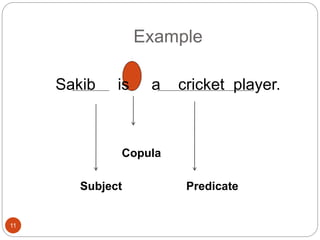
This document provides an introduction to logic, including definitions of key terms like inference, proposition, and truth values. It gives examples of valid logical inferences and explains the basic elements of a proposition - the subject, predicate, and copula. The document also discusses different types of propositions such as categorical, conditional, and disjunctive and provides exercises for identifying subjects, predicates, and copulas in sample propositions.