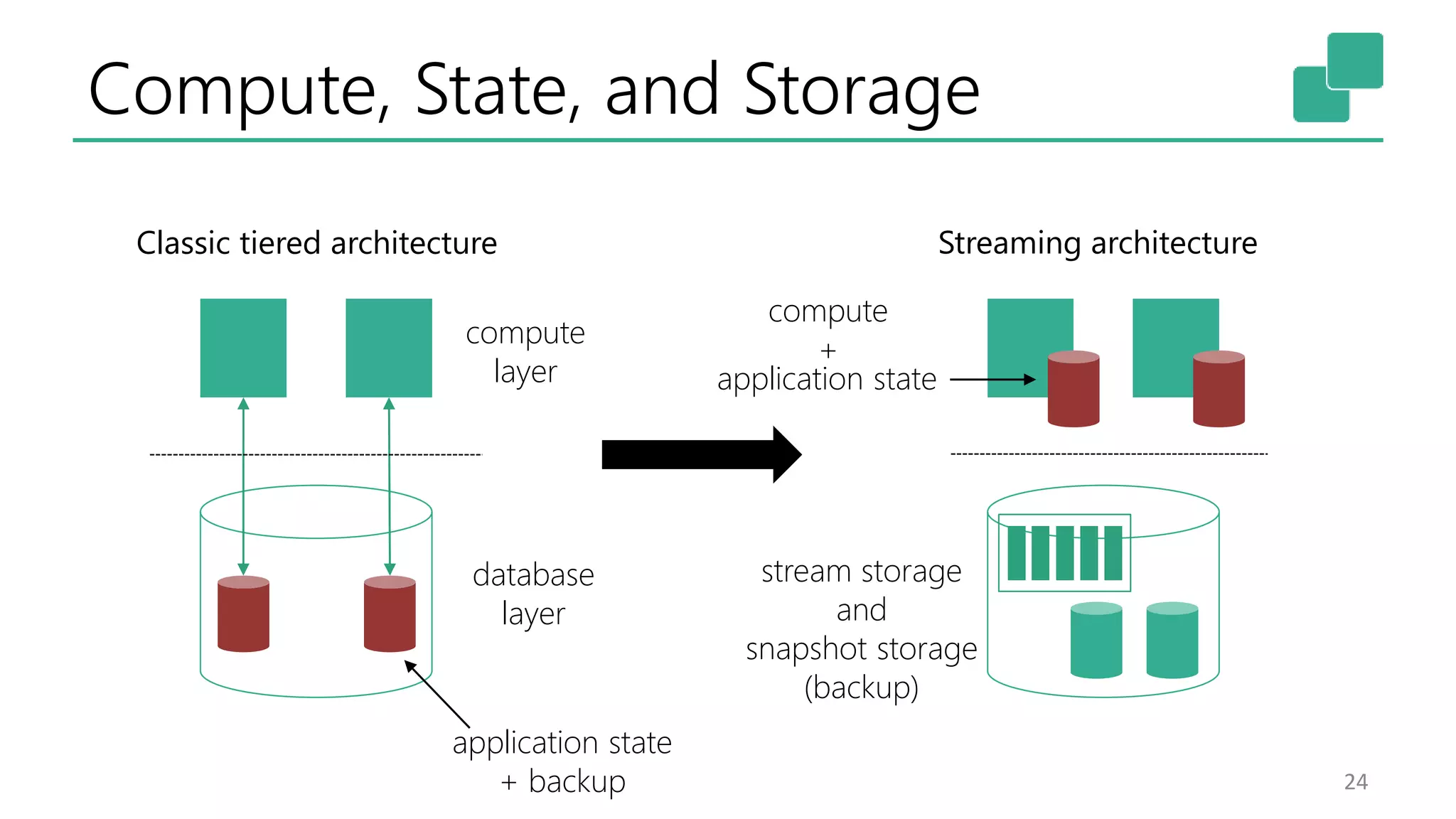
