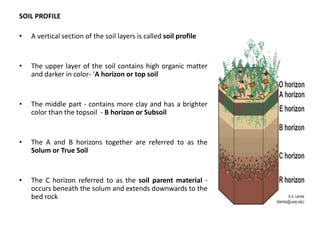
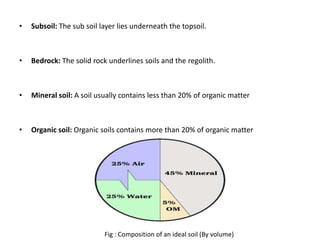
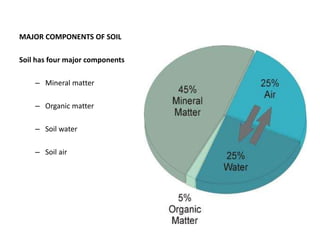
Soil is composed of minerals, organic matter, water and air. It forms in layers with the topsoil at the surface containing more organic matter. Below the topsoil are subsoil and parent material layers. Soil provides nutrients and support for plant growth and is a living ecosystem. The components interact to support life and it is vital for food production.