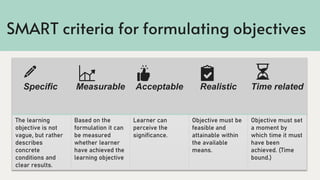
The document discusses the formulation of course objectives, defining them as measurable statements outlining expected learner achievements. It emphasizes the importance of well-defined learning objectives, measurable through performance criteria and grounded in Bloom's taxonomy. Additionally, it highlights the critical nature of clear and attainable objectives in curriculum development, proposing the SMART criteria for effective objective formulation.