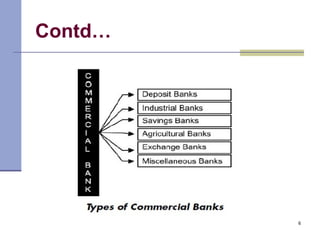
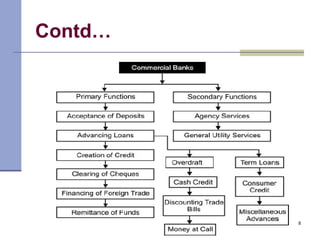
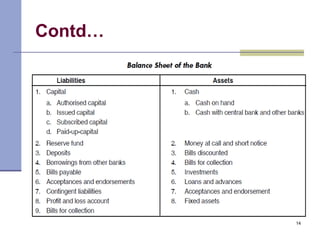
Commercial banks play a key role in the economy by accepting deposits from the public, lending money, clearing checks, and providing other services. They earn income through interest on loans and investments as well as fees. Commercial banks must balance objectives of liquidity, profitability, safety, and diversity in their investment policies. They operate using either a unit banking system with independent banks or a branch banking system where a head office controls local branches. By providing finance, credit, and implementing monetary policy, commercial banks help accelerate capital formation and economic development.