This document discusses conditional statements in VB.NET. It describes if statements, including if-then, if-then-else, and if-then-elseif statements. It also covers nested if statements. Additionally, it explains select case statements and their different forms for exact matches, relational tests, and range checks.








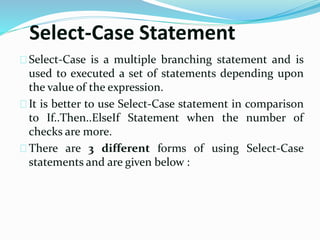
![Different forms of Select-Case
Select Case Expression
Case Value
’visual basic statements
Case Value
’visual basic statements
Case Else
’visual basic statements
End Select
1. Select Case : Simplest Form [Exact match]
Example :
Select Case byMonth
Case 1,3,5,7,8,10,12
number_of_days=31
Case 2
number_of_days=28
Case Else
number_of_days=30
End Select](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ifandselectstatement-141204213019-conversion-gate01/85/If-and-select-statement-10-320.jpg)
![Select Case Expression
Case Is relation
’visual basic statements
Case Is relation
’visual basic statements
Case Else
’visual basic statements
End Select
Example:
Select Case marks
Case Is < 50
Result = “Fail”
Case Is < 60
Result = “Grade B”
Case Is < 75
Result = “Grade A”
Case Else
Result = “Grade A+”
End Select
2.Select Case : Second Form [Relational Test]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ifandselectstatement-141204213019-conversion-gate01/85/If-and-select-statement-11-320.jpg)
![Select Case Expression
Case exp1 To exp2:
’visual basic statements
Case exp1 To exp2:
’visual basic statements
Case Else:
’visual basic statements
End Select
Example :
Select Case Age
Case 2 to 4 : Msgbox(“PreNursery”)
Case 4 to 6 : Msgbox(“Kindergarden”)
Case 6 to 10 : Msgbox(“Primary”)
Case Else : Msgbox(“Others”)
End Select
3.Select Case : Third Format [Range Check]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ifandselectstatement-141204213019-conversion-gate01/85/If-and-select-statement-12-320.jpg)
