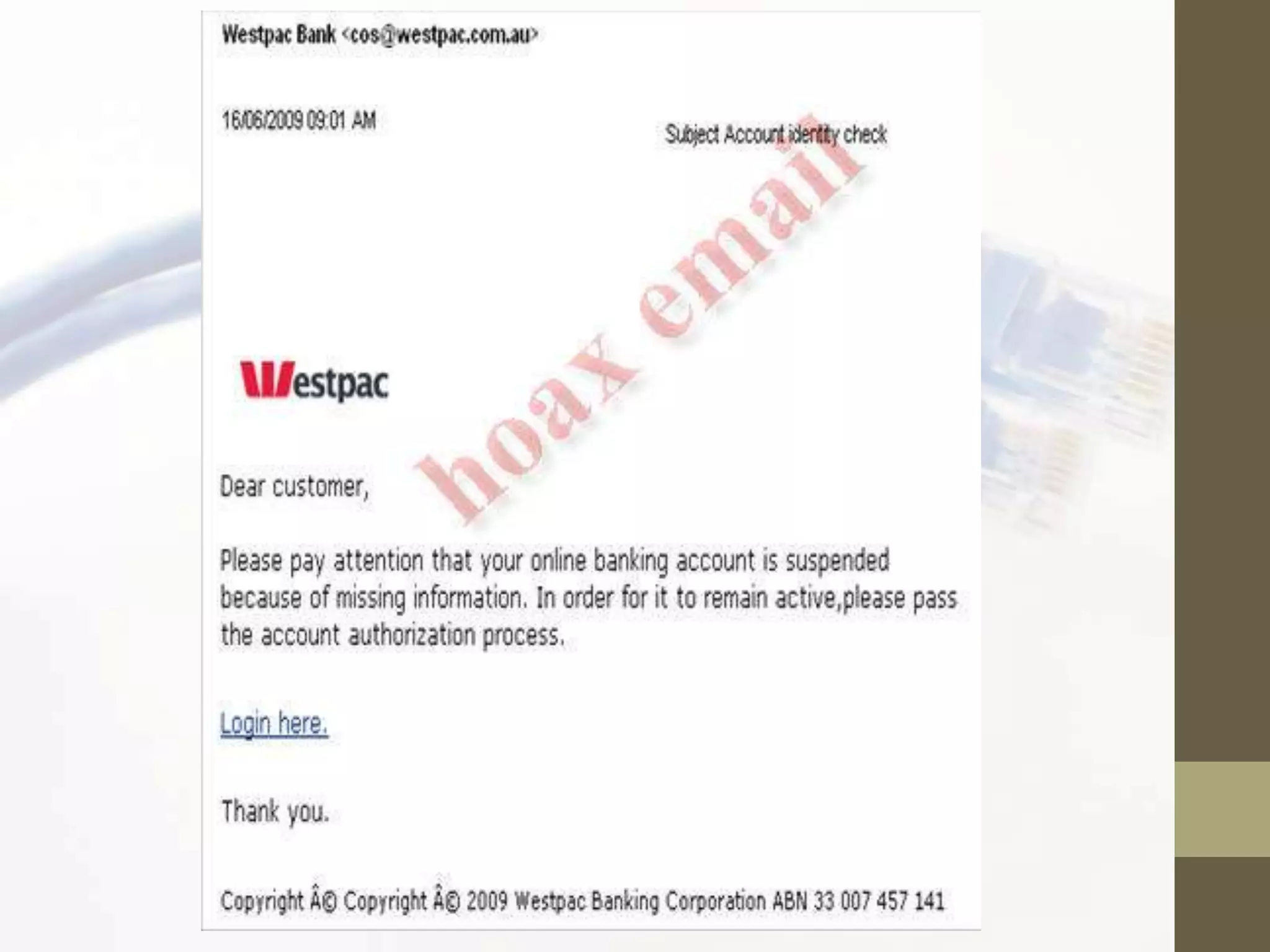
Social engineering exploits human behavior and trust to gain access to sensitive information. It includes technical attacks like phishing emails and pop-up windows, as well as non-technical attacks like dumpster diving. Common human behaviors exploited include curiosity, fear, and thoughtlessness. To help mitigate social engineering risks, organizations should educate employees, implement security policies, conduct audits, and use technical defenses like email filters and firewalls. Regular awareness training can help motivate employees to follow best practices.