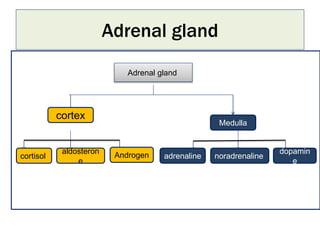
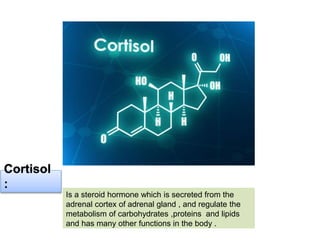
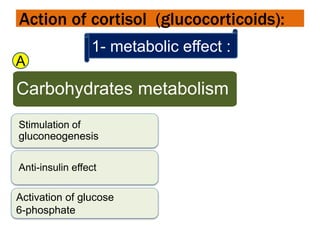
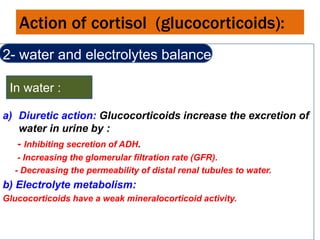
Cortisol is a steroid hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex. It regulates carbohydrate, protein, and lipid metabolism. It has metabolic effects such as stimulating gluconeogenesis and lipolysis. Cortisol also helps regulate water and electrolyte balance as well as having anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, and stress response effects. It works through various mechanisms including increasing response to catecholamines and inhibiting inflammatory reactions.