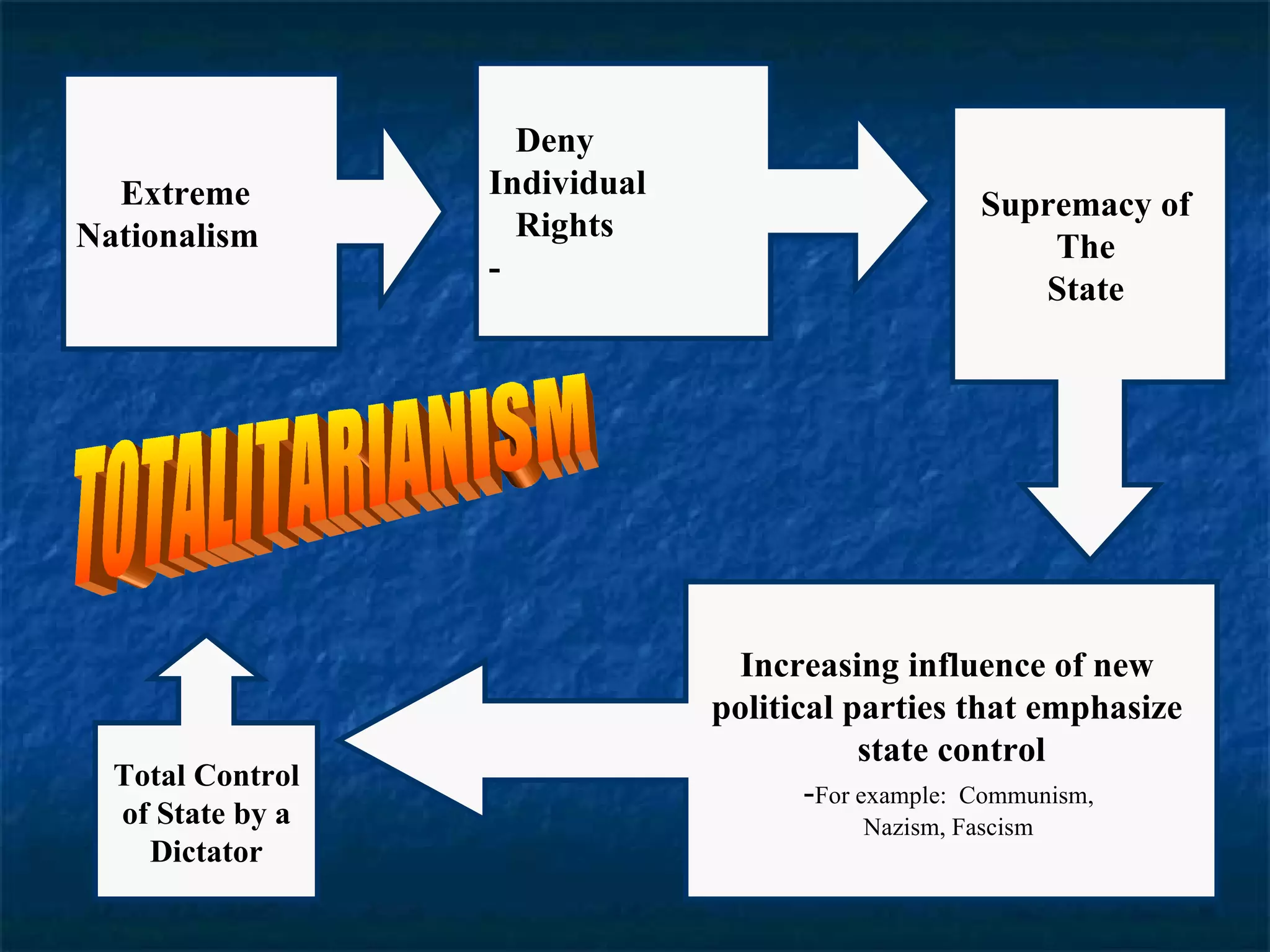
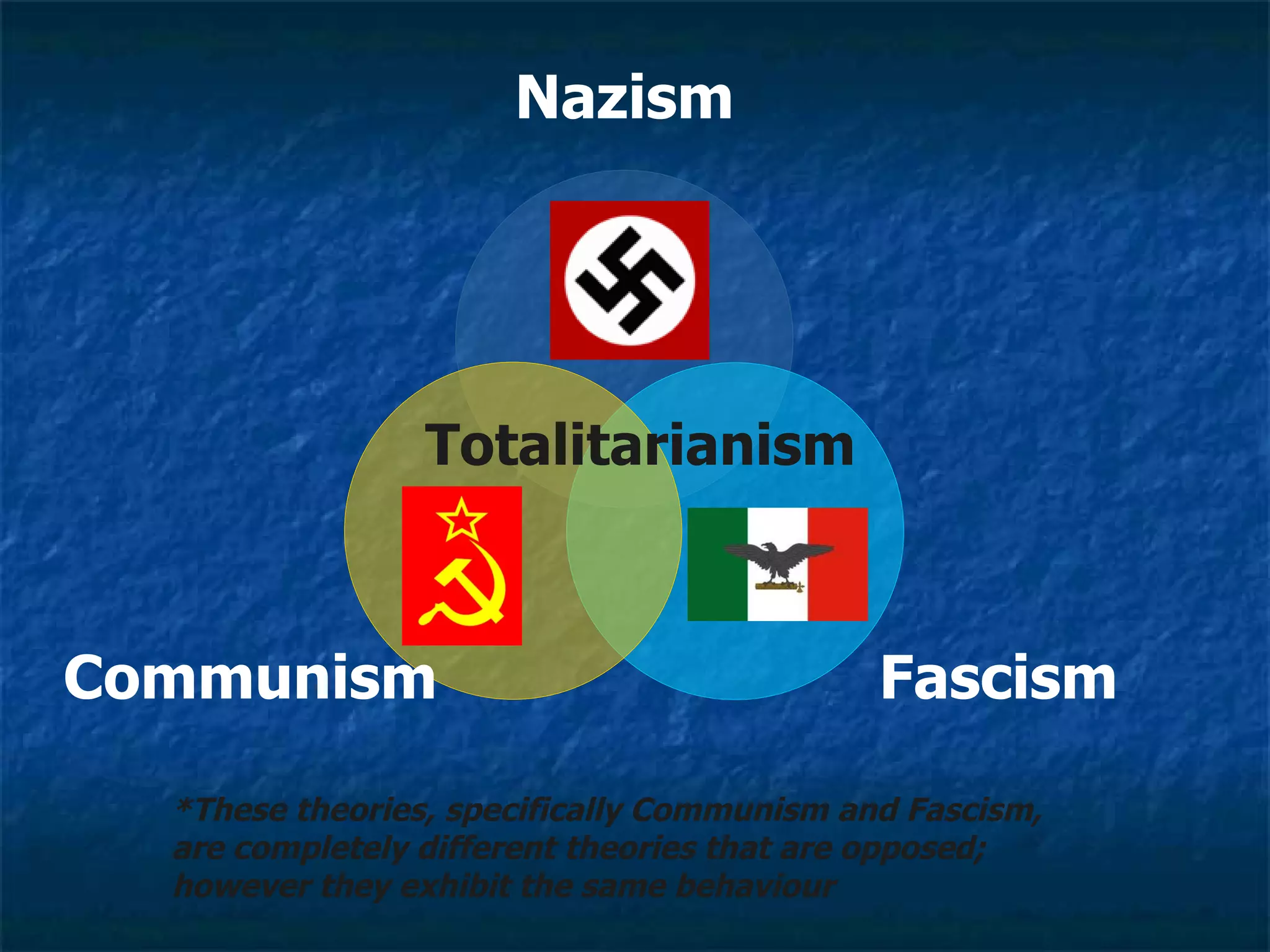
1. During the 1930s, new political ideologies like Communism, Nazism and Fascism gained increasing influence in Europe. These ideologies emphasized extreme nationalism and state control over individual rights.
2. Totalitarianism is a form of government that establishes complete state control over all aspects of society. Totalitarian states are highly nationalistic, use strict laws and censorship, and are led by a single authoritarian dictator.
3. While different in their economic theories, both Communism under Stalin and Fascism under Mussolini and Hitler exhibited totalitarian behaviors with strict state control and emphasis on nationalism. Nazism in particular promoted racist beliefs in Aryan supremacy and anti-Semitism.