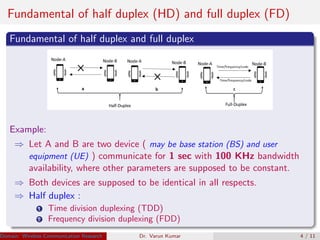
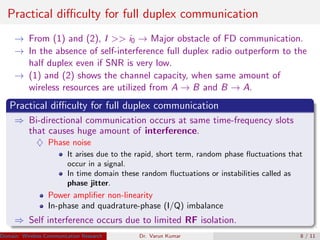
Full duplex radio communication allows simultaneous two-way communication using the same frequency band. This doubles the spectral efficiency compared to half-duplex communication, which requires allocating separate frequency bands or time slots for the two directions of communication. However, full duplex faces significant challenges from self-interference caused by the high-power transmitted signal overwhelming the weak received signal. Recent research has developed interference cancellation techniques using passive suppression, analog cancellation, and digital cancellation to mitigate self-interference and realize the benefits of full duplex radio communication.