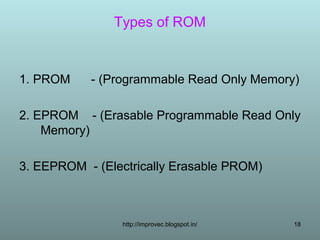
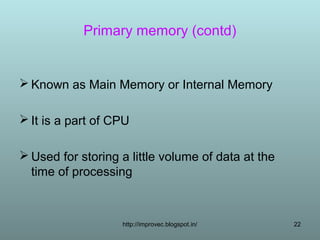
The document discusses the functions and types of computer memory. It describes memory as a device that stores data and programs, and notes its functions include keeping information for processing and storing results temporarily. The document outlines the memory hierarchy including primary memory (RAM, ROM) and secondary memory (hard disks, USB drives). It differentiates between volatile and non-volatile memory and discusses specific types like DRAM, SRAM, and cache memory.