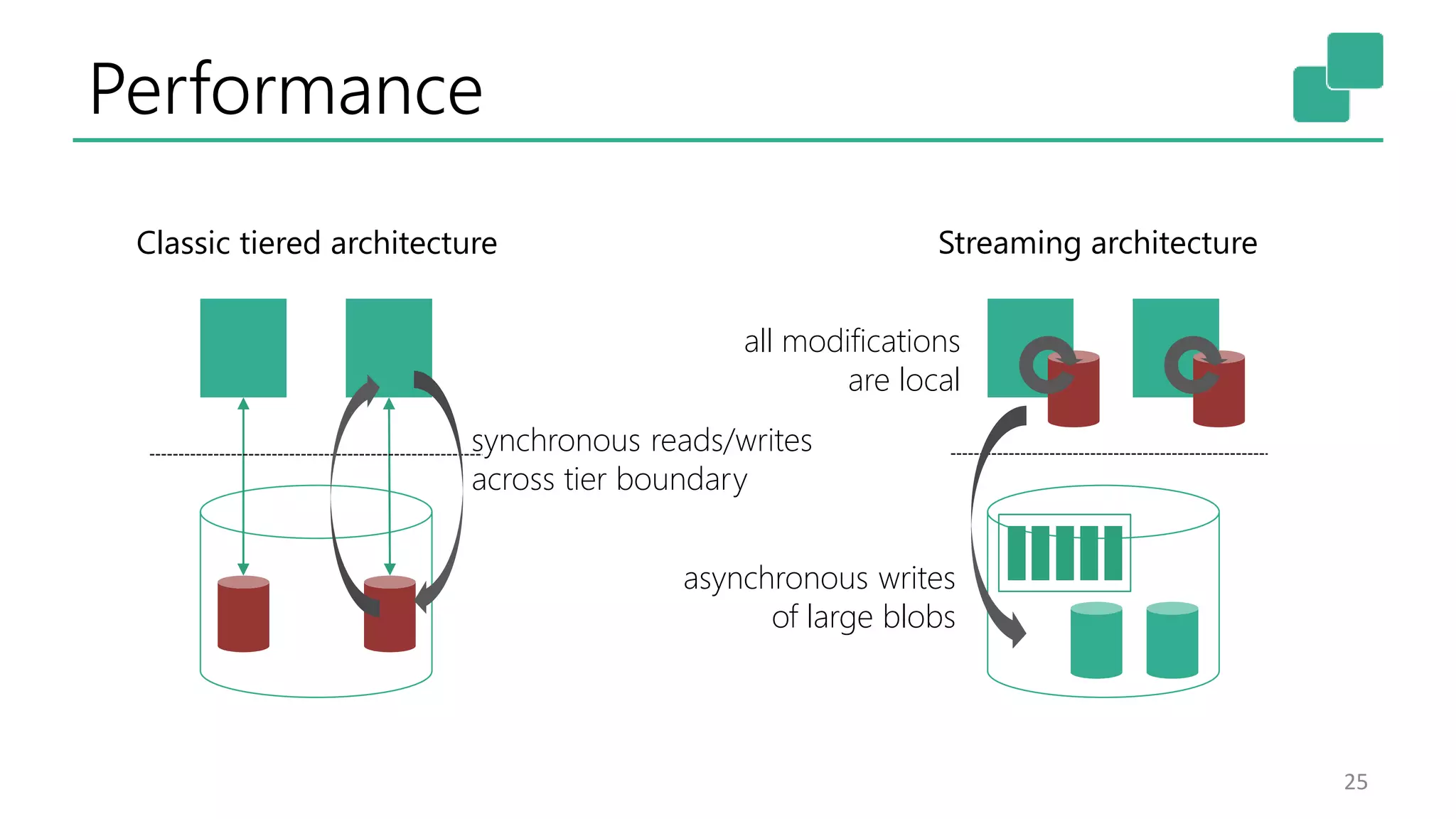
