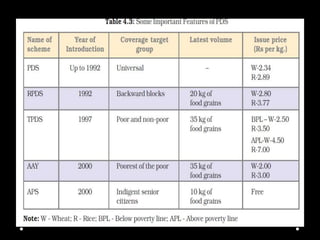
Food security in India depends on the availability, accessibility, and affordability of food. Natural disasters like droughts can negatively impact food security by decreasing food production and increasing prices. The poorest sections of society and those impacted by disasters are most vulnerable to food insecurity. The 1943 Bengal famine killed over 3 million people. Public distribution systems and food subsidies aim to ensure food security, but have faced criticisms around efficiency and targeting of those most in need. Cooperative organizations also play a role in increasing access to affordable food.