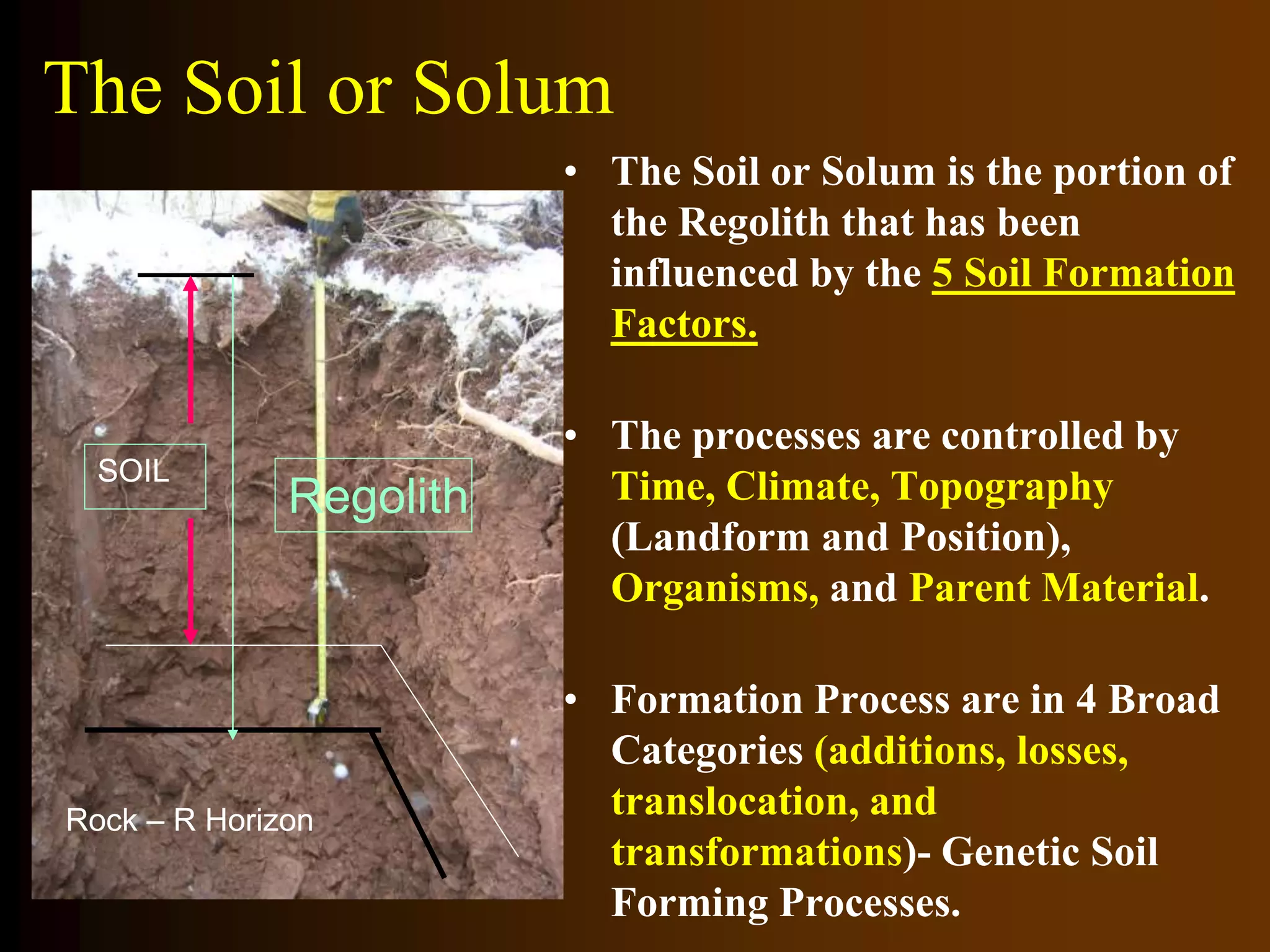
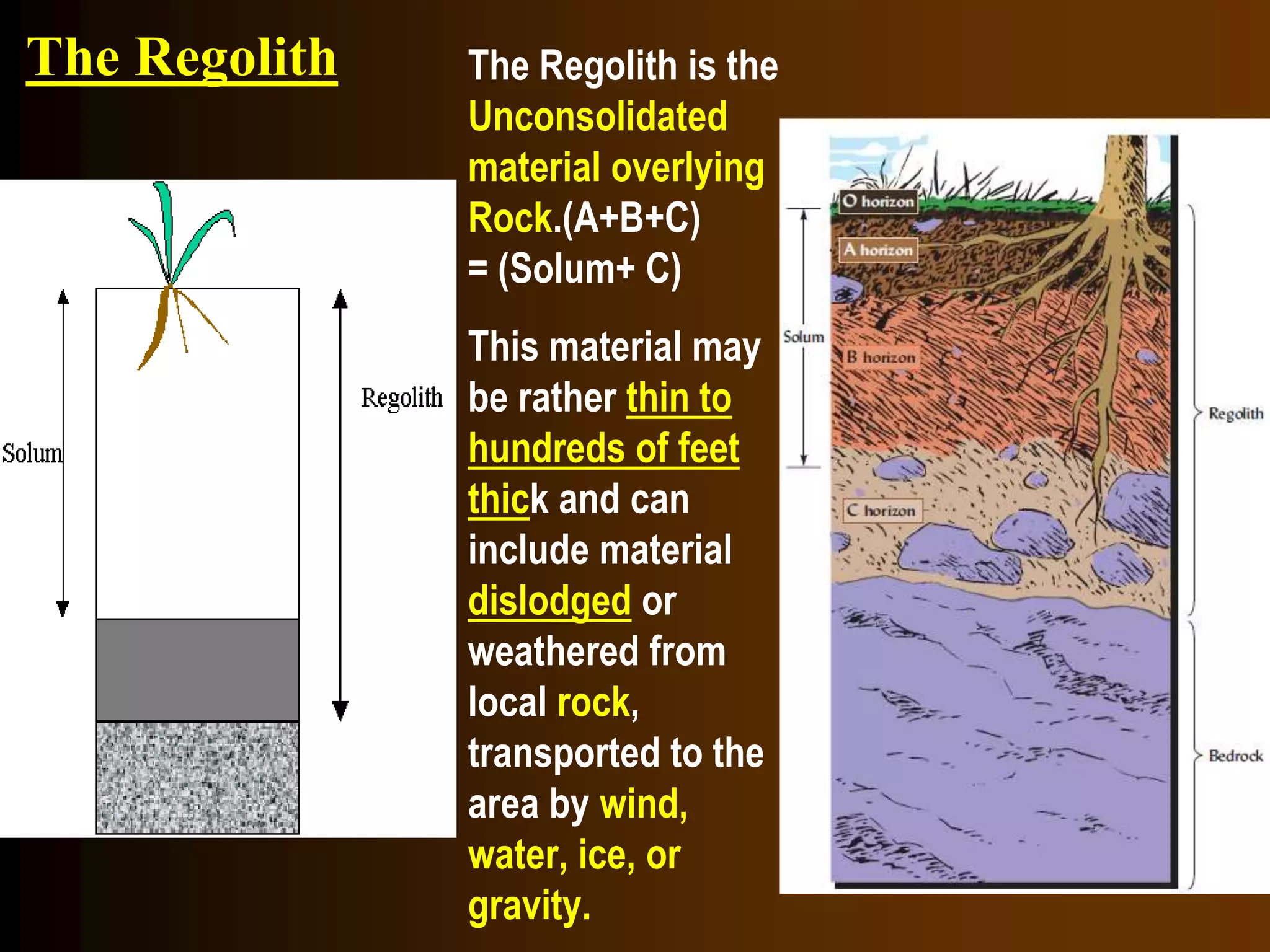
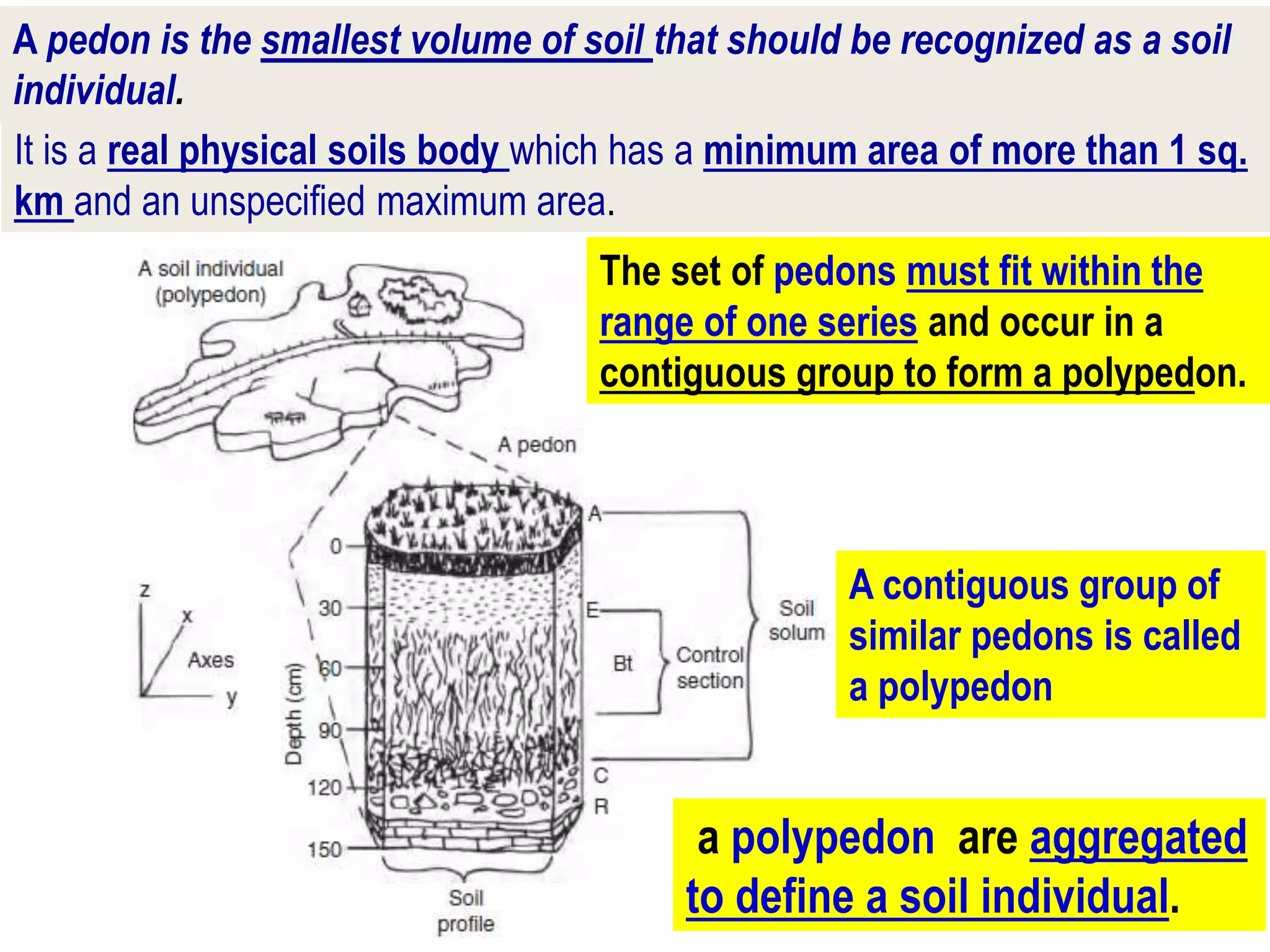
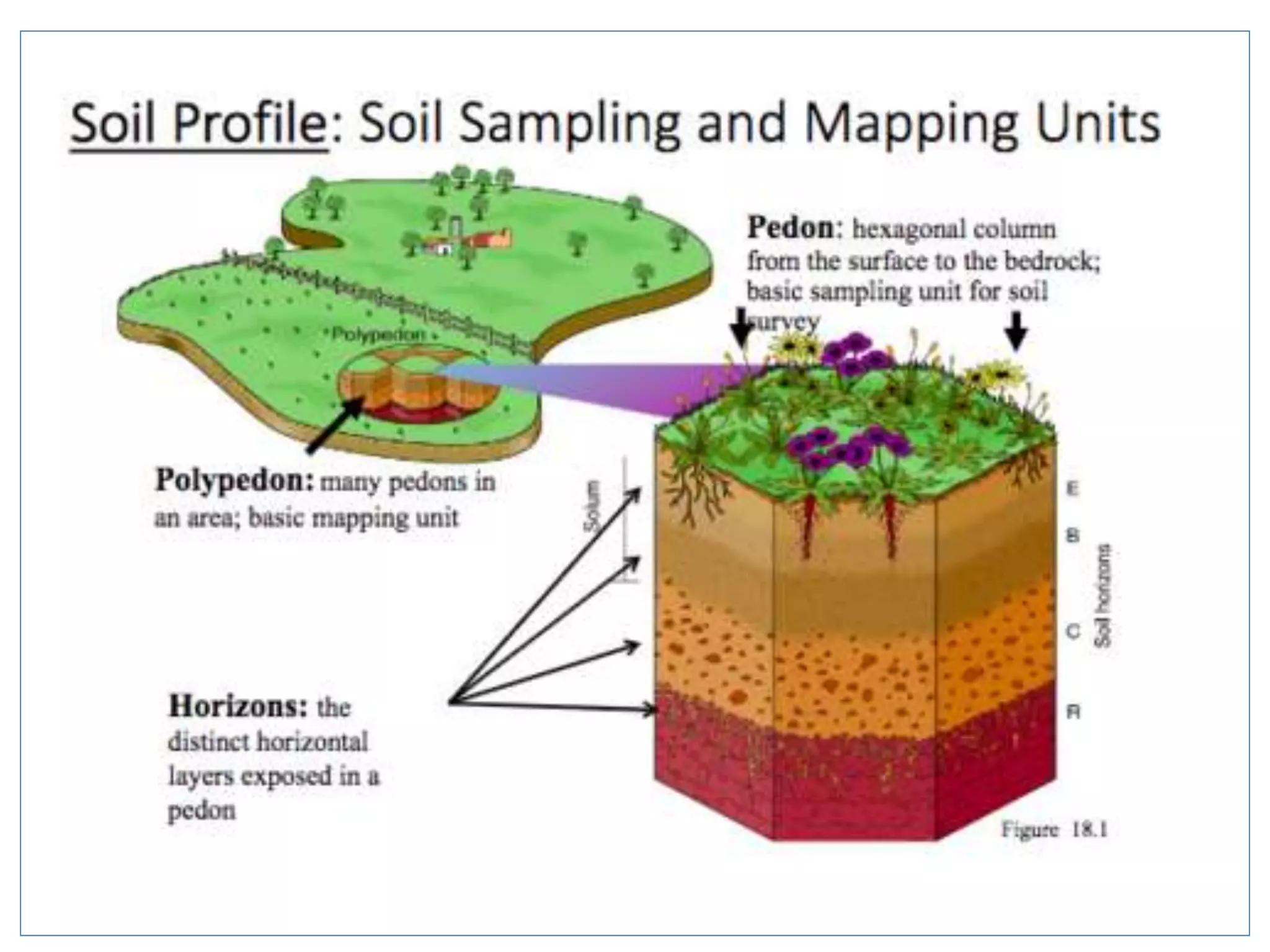
The document discusses fundamentals of soil science. It defines key terms like pedosphere, pedon, and polypedon. The pedosphere is the outermost layer of the Earth composed of soil and subject to soil formation processes. A pedon is the smallest volume of soil recognized as an individual soil. A polypedon is a contiguous group of similar pedons that together define a soil individual. The document also summarizes the six key functions of soil and outlines the two branches of soil science - pedology and edaphology.