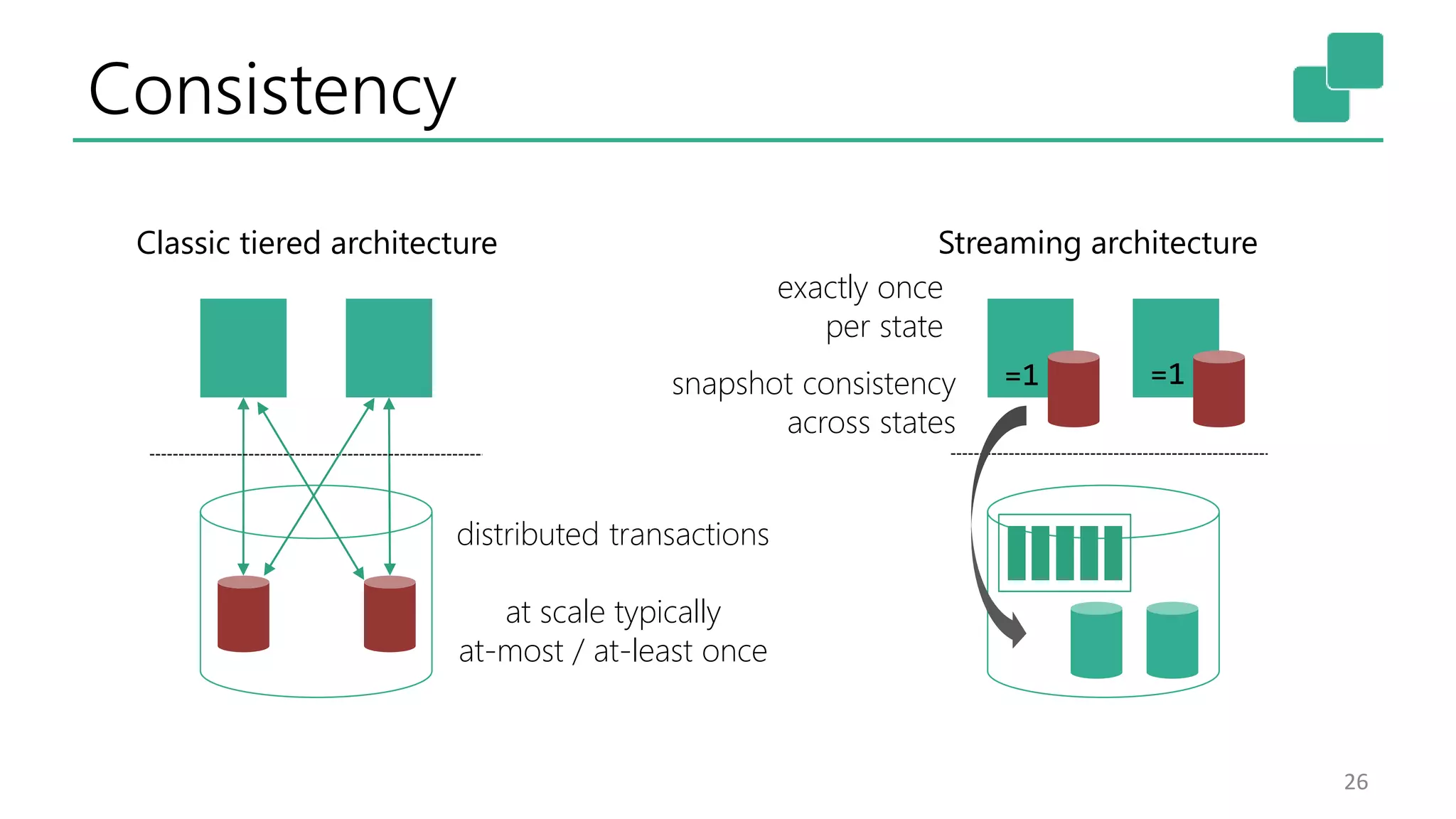
