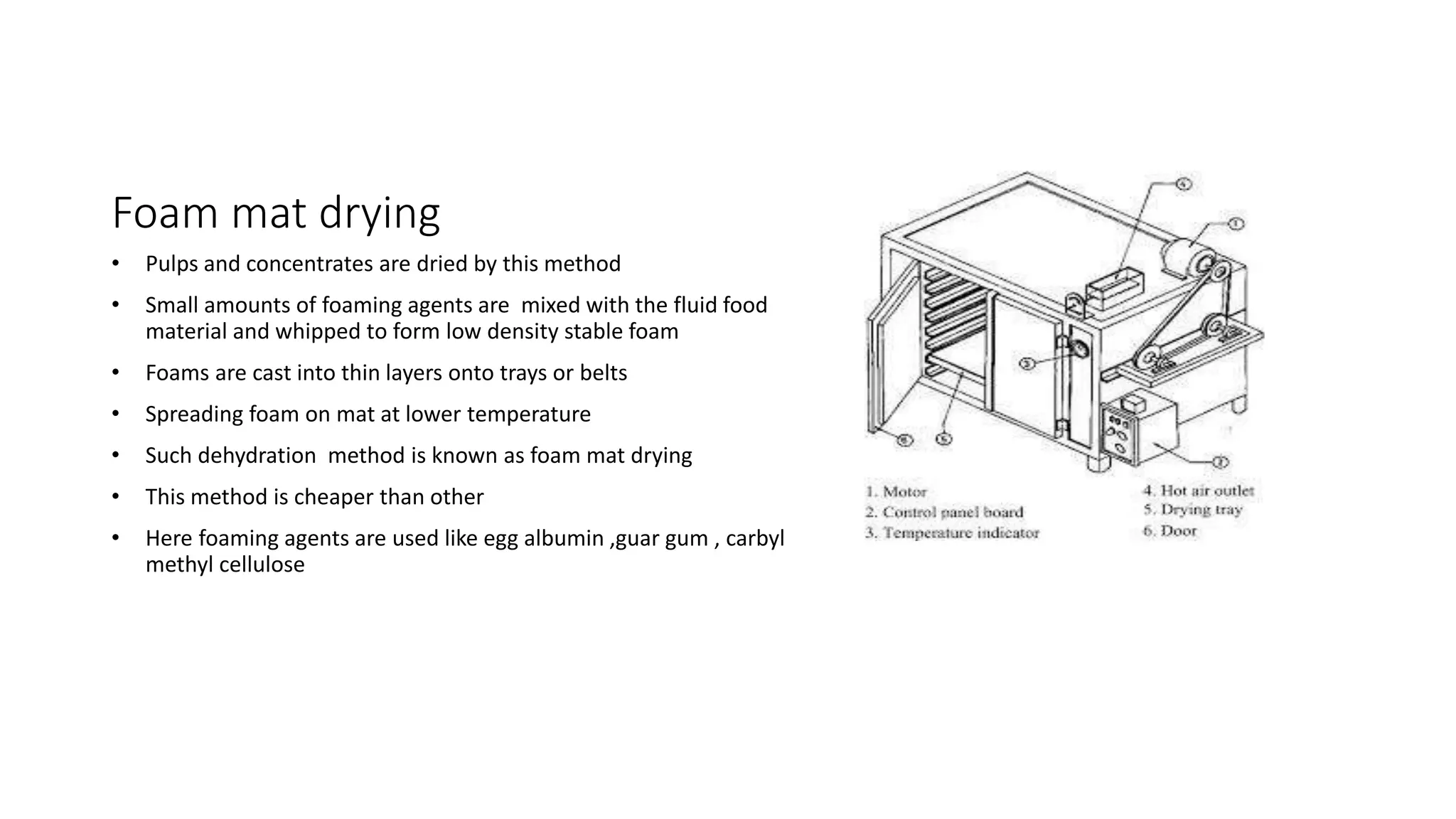
The document discusses various methods for preserving foods through drying. It describes the principles of drying foods to reduce moisture levels and prevent microbial growth. Several drying techniques are outlined including sun drying, solar drying, shade drying, and various mechanical dryers like oven dryers, kiln dryers, and fluidized bed dryers. The factors that influence the drying process and steps involved from selection and sorting of foods to drying, sweating and packing are also summarized.