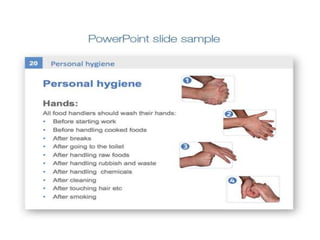
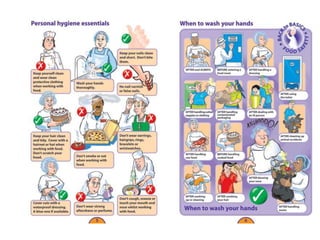
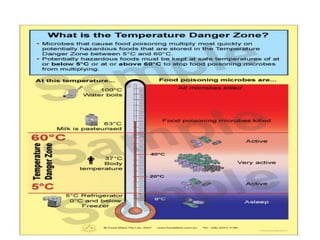
The document outlines various food hygiene hazards, including physical, chemical, and biological contamination, with bacterial contamination being a leading cause of food poisoning. It emphasizes the importance of proper handwashing, cross-contamination prevention, and cooking food to safe temperatures to ensure safety. Additionally, it advises on proper food storage temperatures and handling techniques to minimize risks.