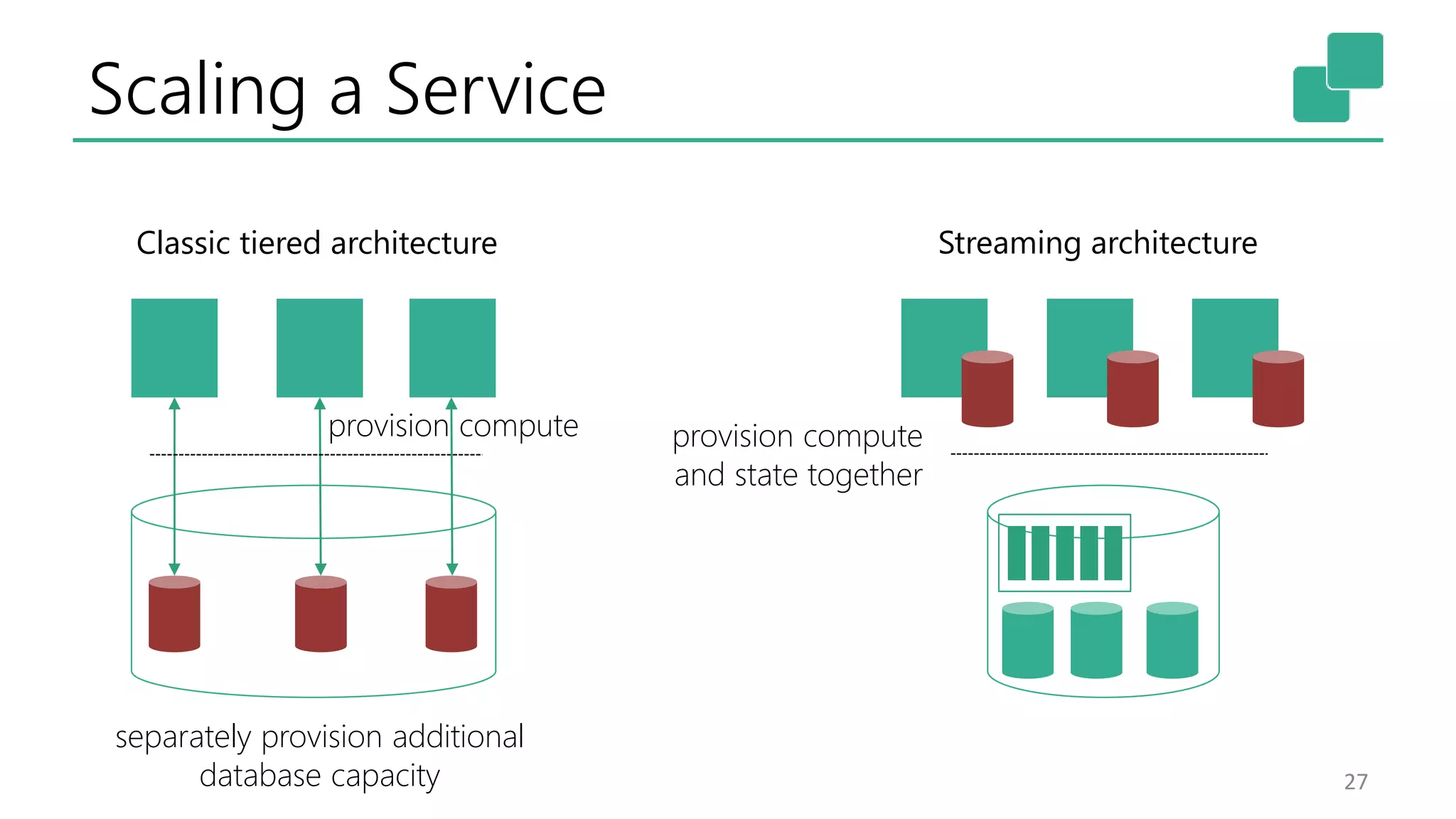
