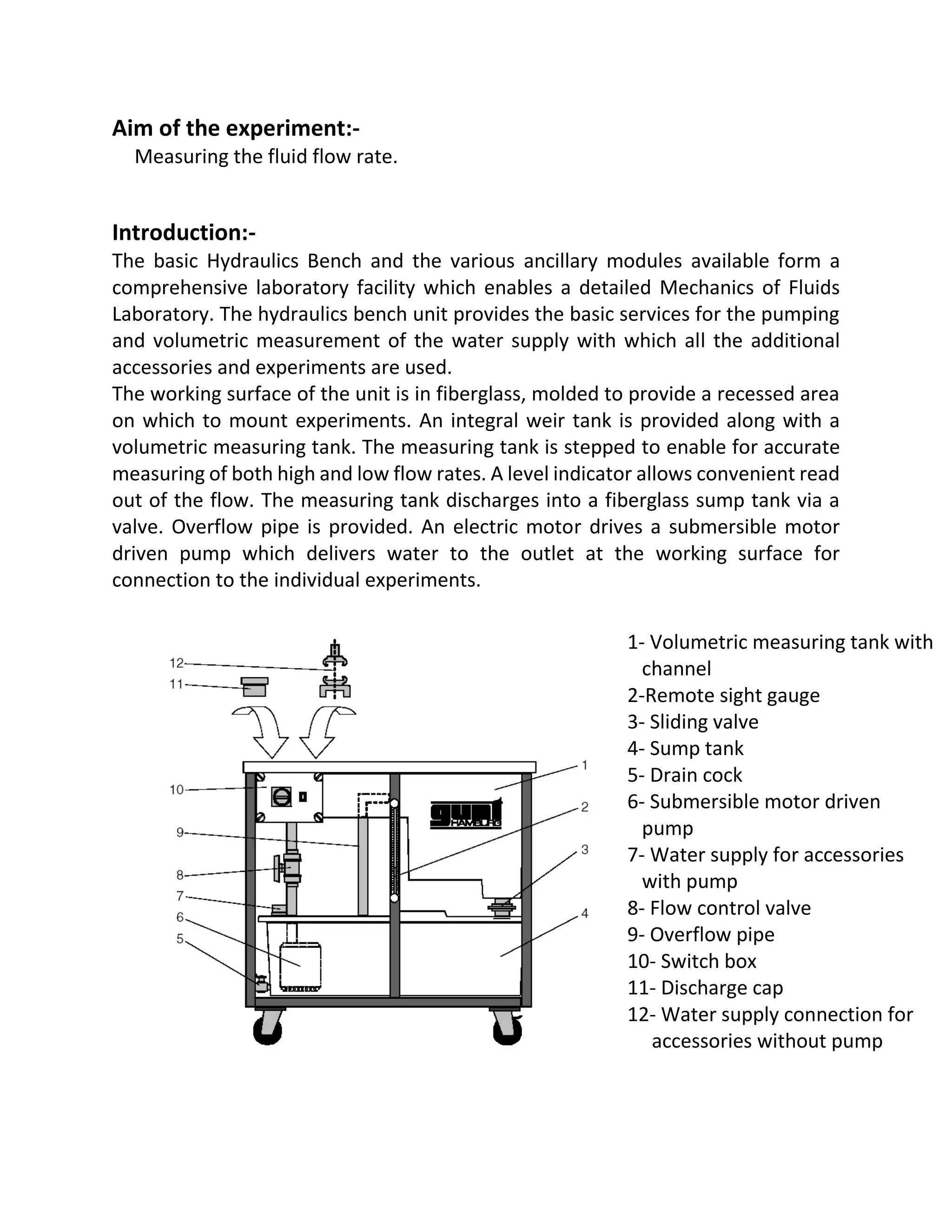
The document details an experiment aimed at measuring fluid flow rates using a hydraulics bench equipped with various components for volumetric measurement. It outlines the experiment procedure, calculations for volume flow rate, mass flow rate, and weight flow rate, along with results from multiple trials. The discussion highlights the relationship between discharge, mass flow rate, and weight flow rate, noting that they increase together but their relationship with discharge over time is inverse.