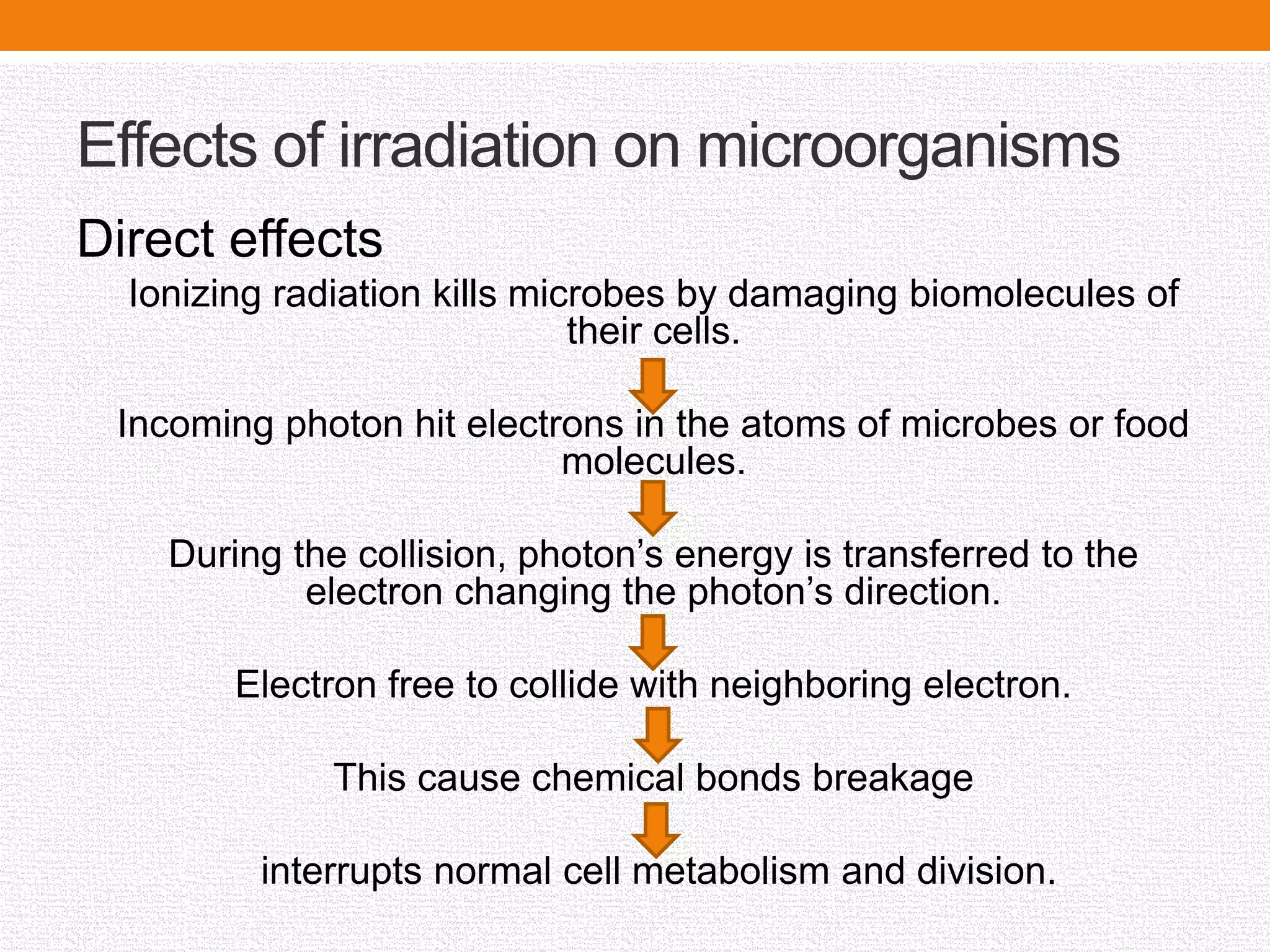
Food irradiation uses ionizing radiation to eliminate microbes and extend the shelf life of food. Various sources of radiation, such as gamma rays and electron beams, can be used in this process, which is effective at different doses for different purposes, including pest control and sterilization. Regulatory approval is required for irradiated foods, and while consumer awareness of its benefits is increasing, proper food handling practices remain essential to prevent foodborne illnesses.