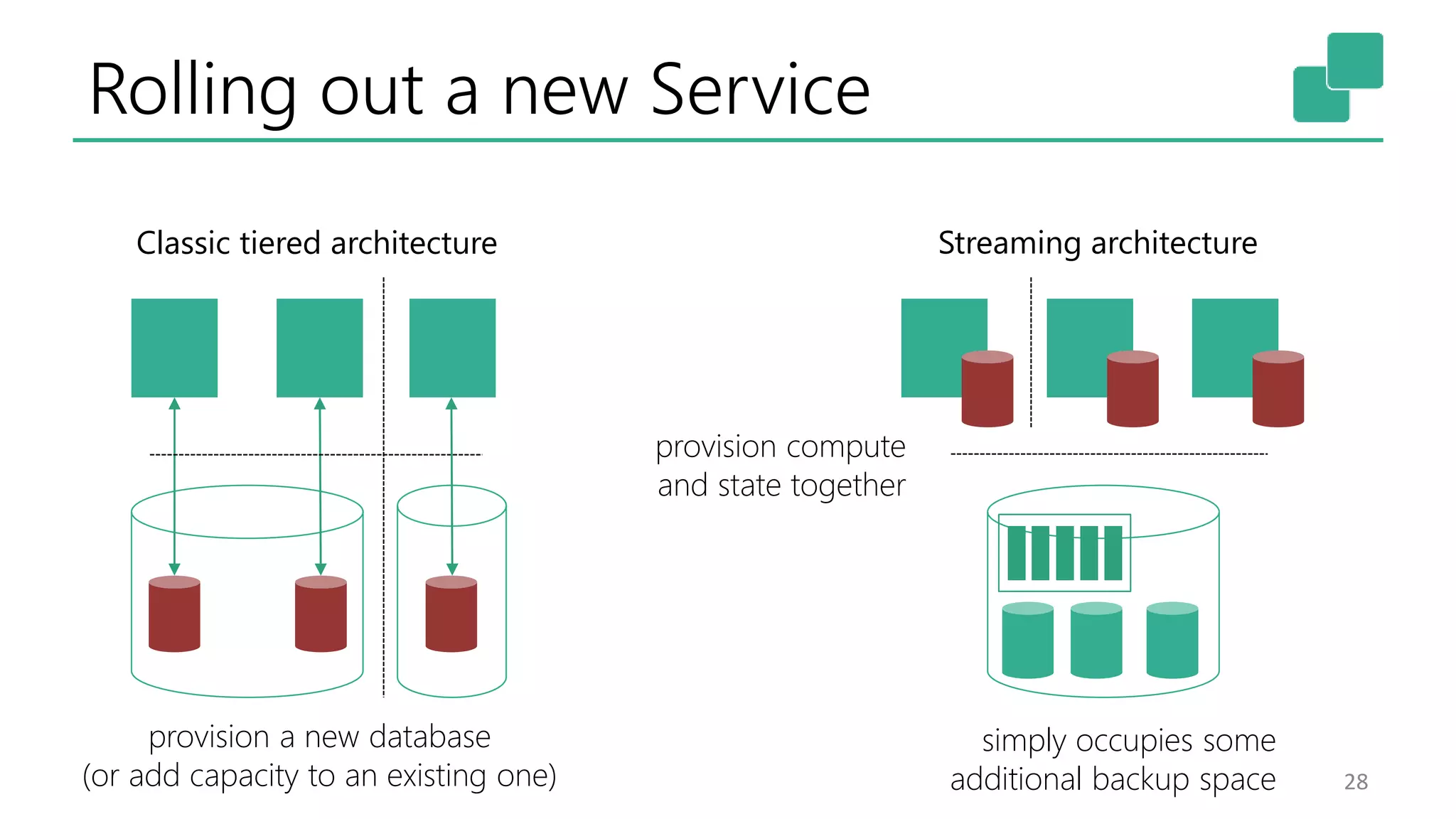
