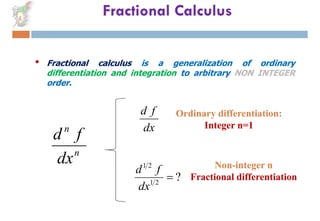
Fractional calculus is a generalization of differentiation and integration to non-integer orders. Some key points:
1) Fractional differentiation allows for differentiation of arbitrary non-integer order, not just integers like 1, 2, 3.
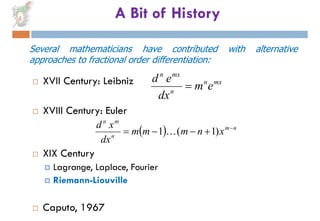
2) The concept was first explored in the 17th century but several mathematicians contributed definitions and approaches over subsequent centuries.
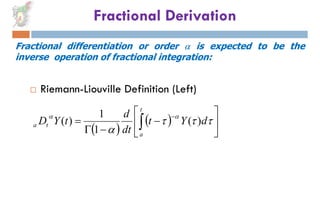
3) Fractional integration involves taking the nth integral of a function where n is any real number, not just integers. This can be done using the Riemann-Liouville definition or the Laplace transform.