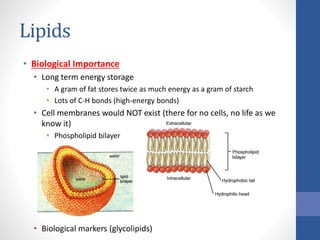
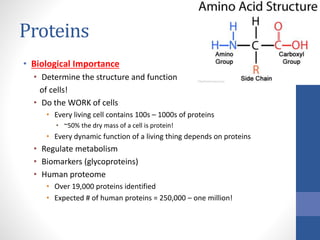
The document discusses the four major classes of macromolecules - carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. It provides details on their biological importance, dietary sources, and functional groups. Carbohydrates are an important energy source and make up cell walls and exoskeletons. Lipids are used for long-term energy storage and are essential components of cell membranes. Proteins determine cell structure and function and carry out all cellular processes. Nucleic acids control reproduction through DNA and protein production via DNA and RNA. ATP stores and transfers energy within cells and fuels all cellular metabolism.