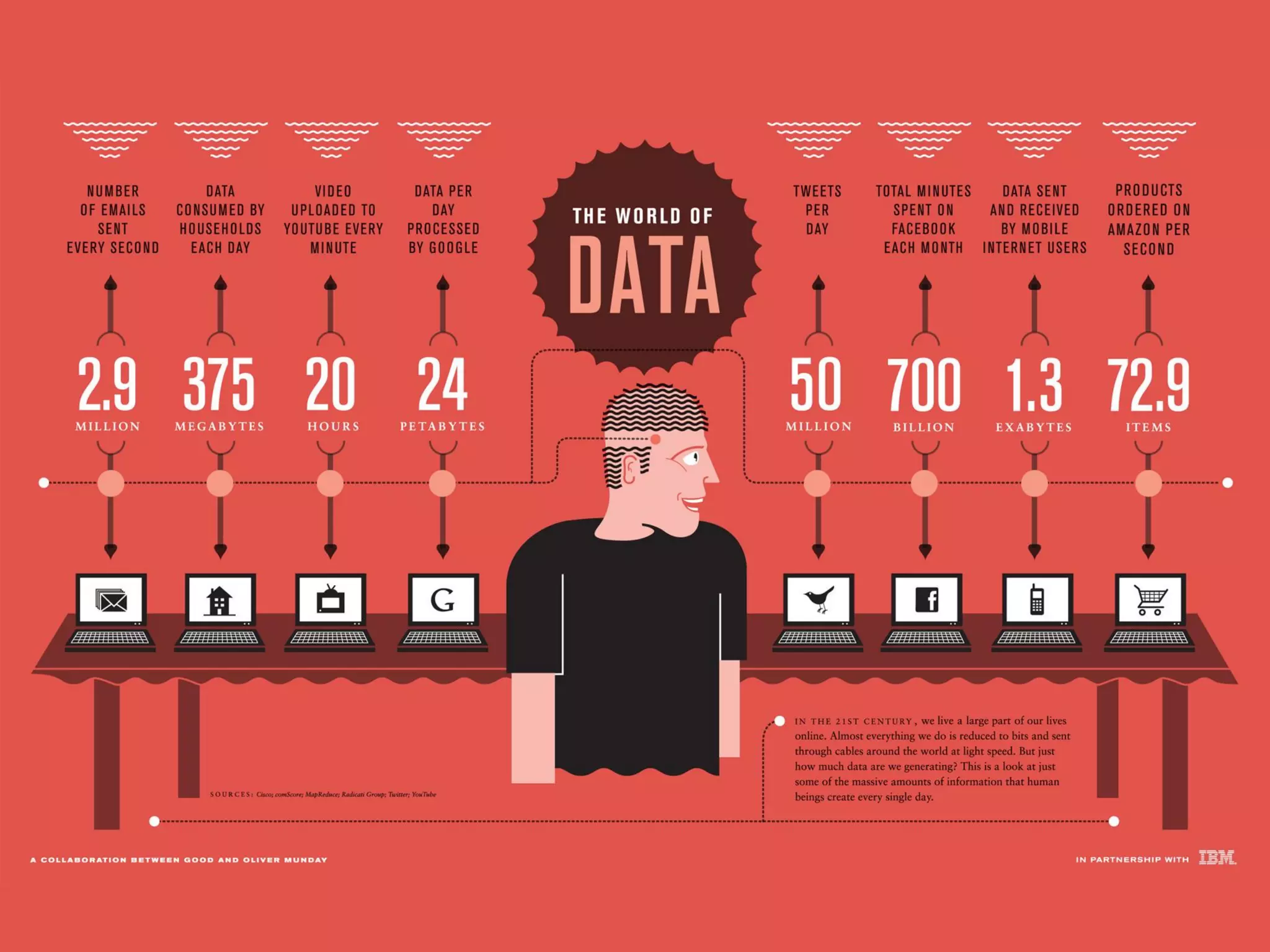
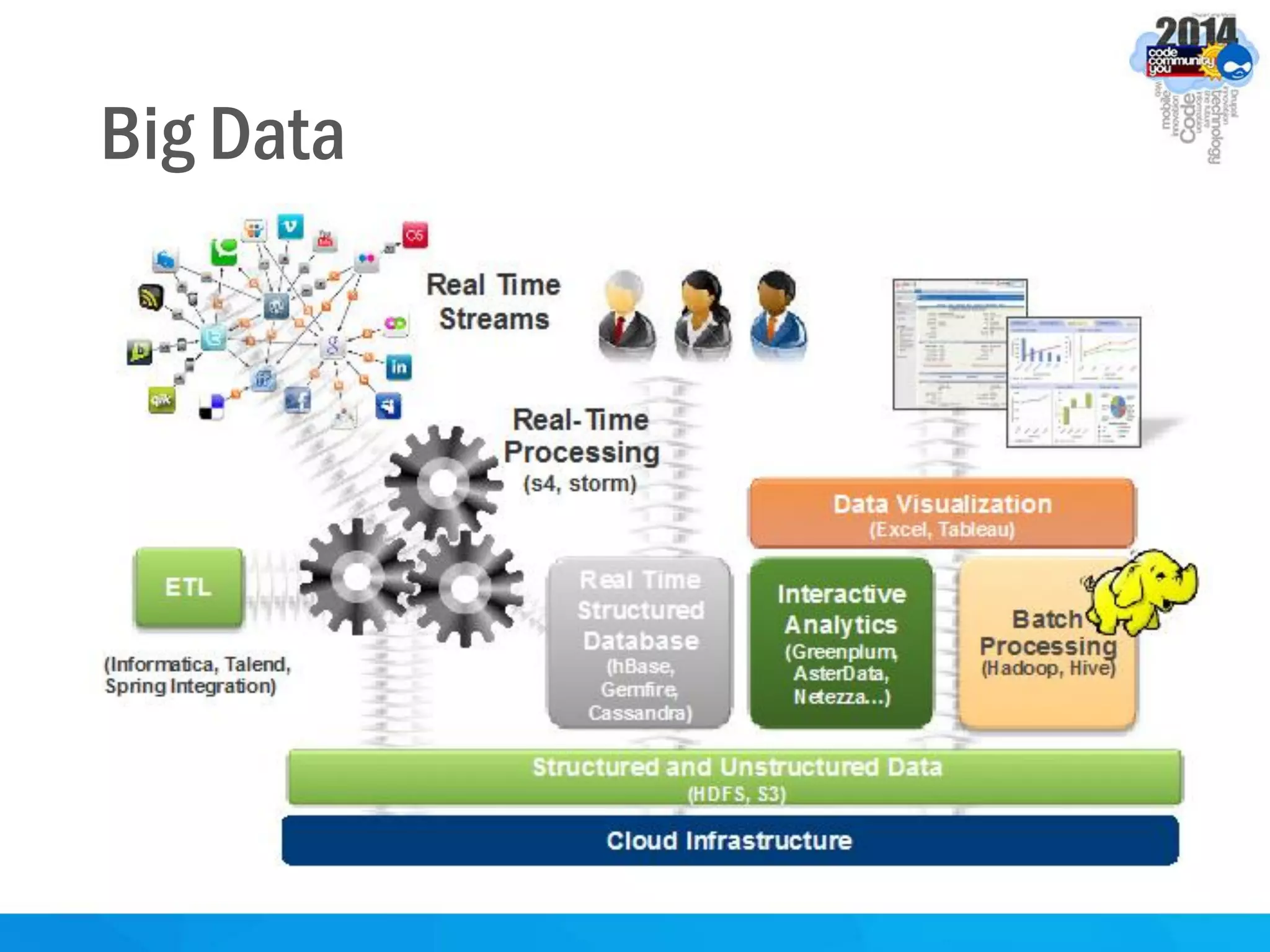
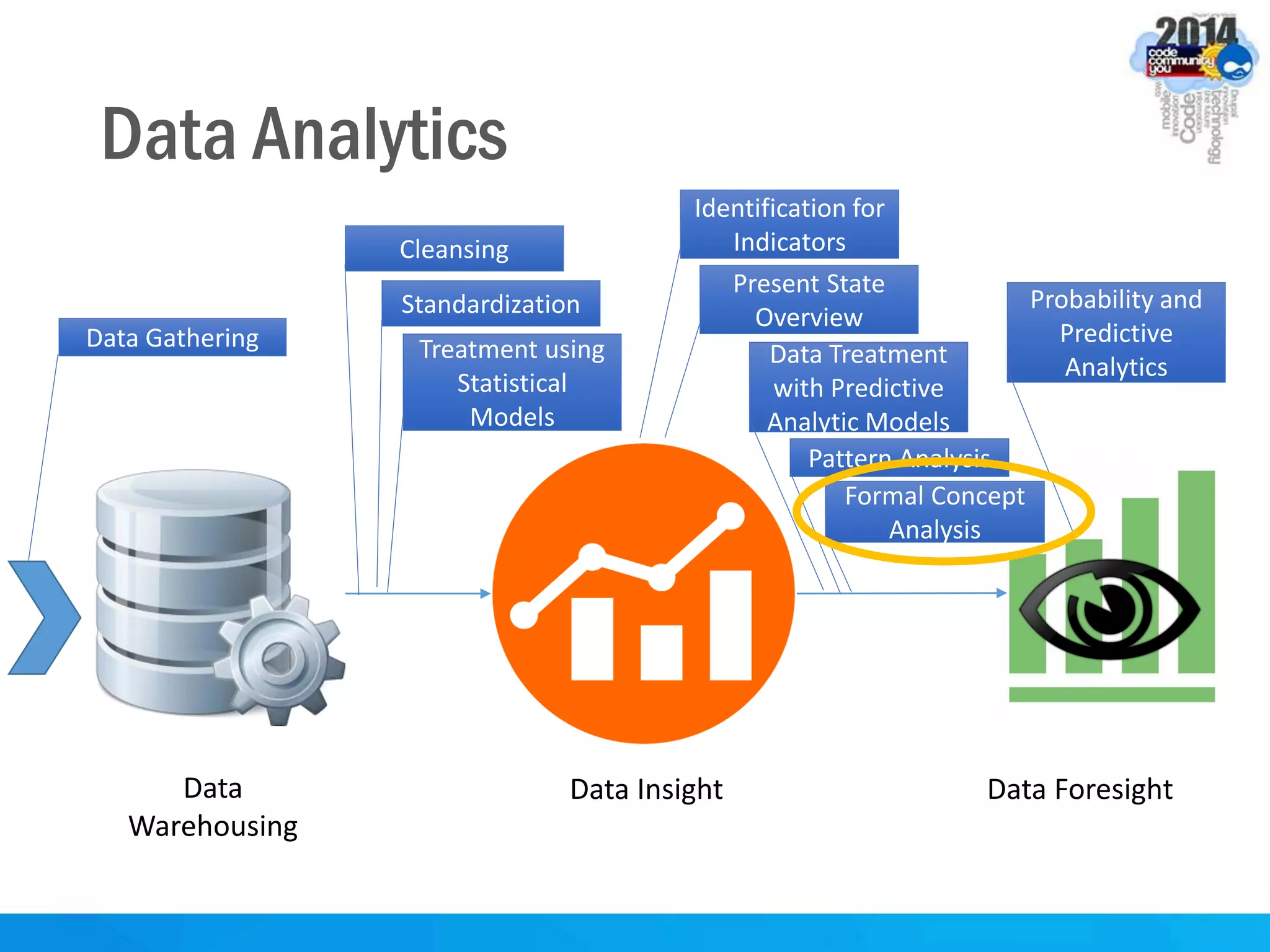
