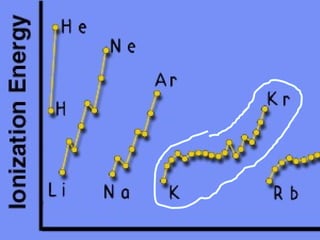
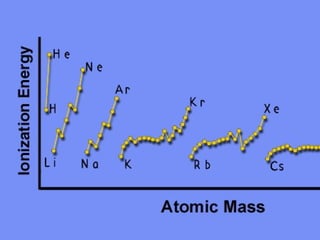
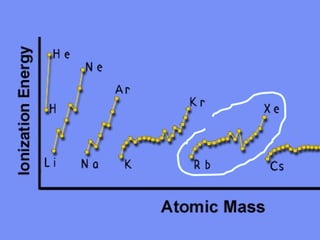
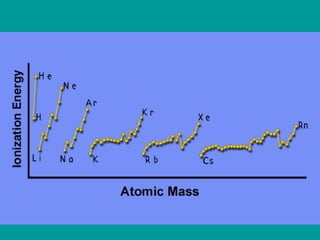
The document discusses key concepts in chemistry including:
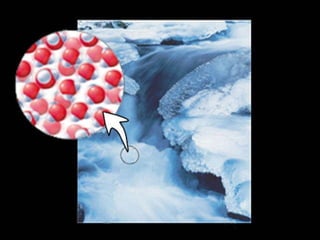
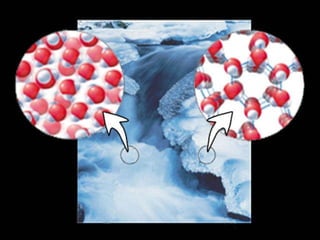
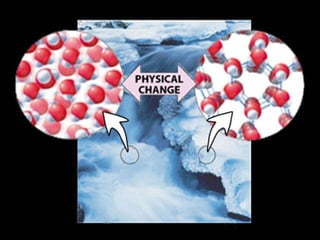
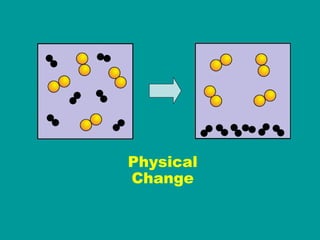
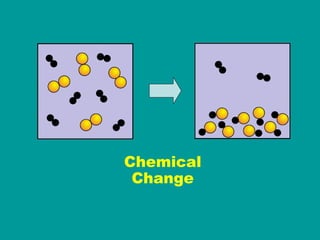
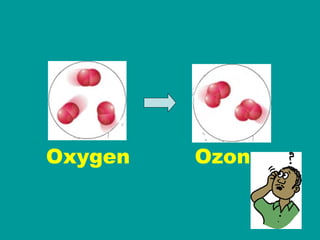
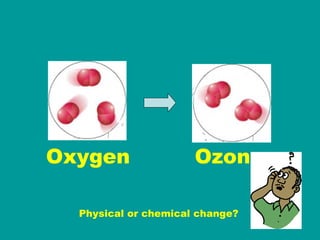
1) Matter can be classified as having physical or chemical properties, with physical changes altering physical properties but not chemical composition and chemical changes resulting in new substances.
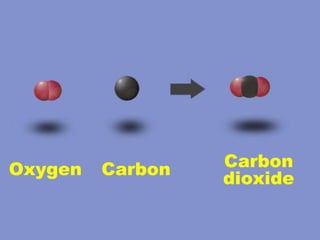
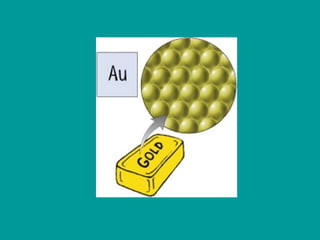
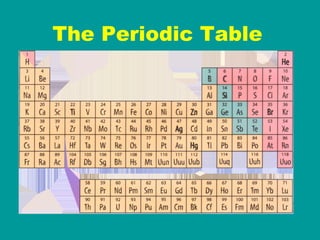
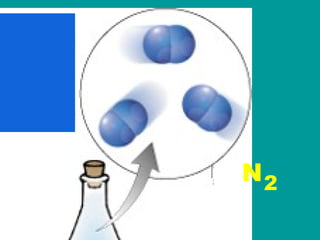