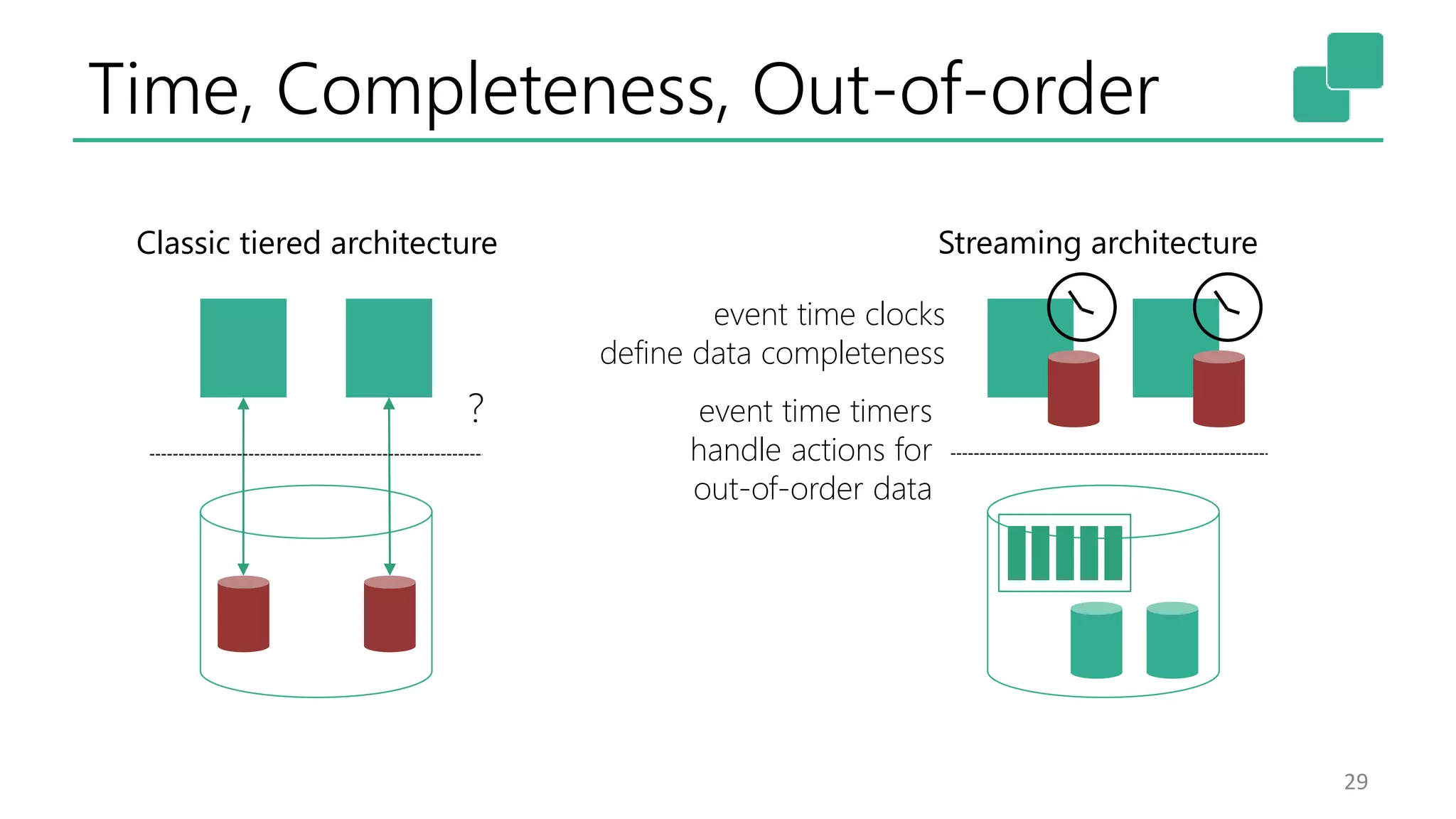
