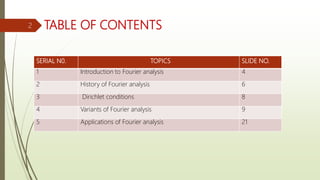
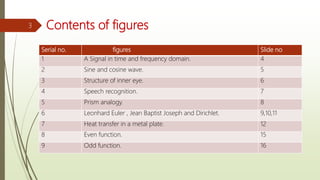
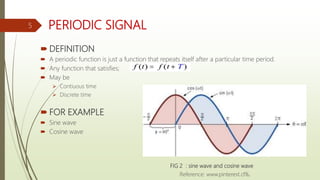
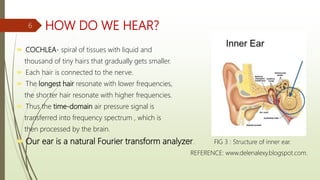
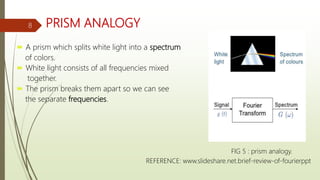
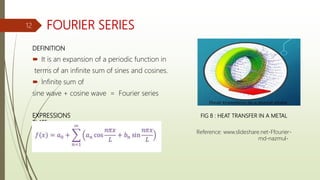
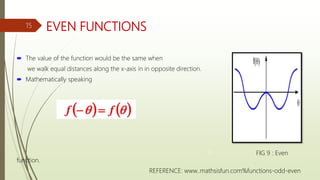
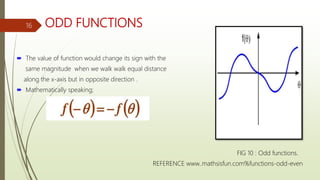
This document provides an overview of Fourier analysis in 3 paragraphs or less:
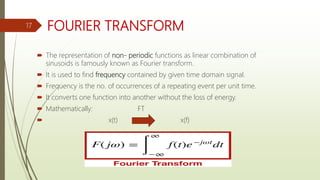
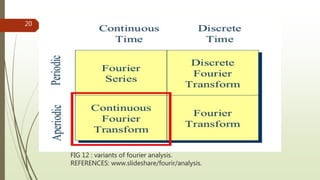
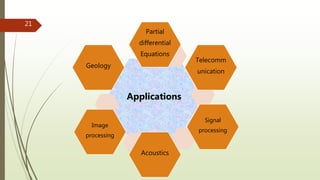
Fourier analysis is a method of representing periodic and aperiodic functions as the sum of trigonometric functions like sines and cosines. It was developed by Joseph Fourier who showed that any signal could be represented as a sum of pure tones. The Fourier transform converts signals between the time and frequency domains, allowing signals to be analyzed by their frequency content. Fourier analysis has applications in fields like signal processing, image processing, acoustics, telecommunications, partial differential equations, geology and more. It provides the foundation for understanding how signals are represented and processed in both continuous and discrete settings.