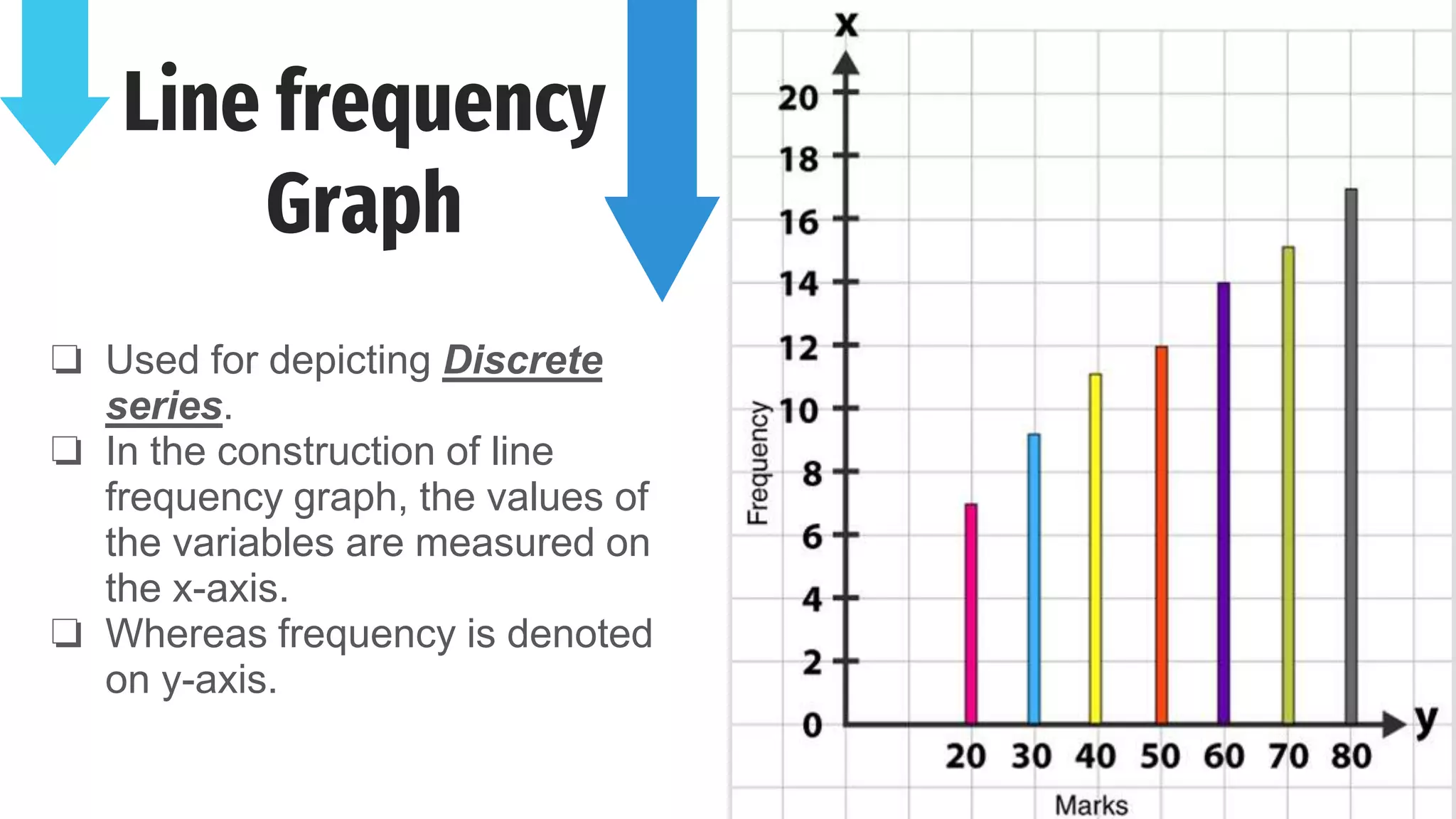
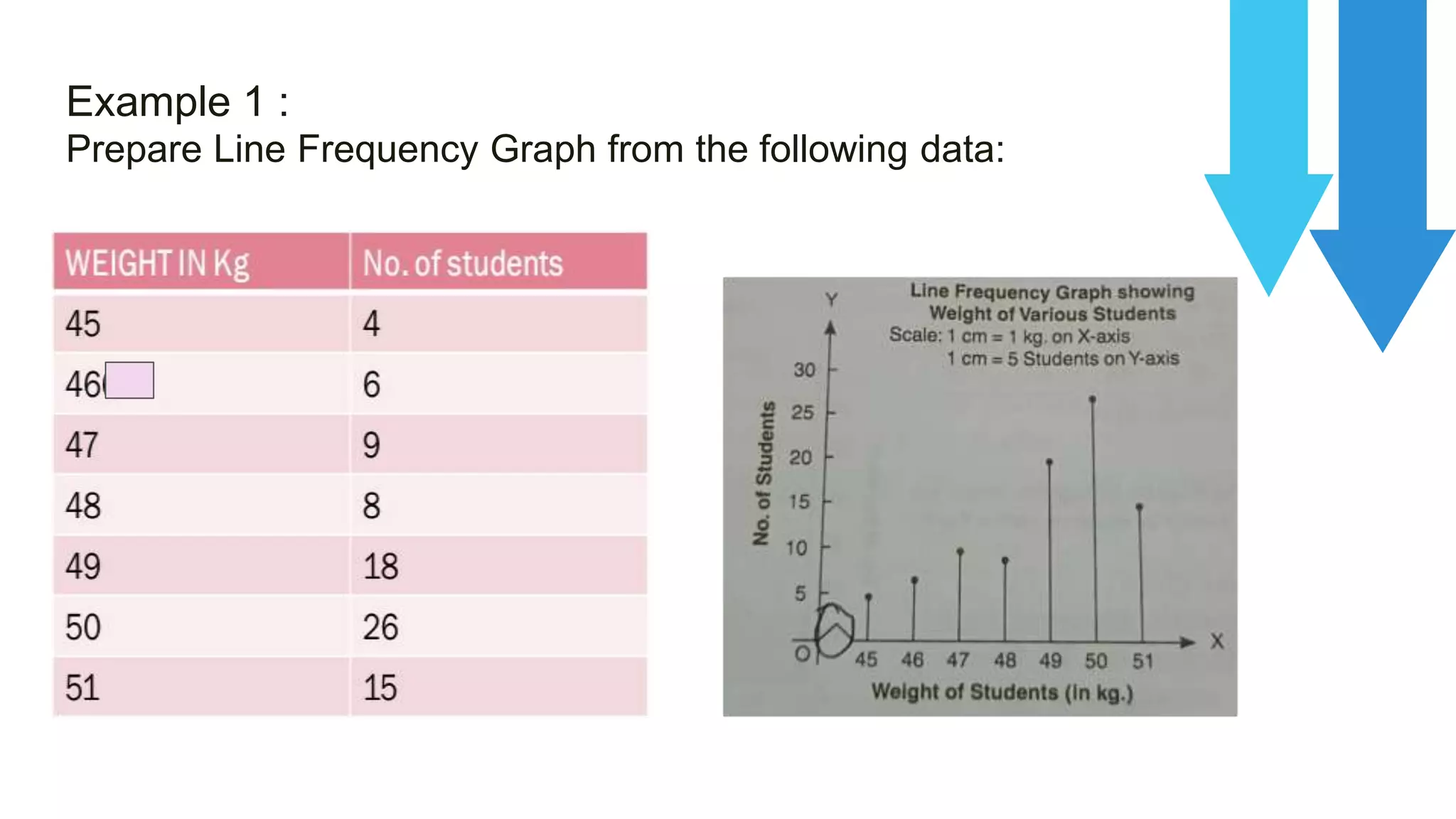