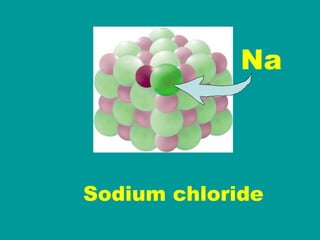
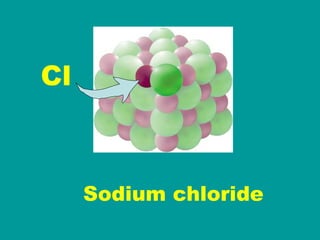
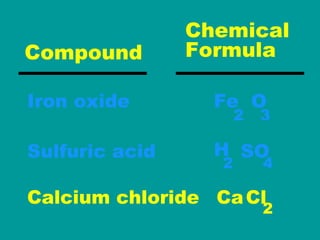
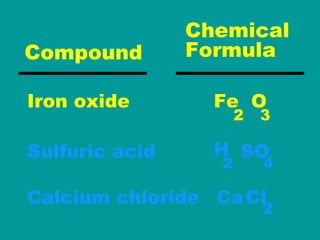
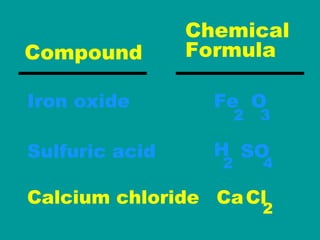
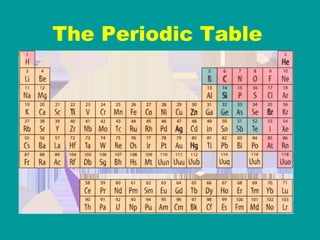
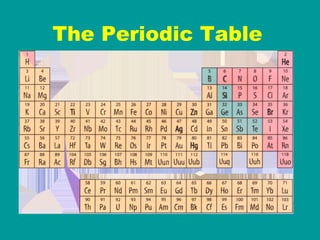
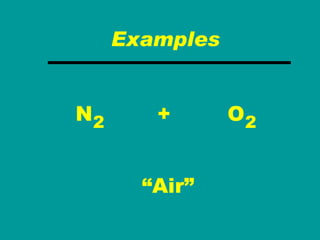
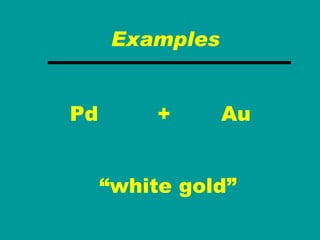
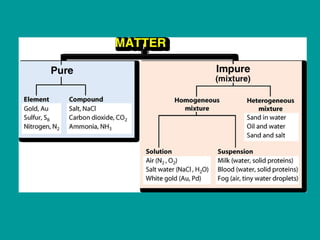
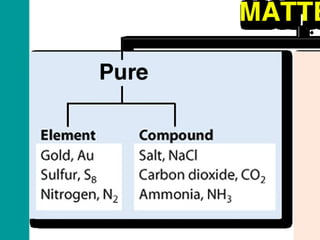
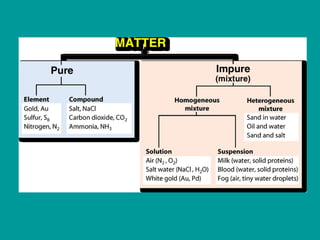
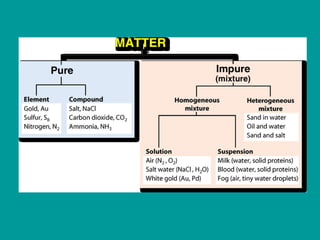
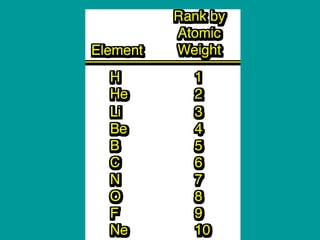
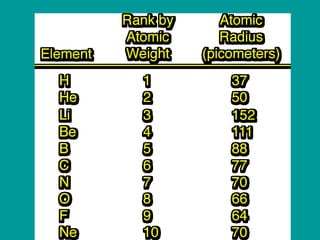
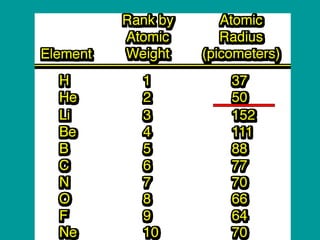
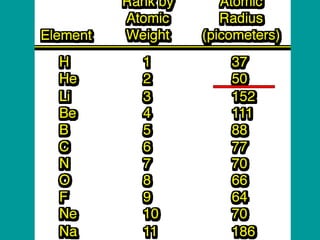
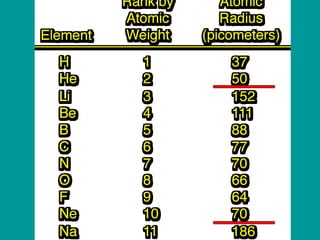
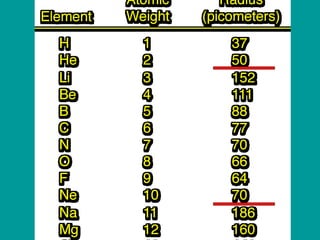
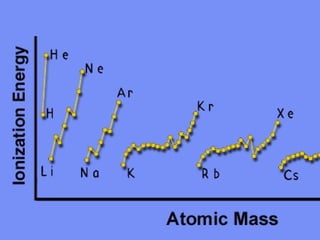
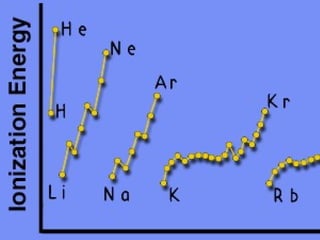
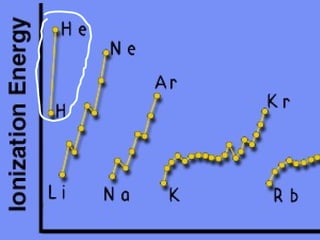
