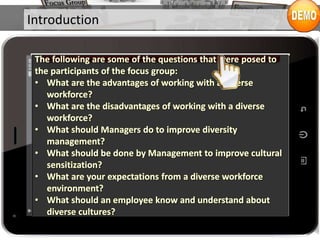
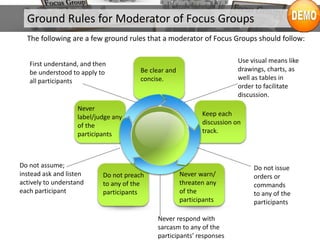
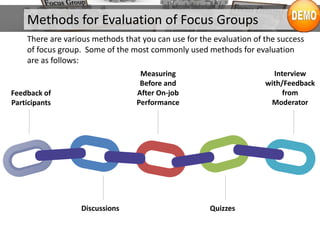
The document provides an overview of focus groups, including their objectives, advantages and disadvantages, types, question design, moderation, and evaluation. Focus groups involve interviewing 6-12 individuals to understand attitudes and behaviors. They are a tool for marketing research and exploration. Key aspects covered include sampling, moderation ground rules, blocking roles, question ordering, and feedback methods.