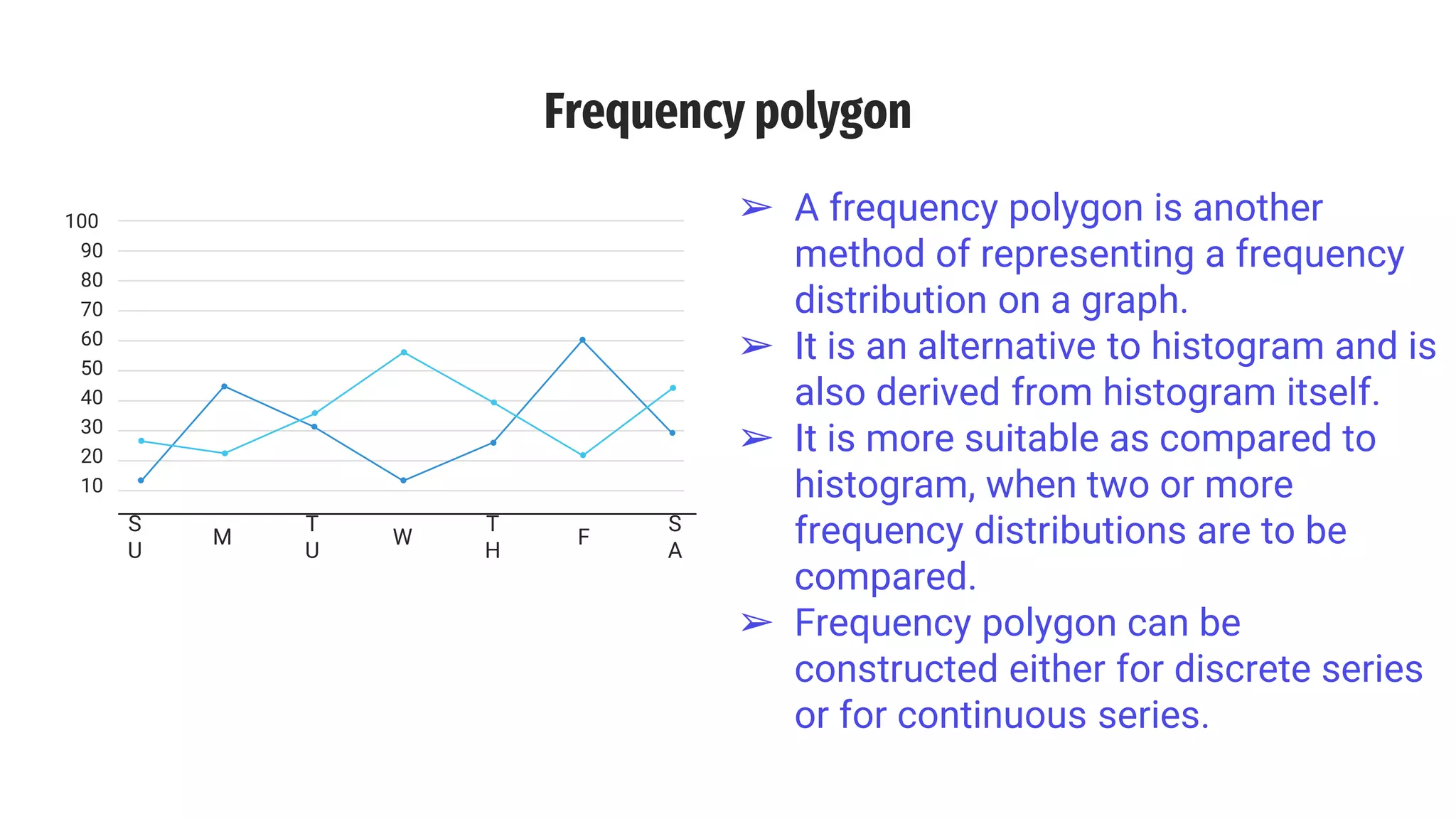
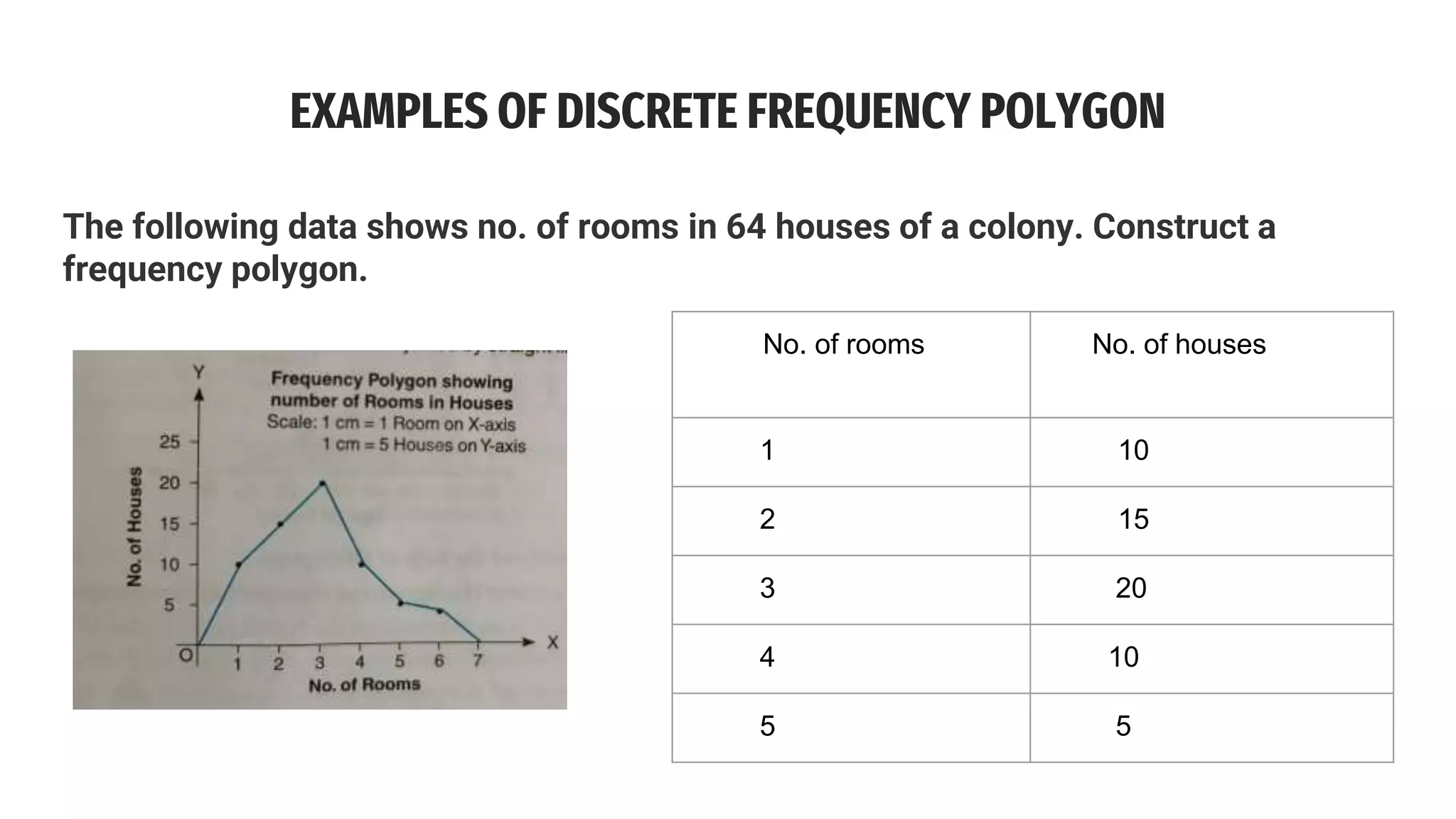
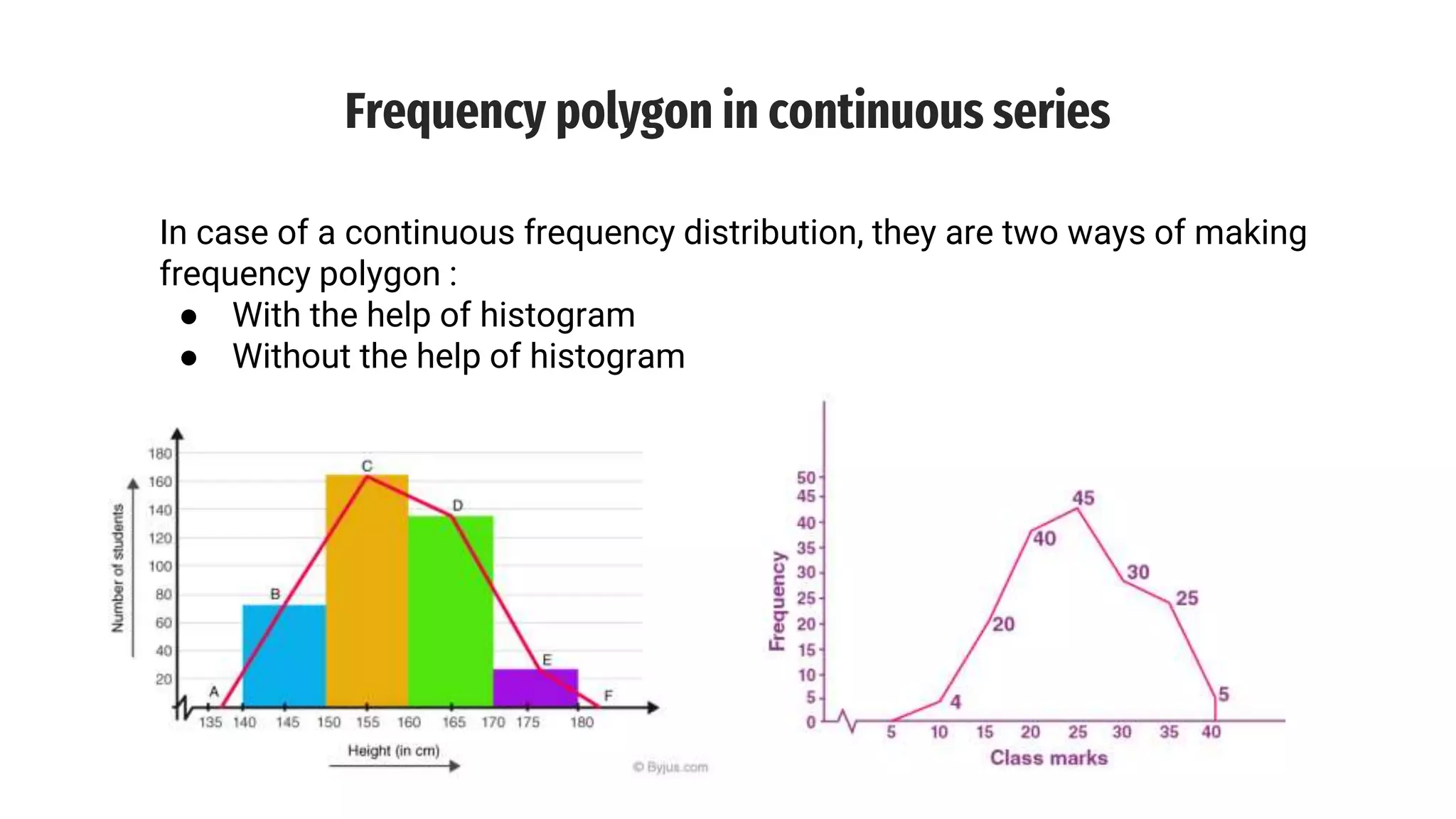
