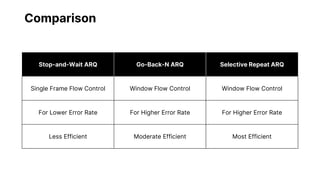
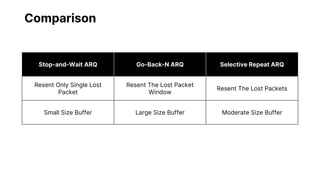
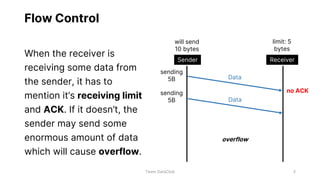
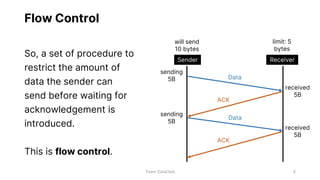
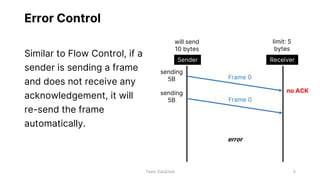
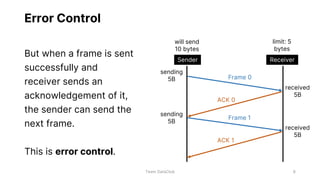
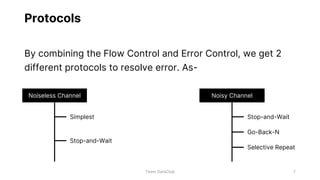
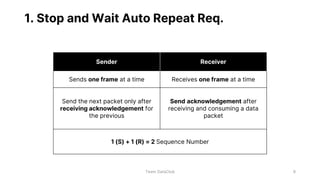
Flow control and error control are responsible for managing data transmission rates and ensuring reliable data transmission on the data link layer of the OSI model. Flow control involves the receiver notifying the sender of its buffer limit and acknowledging received data so the sender does not overflow the receiver's buffer. Error control involves the sender retransmitting frames if acknowledgment of receipt is not received. Three common error control protocols are stop-and-wait ARQ, go-back-N ARQ, and selective repeat ARQ, which differ in their window sizes and retransmission strategies.






![2. Go-Back-N Auto Repeat Req.
Team DataClub 13
Sender Receiver
Sender Window 2m - 1 Receiver Window 1
Send one or more packet only after
receiving acknowledgement
in order
Send acknowledgement after
receiving and consuming a data
packet
( 2m – 1 ) + 1 Sequence Number [( 2m – 1 ) = N]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csc-465-b-group-dataclub-presentation-spring-2023-230501072846-cb54b055/85/Flow-Control-and-Error-Control-13-320.jpg)






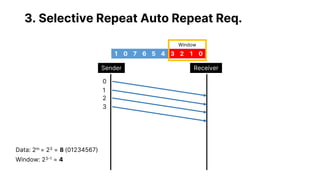
![3. Selective Repeat Auto Repeat Req.
Sender Receiver
Sender Window 2m - 1 Receiver Window 2m - 1
Sends the packets with error or
packets with no ACK when timed
out
Send acknowledgement after
receiving and consuming a data
packet
2 x (2m - 1) Sequence Number [( 2m – 1 ) = N]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csc-465-b-group-dataclub-presentation-spring-2023-230501072846-cb54b055/85/Flow-Control-and-Error-Control-20-320.jpg)