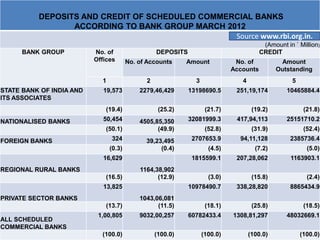
Scheduled commercial banks in India must meet certain criteria set by the Reserve Bank of India, such as maintaining a minimum paid capital and funds. These banks can access loans from the RBI and automatically become members of the clearing house. The main types of scheduled commercial banks are public sector banks, private sector banks, foreign banks, and regional rural banks. The key differences between scheduled commercial banks and regular commercial banks are that scheduled banks must meet RBI's criteria and enjoy special facilities, while commercial banks exist globally without these distinguishing Indian features.