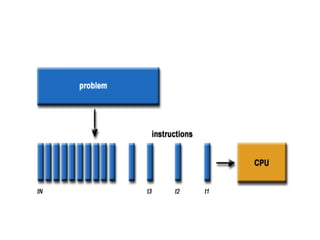
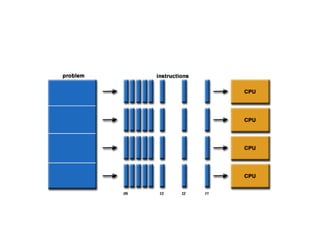
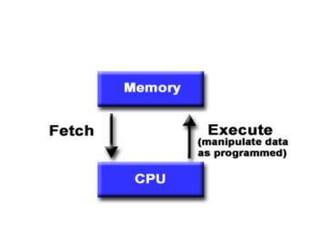
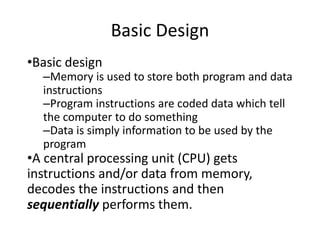
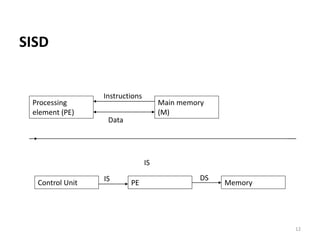
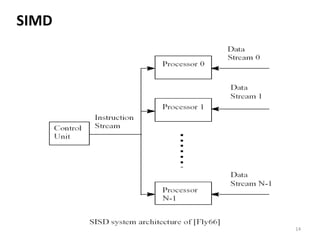
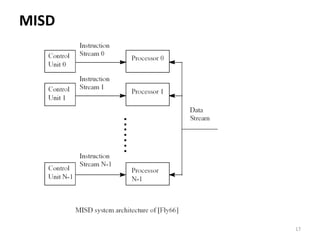
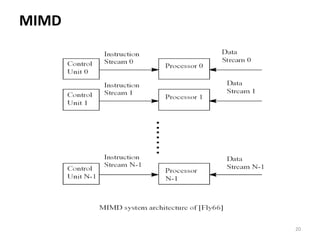
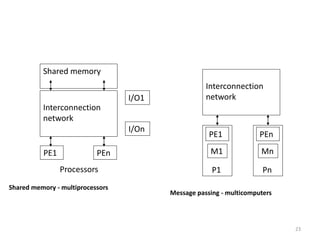
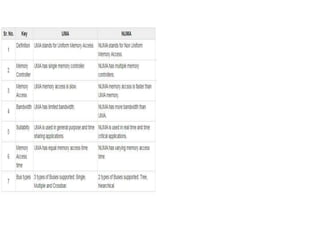
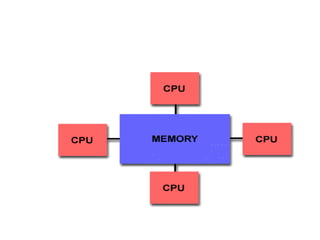
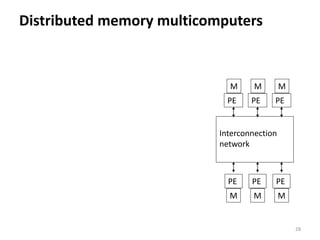
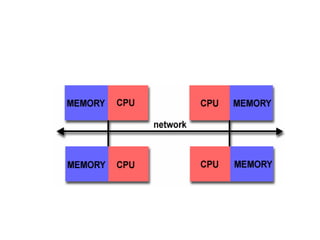
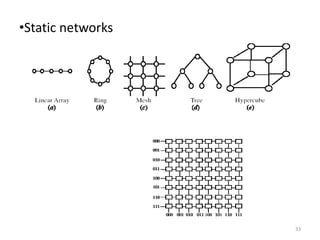
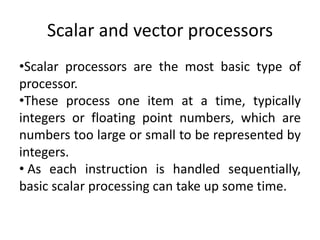
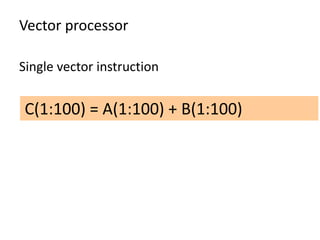
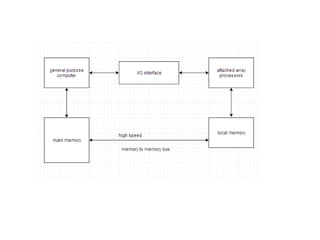
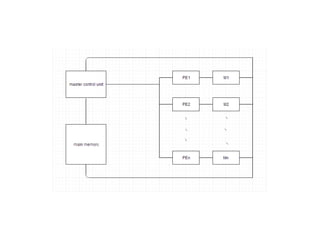
Parallel computing involves using multiple processing units simultaneously to solve computational problems. It can save time by solving large problems or providing concurrency. The basic design involves memory storing program instructions and data, and a CPU fetching instructions from memory and sequentially performing them. Flynn's taxonomy classifies computer systems based on their instruction and data streams as SISD, SIMD, MISD, or MIMD. Parallel architectures can also be classified based on their memory arrangement as shared memory or distributed memory systems.