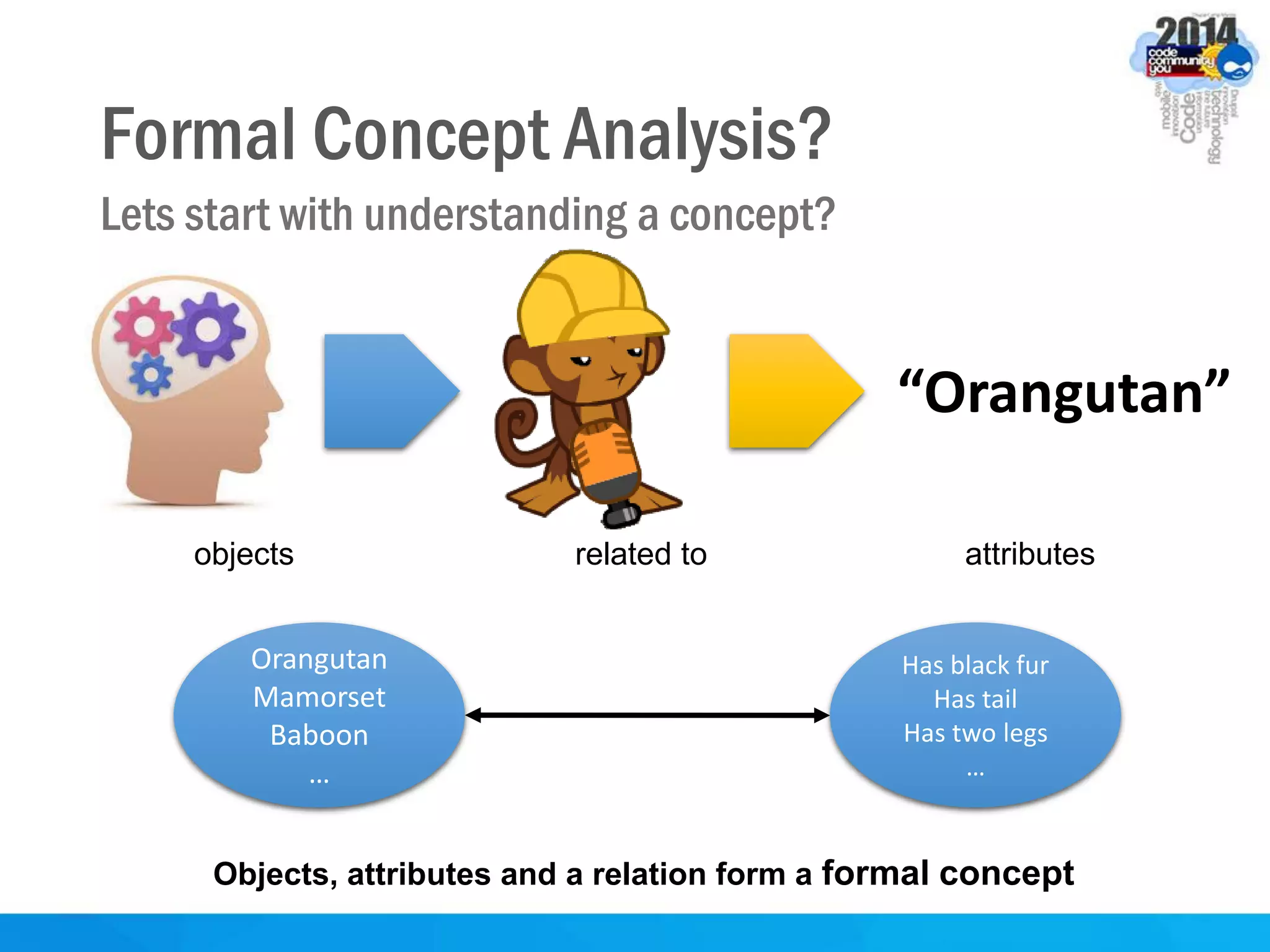
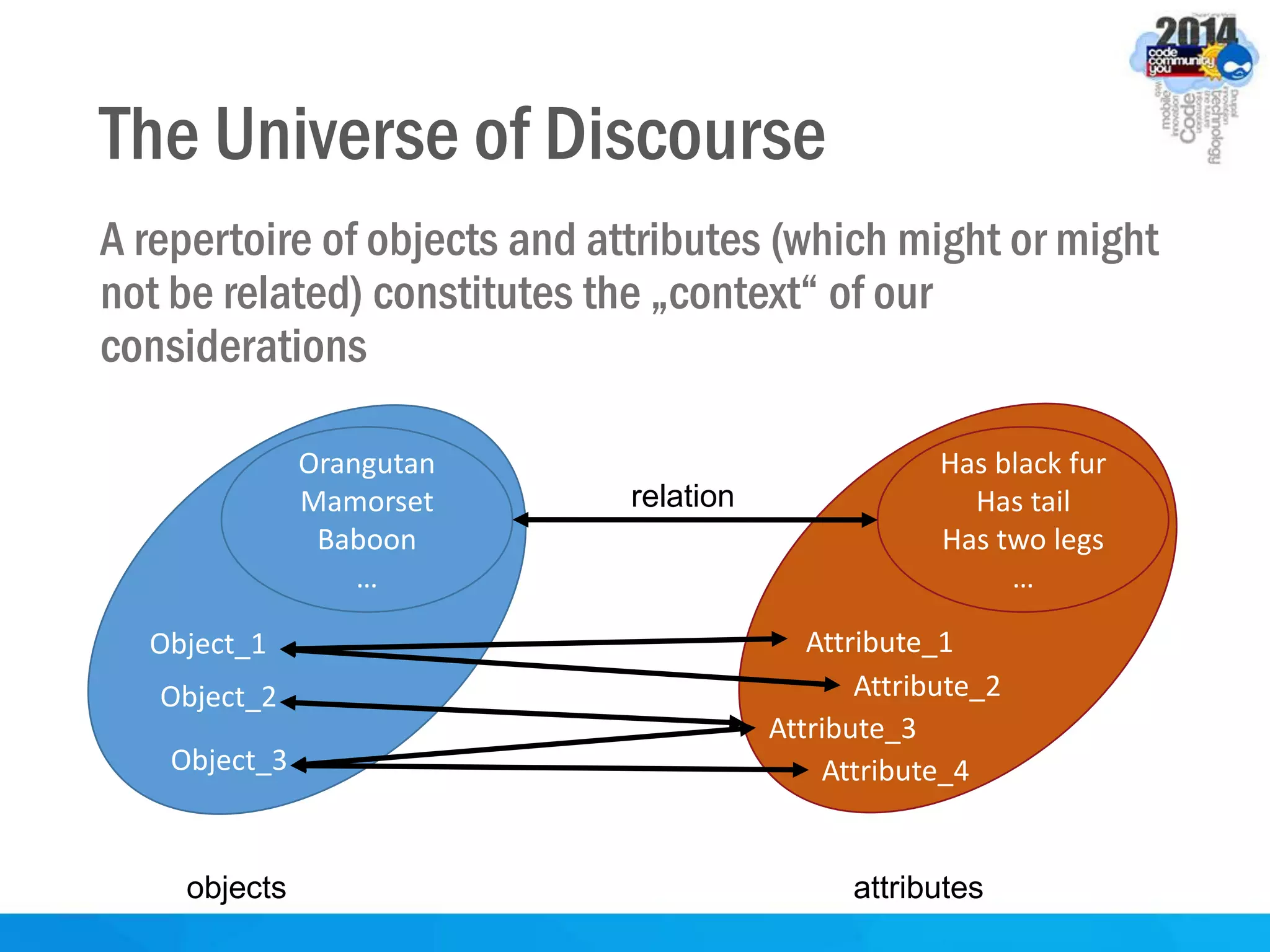
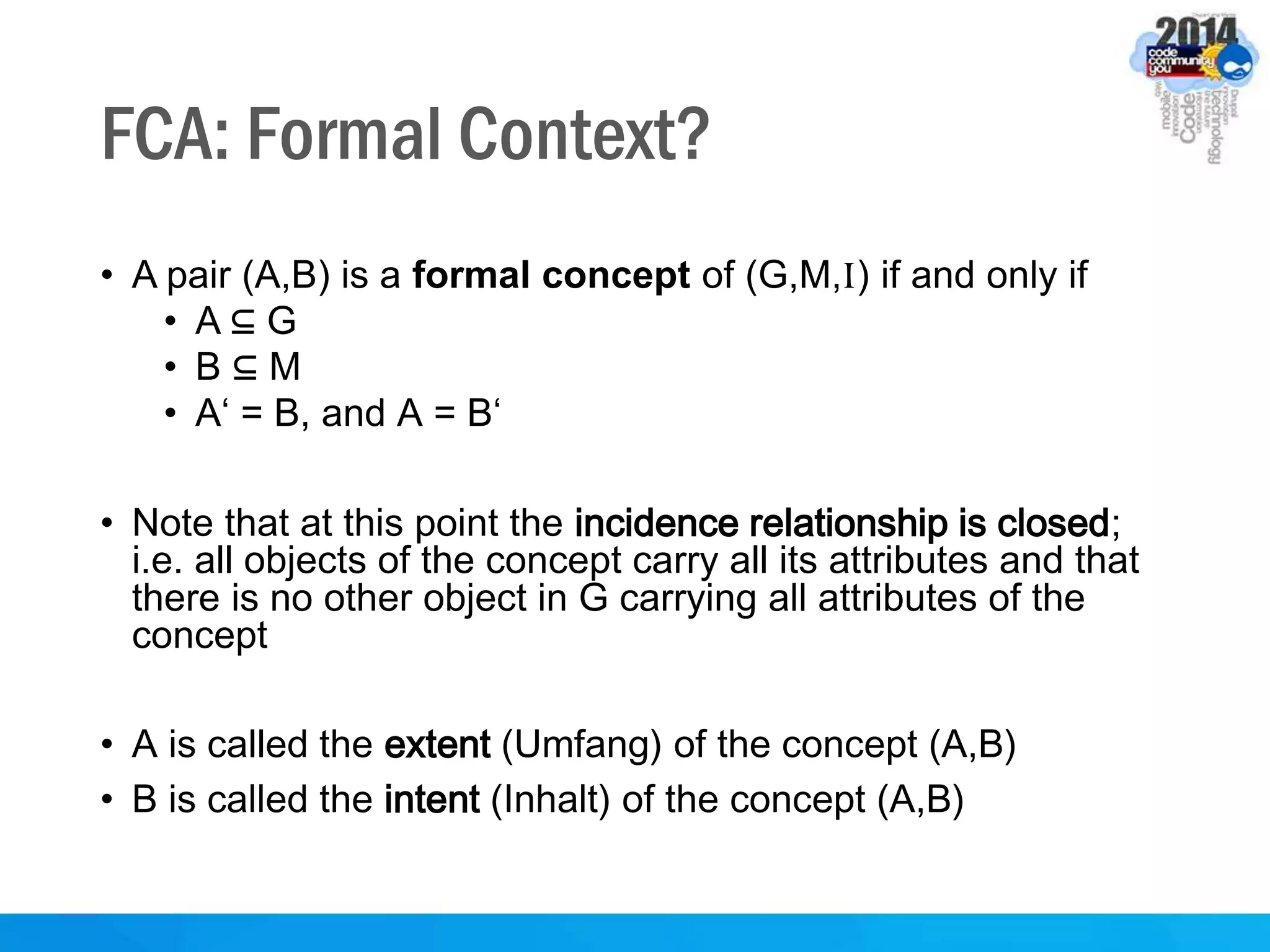
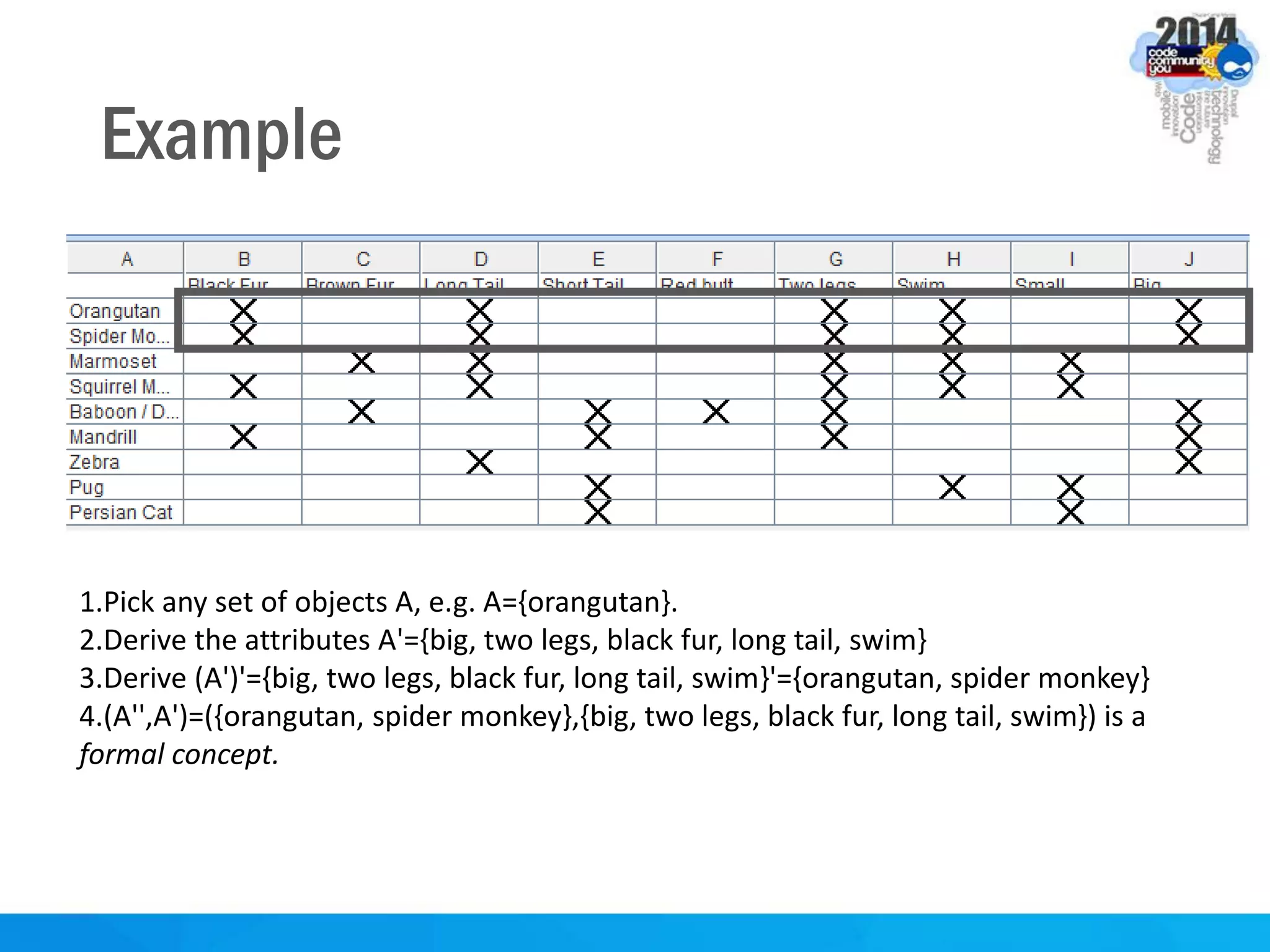