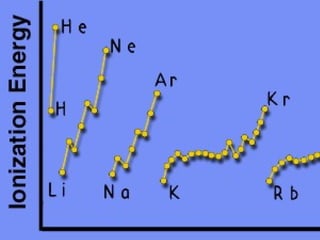
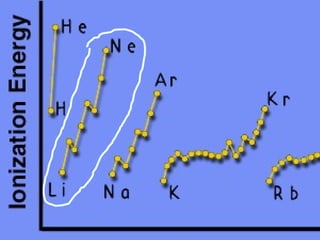
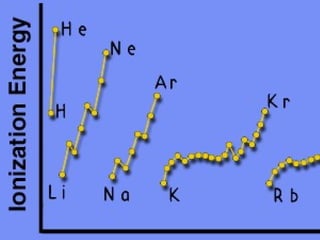
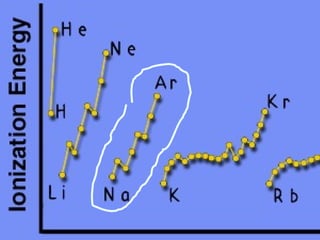
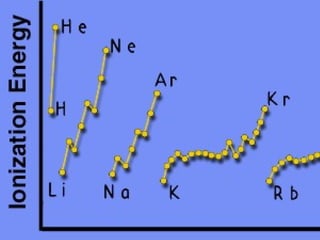
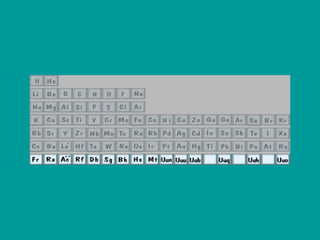
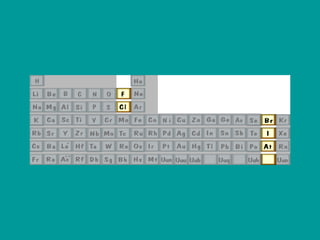
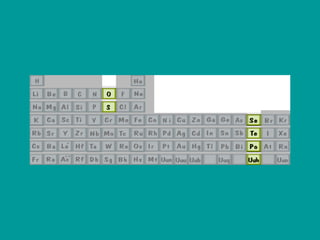
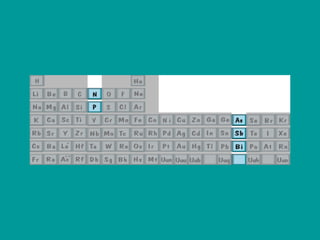
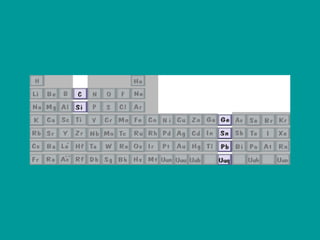
2) Elements are the fundamental components of matter and are represented by atomic symbols on the periodic table, while compounds are formed by chemical bonds between different elements represented by chemical formulas.
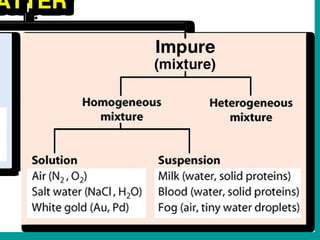
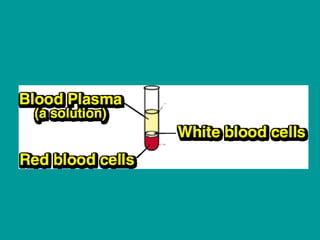
3) Most materials are mixtures that combine substances without chemical change, whereas pure substances consist of only one type of element or compound.