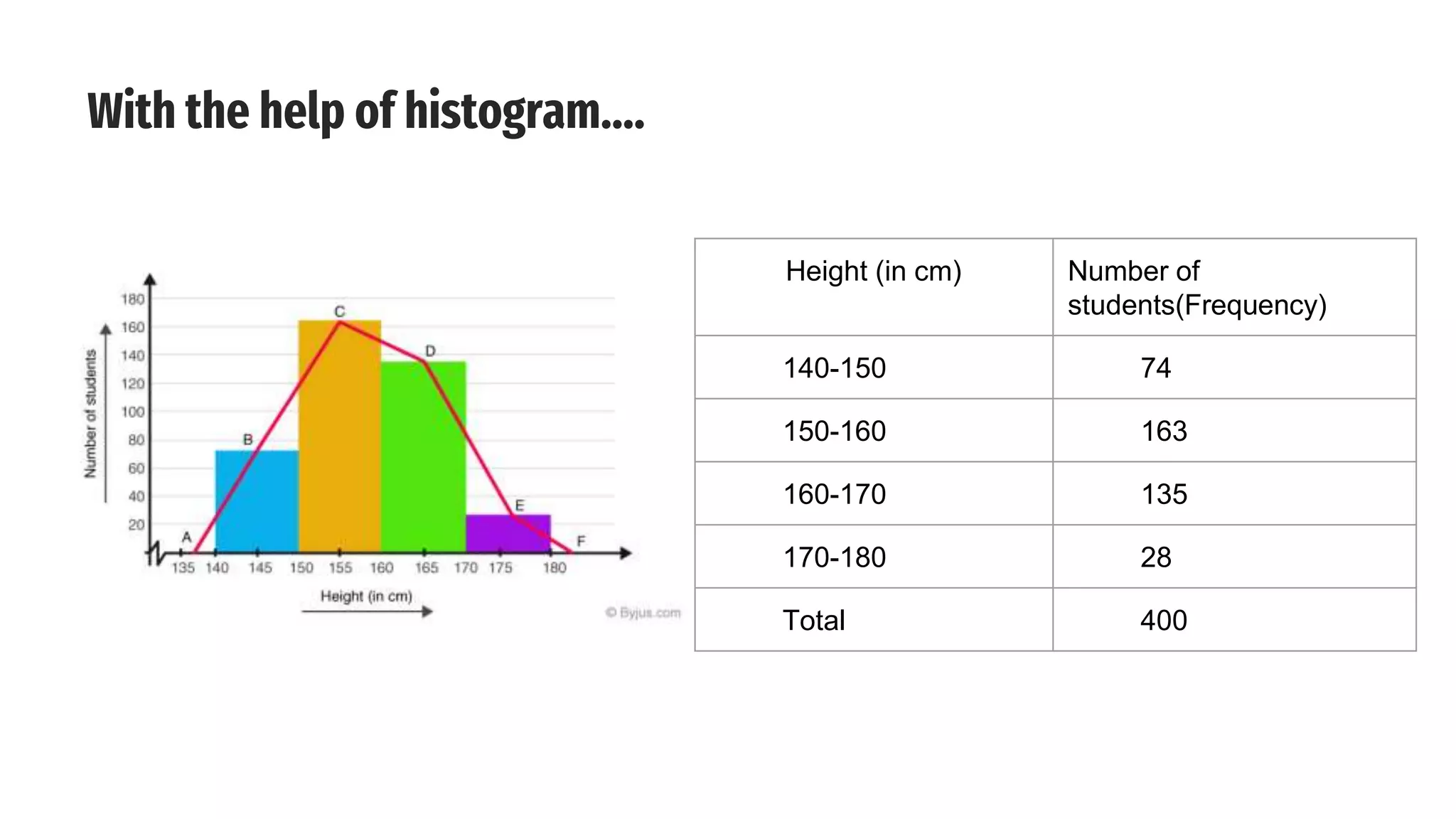
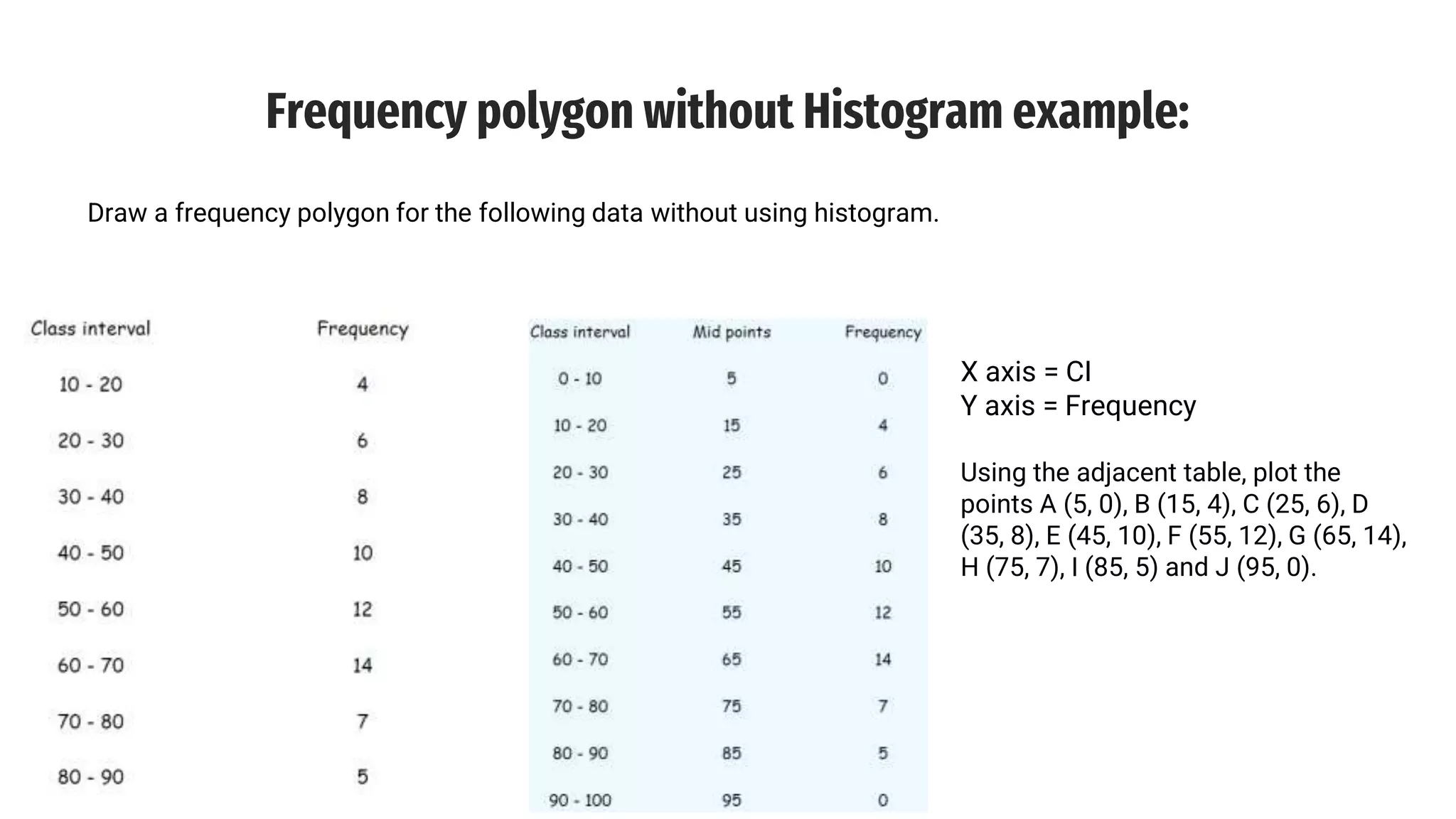
