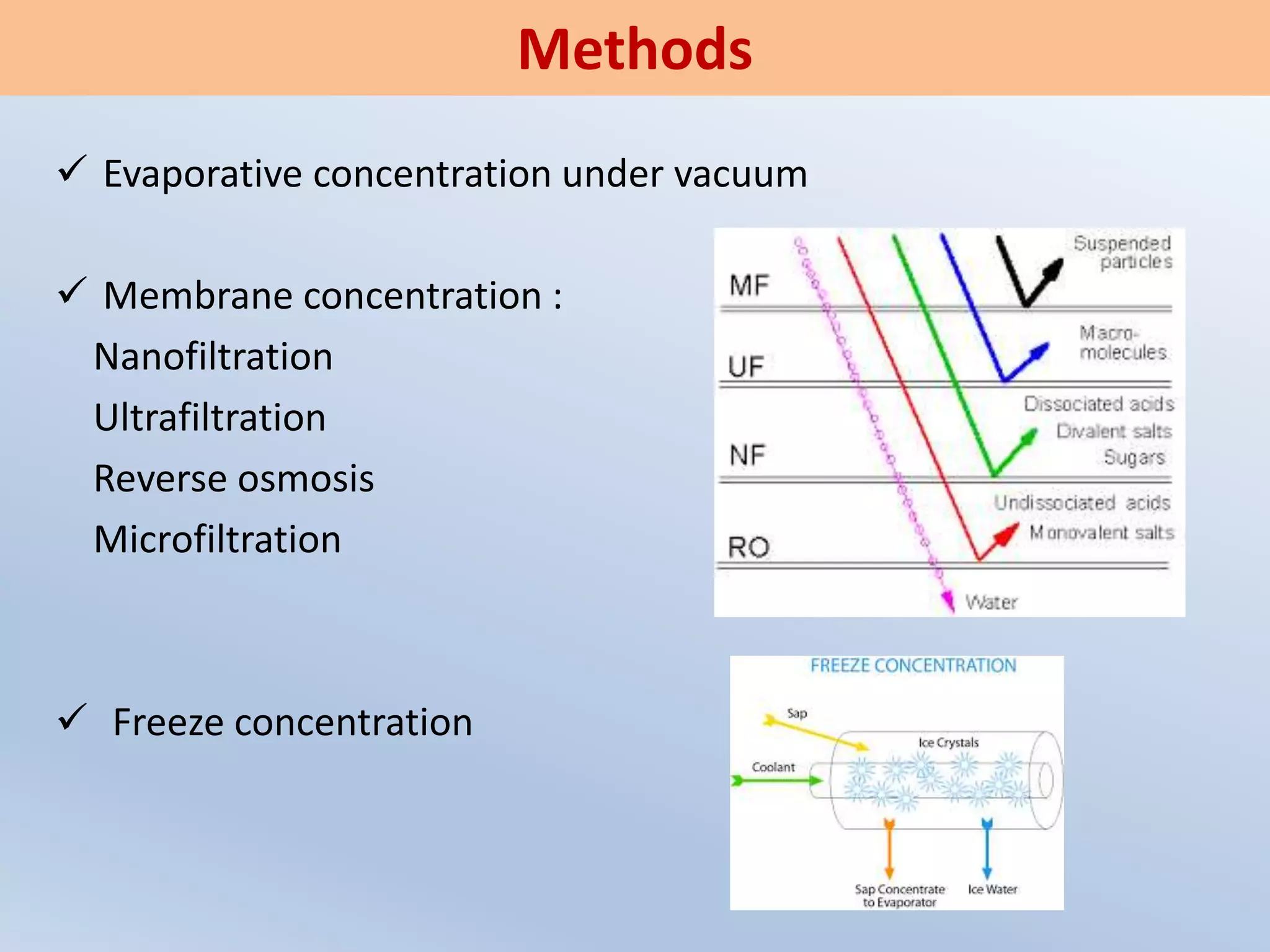
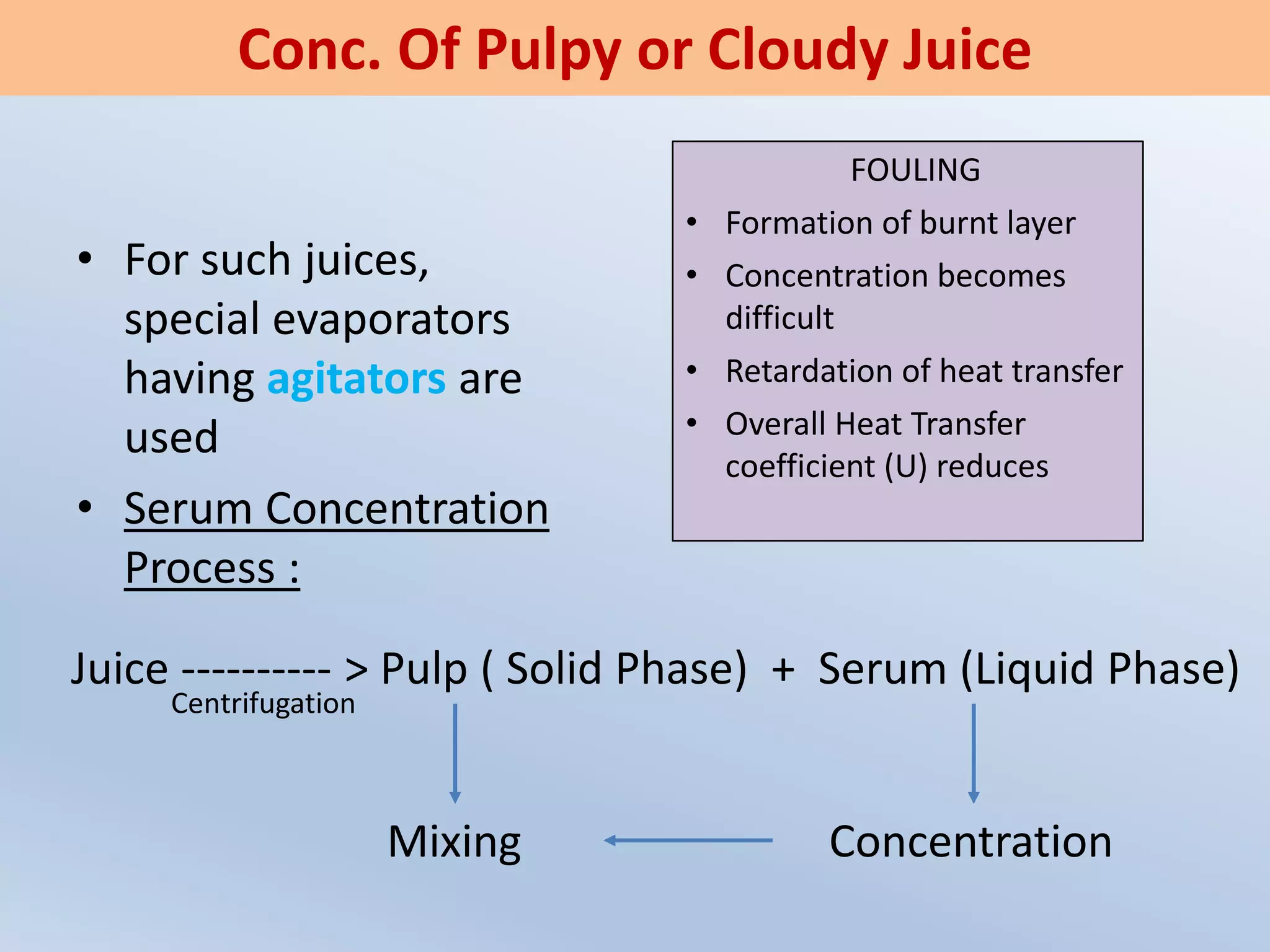
The document provides an overview of fruit juice concentrates, detailing the processes used for concentrating fruit juice, including evaporative, membrane, and freeze concentration methods. It highlights the advantages, such as microbiological stability and improved flavor retention, as well as disadvantages like potential nutrient loss and high operational costs. Additionally, it discusses various drying techniques for fruit juices and concentrates, emphasizing methods like spray drying and freeze drying for preserving quality and extending shelf life.