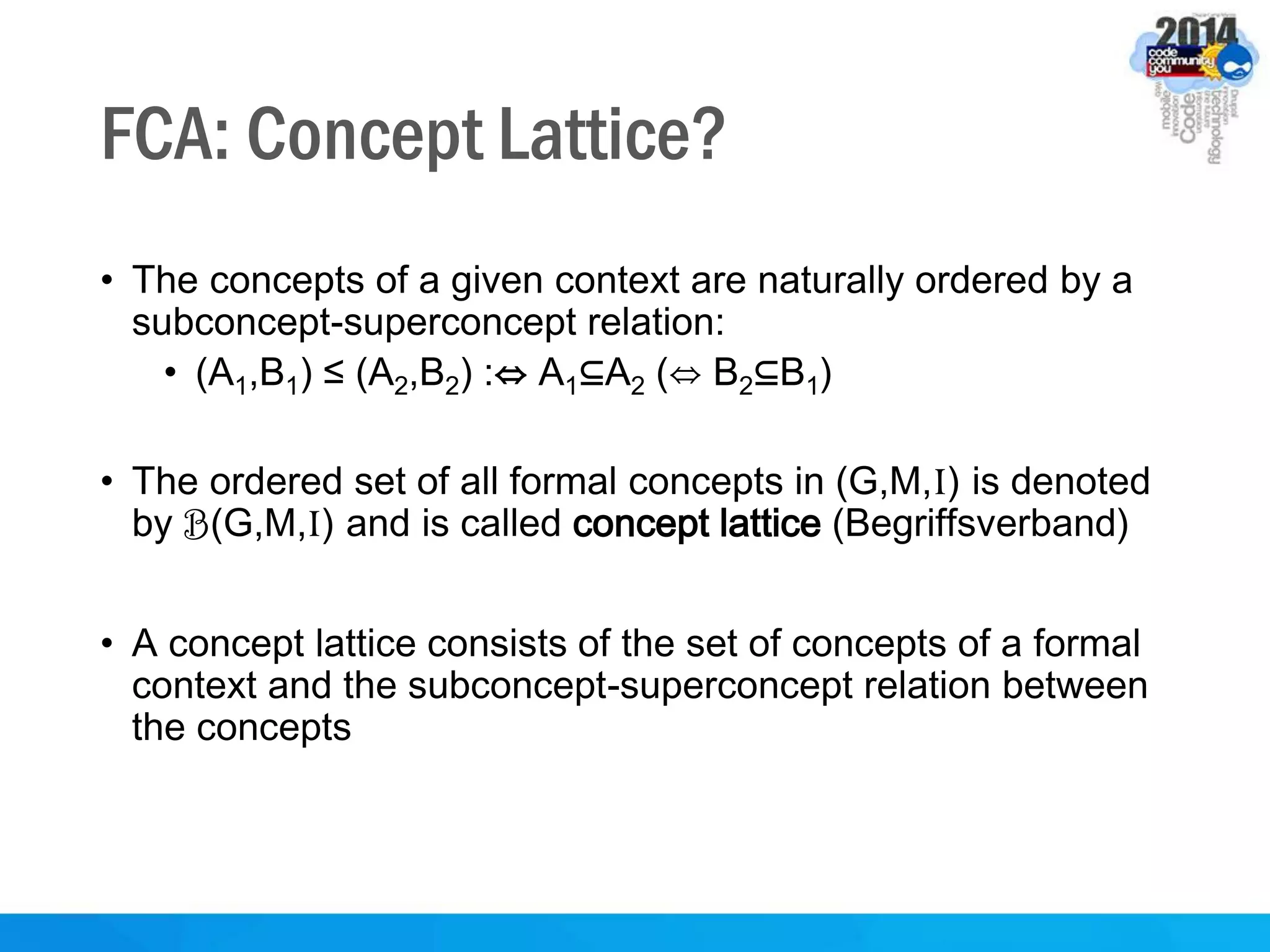
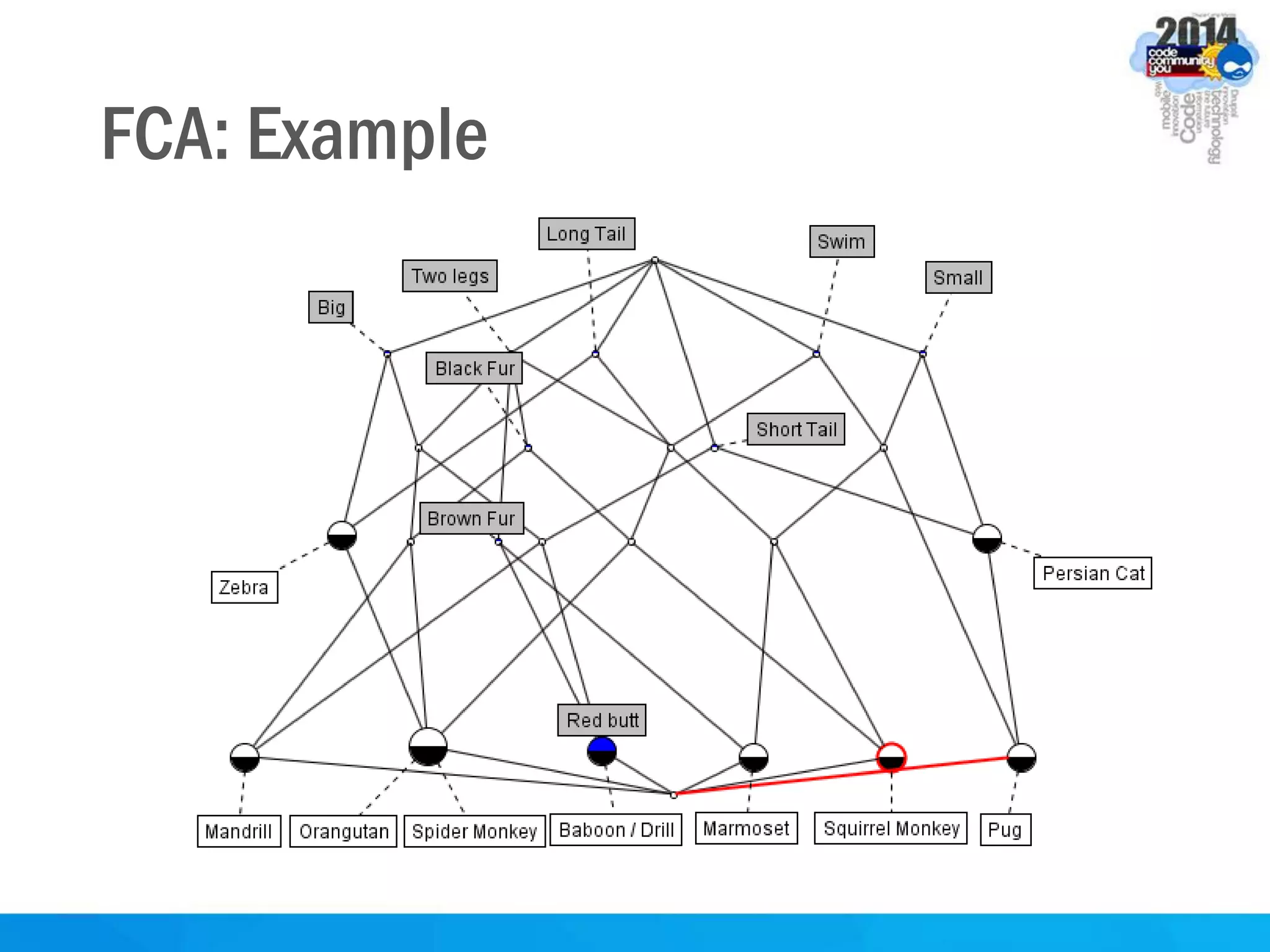
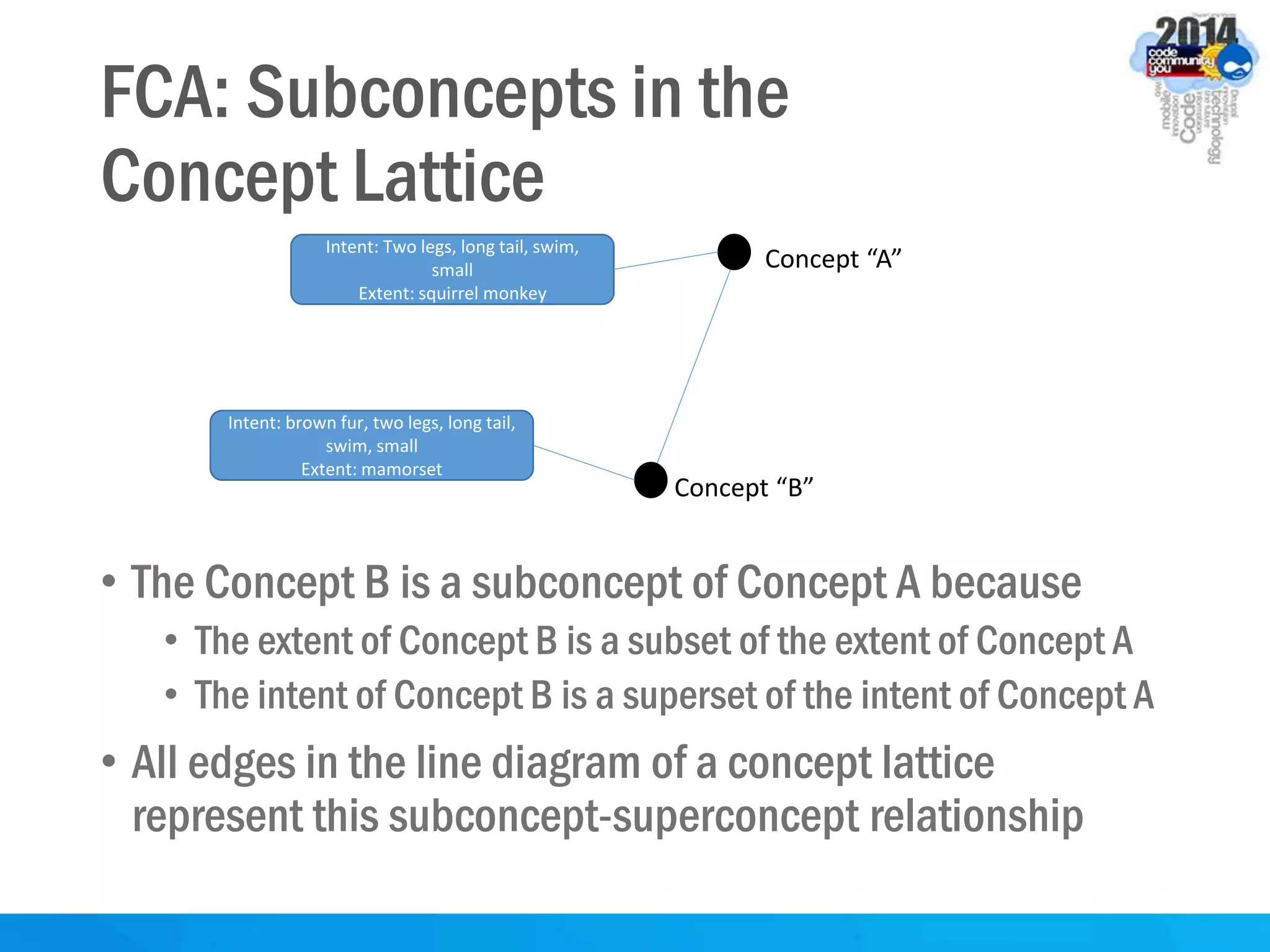
