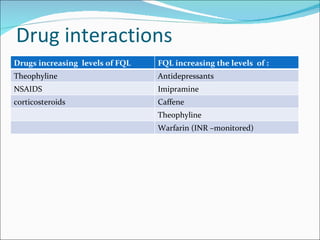
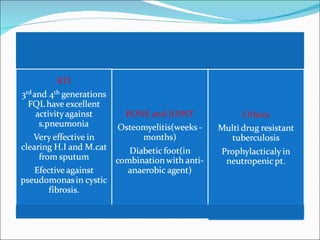
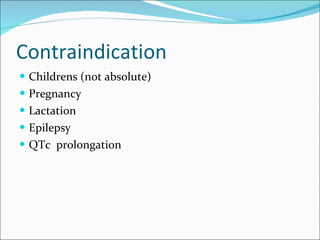
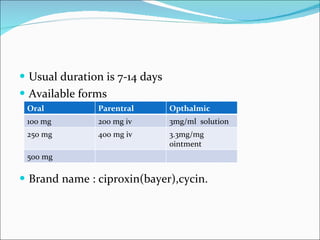
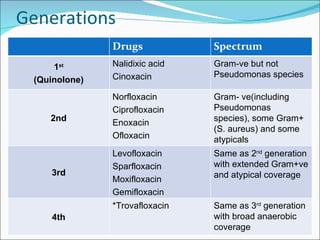
Fluoroquinolones are a class of broad-spectrum antibacterial agents derived from nalidixic acid. They work by inhibiting bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, blocking DNA synthesis. Resistance can occur via mutations in the quinolone binding region of these target enzymes or changes in bacterial permeability. Fluoroquinolones are classified into generations based on spectrum of activity and are well-absorbed orally with varying tissue distribution and drug interactions. Common adverse effects include GI issues, CNS effects, and QT prolongation. Ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin are two commonly used fluoroquinolones with activity against a variety of gram-negative and some gram-



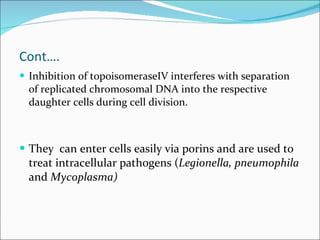



![Distribution [Conc] > serum: Prostate tissue Stool Bile Lung Kidneys Neutrophils Macrophages [Conc] < serum: Prostatic fluid Bone CSF](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fluroquinolones2-110307004430-phpapp01/85/Fluroquinolones-2-10-320.jpg)