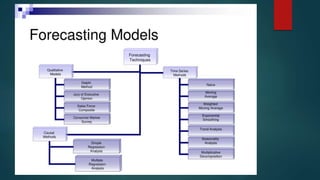
The document discusses forecasting as a method of predicting future events based on past data, emphasizing its importance for business decision-making. It explains the weighted moving average (WMA) technique, which prioritizes recent data over older data and provides a formula for calculation. An example is provided using attendance data from amusement and water parks to illustrate how to forecast future attendance using the WMA method.