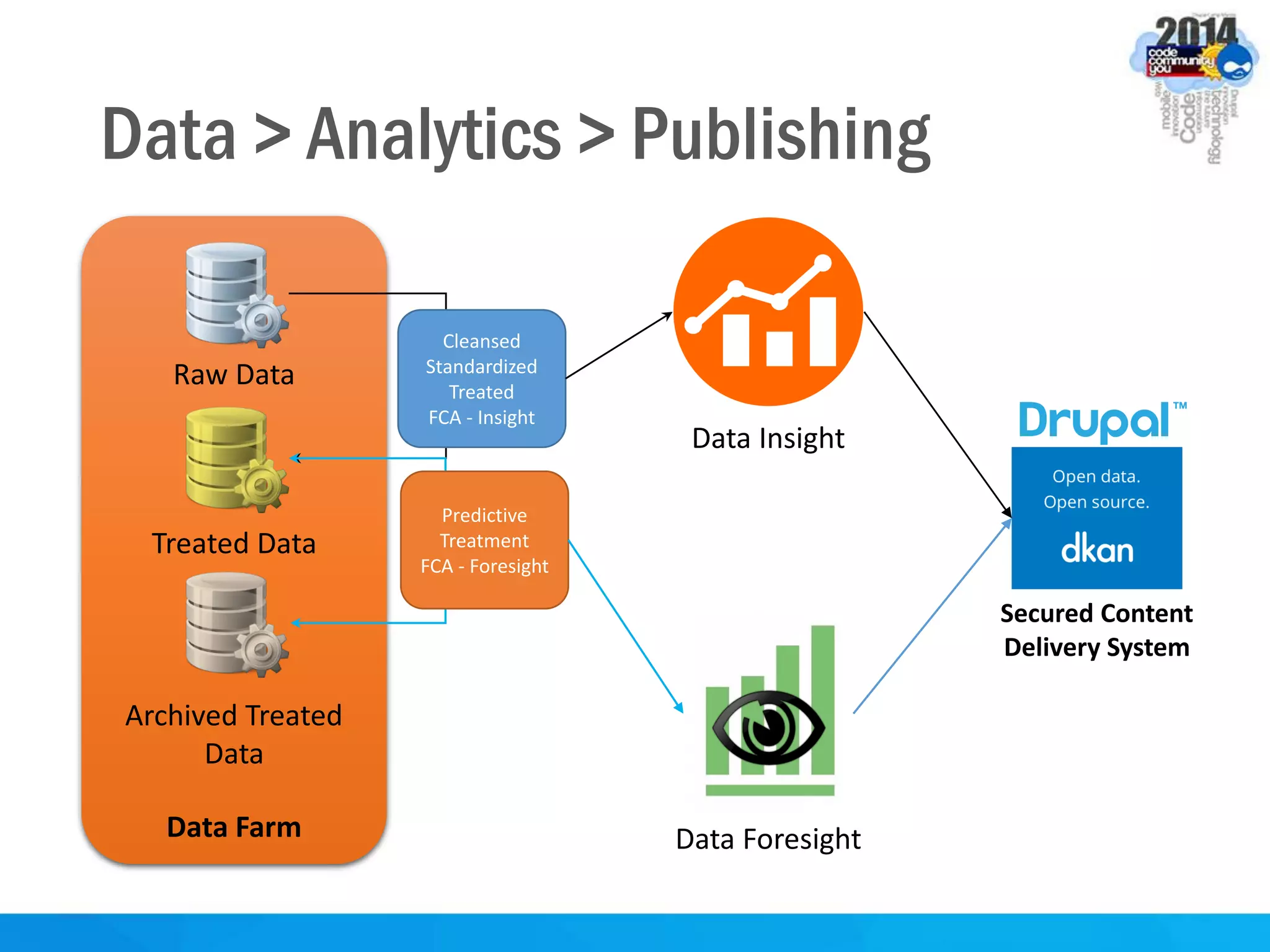
This document discusses formal concept analysis (FCA) as a method for analyzing data. FCA takes a data set consisting of objects and their attributes and identifies natural clusters of objects that share attributes and natural clusters of attributes shared by objects. These clusters form a concept lattice that represents the conceptual relationships in the data. FCA can be used to gain insight from data, foresee patterns and relationships, and structure data for delivery and presentation. The document provides examples and explanations of key FCA terms and processes like formal contexts, derivation, concepts and implications.