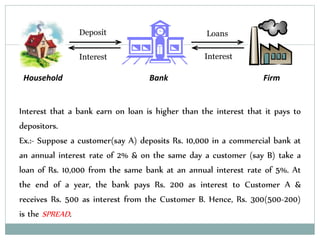
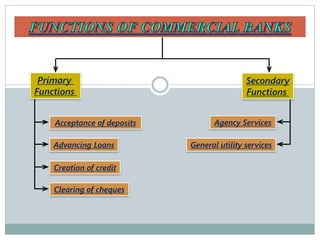
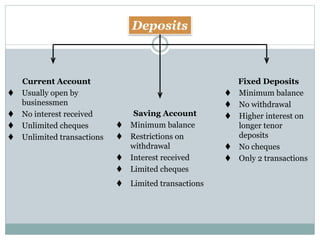
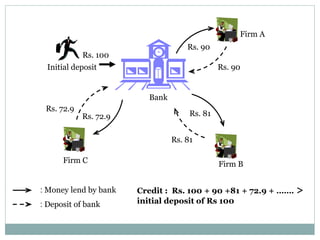
Commercial banks perform the primary functions of accepting deposits, granting loans, and creating credit. They earn profits from the spread between the interest paid on deposits and the higher interest received from loans. Deposits include current accounts, savings accounts, and fixed deposits. Loans include overdraft facilities, term loans, money at call, and consumer credit. Banks also perform secondary functions such as clearing of cheques, agency services like collecting payments and buying/selling securities, and general utility services including locker facilities, traveler's cheques, and business information.