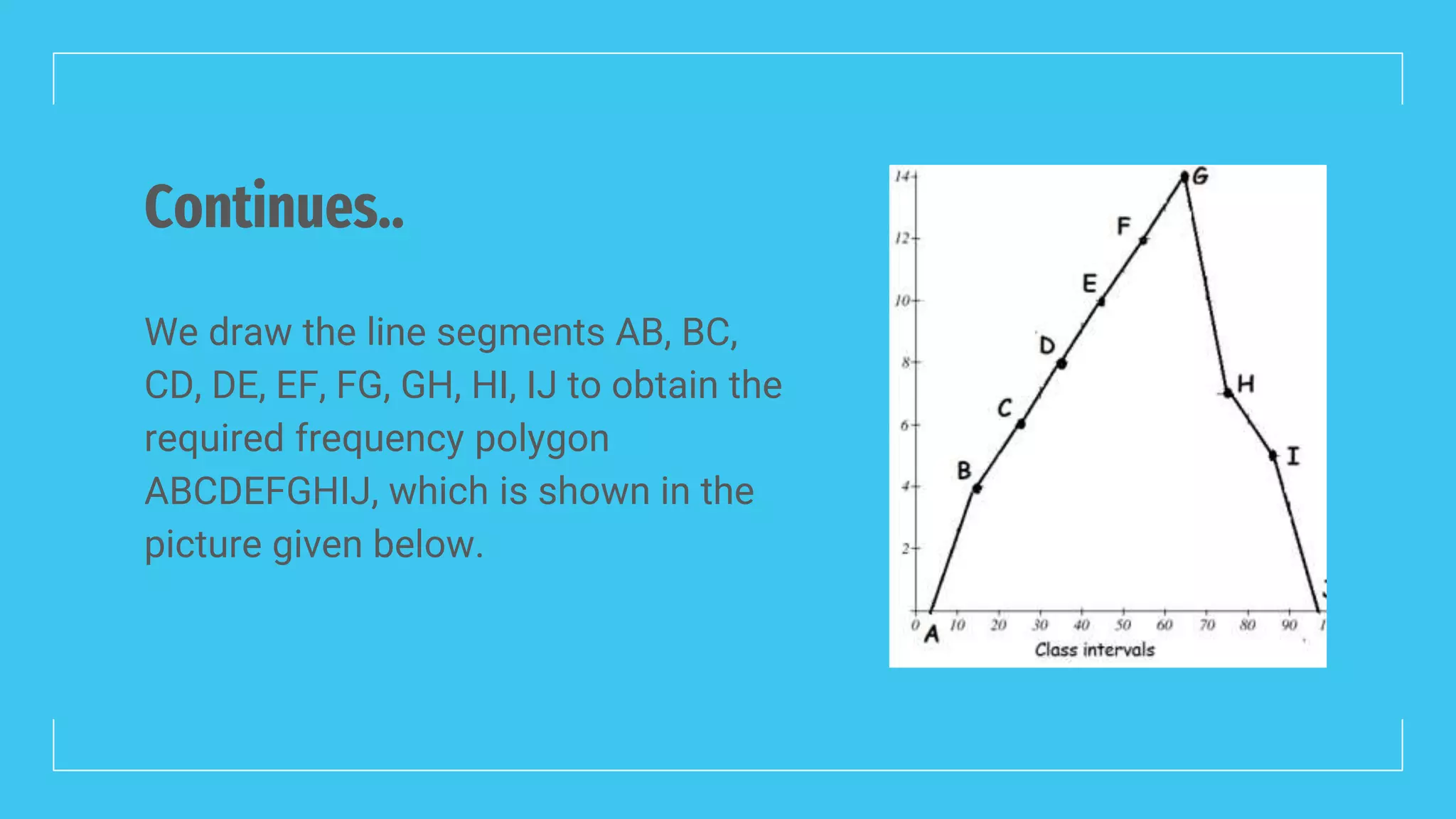
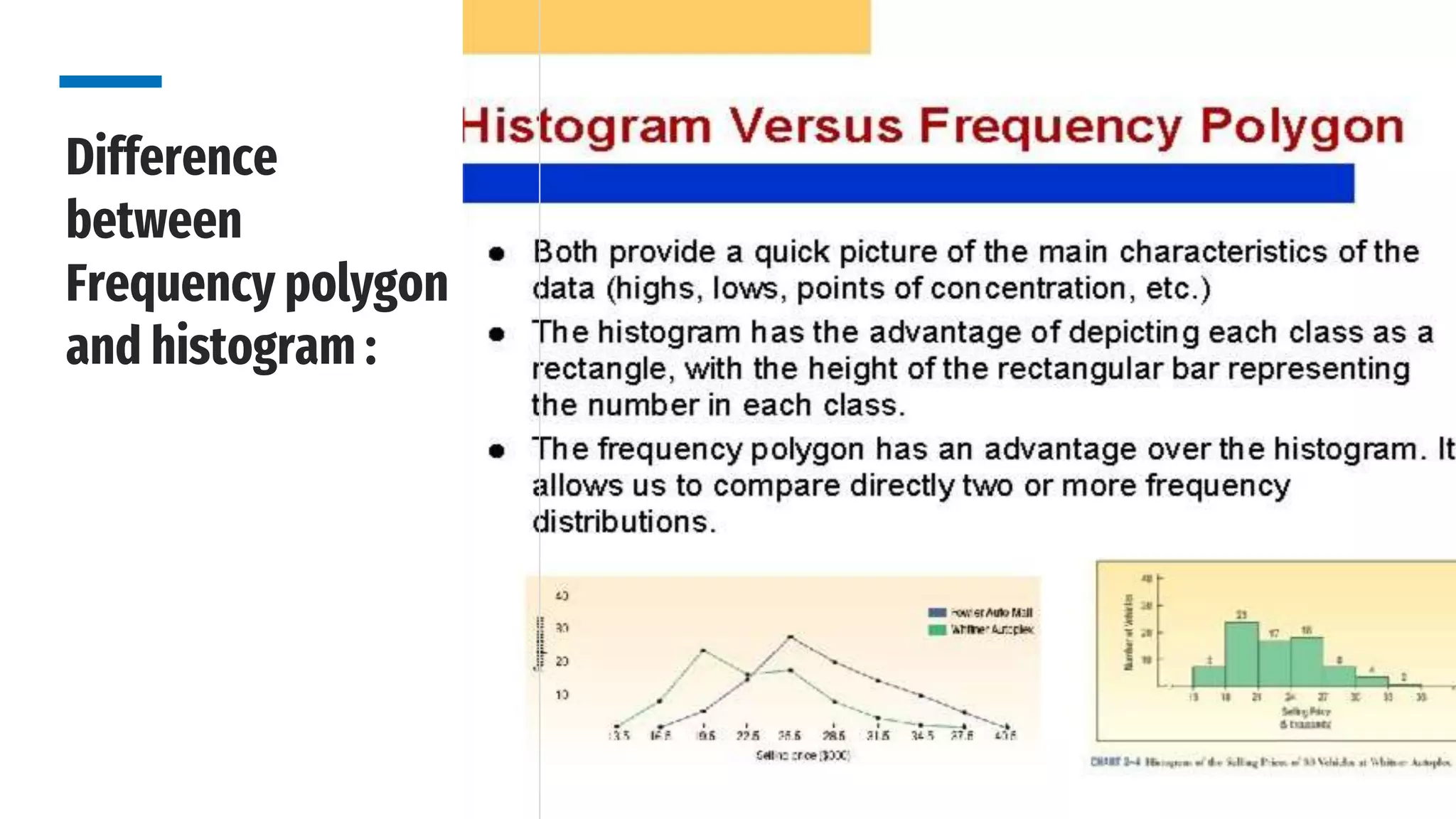
The document discusses line frequency graphs and frequency polygons, outlining their construction and use for representing frequency distributions. It details methods for creating frequency polygons for both discrete and continuous series, highlighting steps and examples. Additionally, it compares frequency polygons to histograms, emphasizing the advantages of using polygons for comparing multiple distributions.