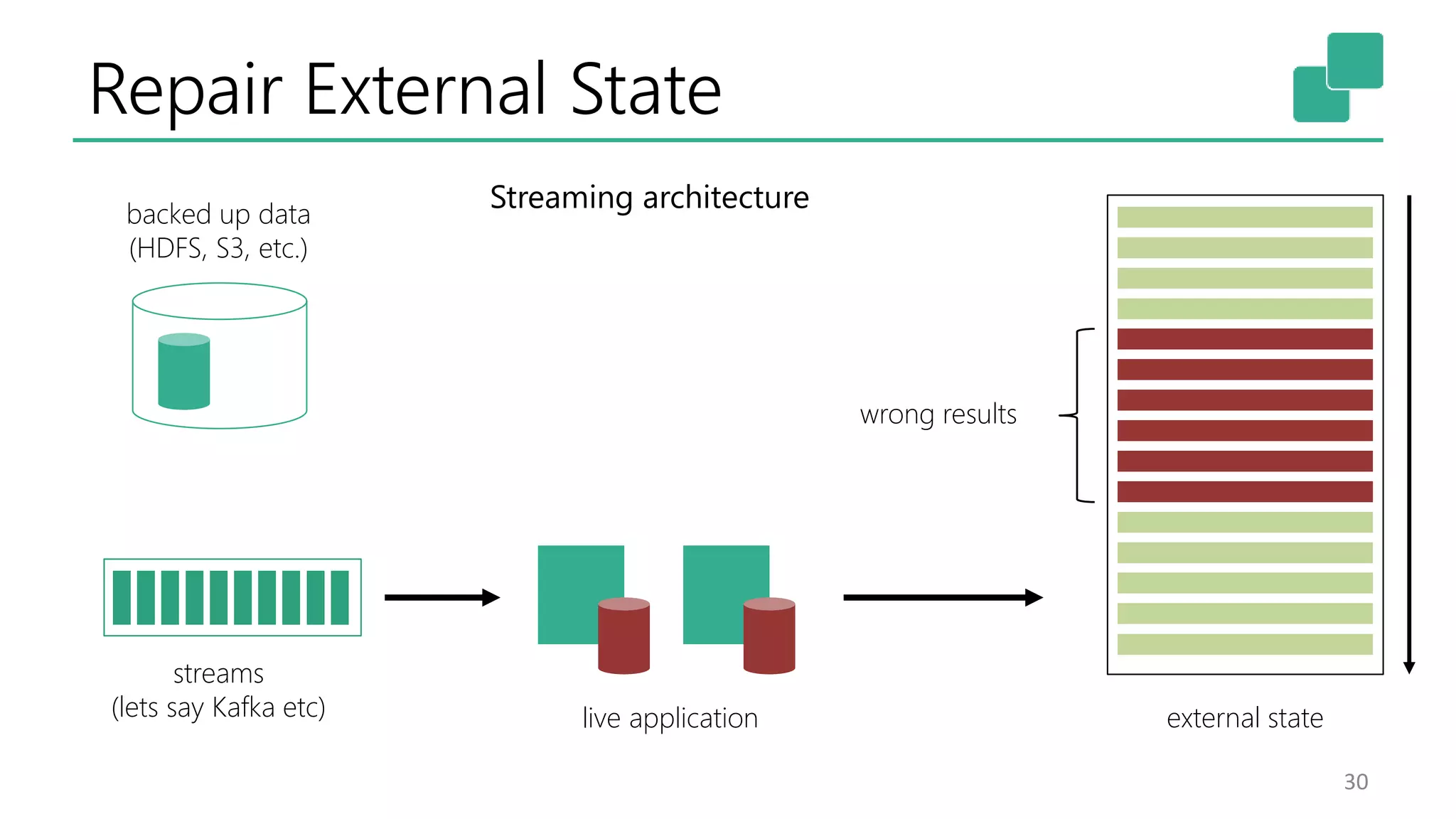
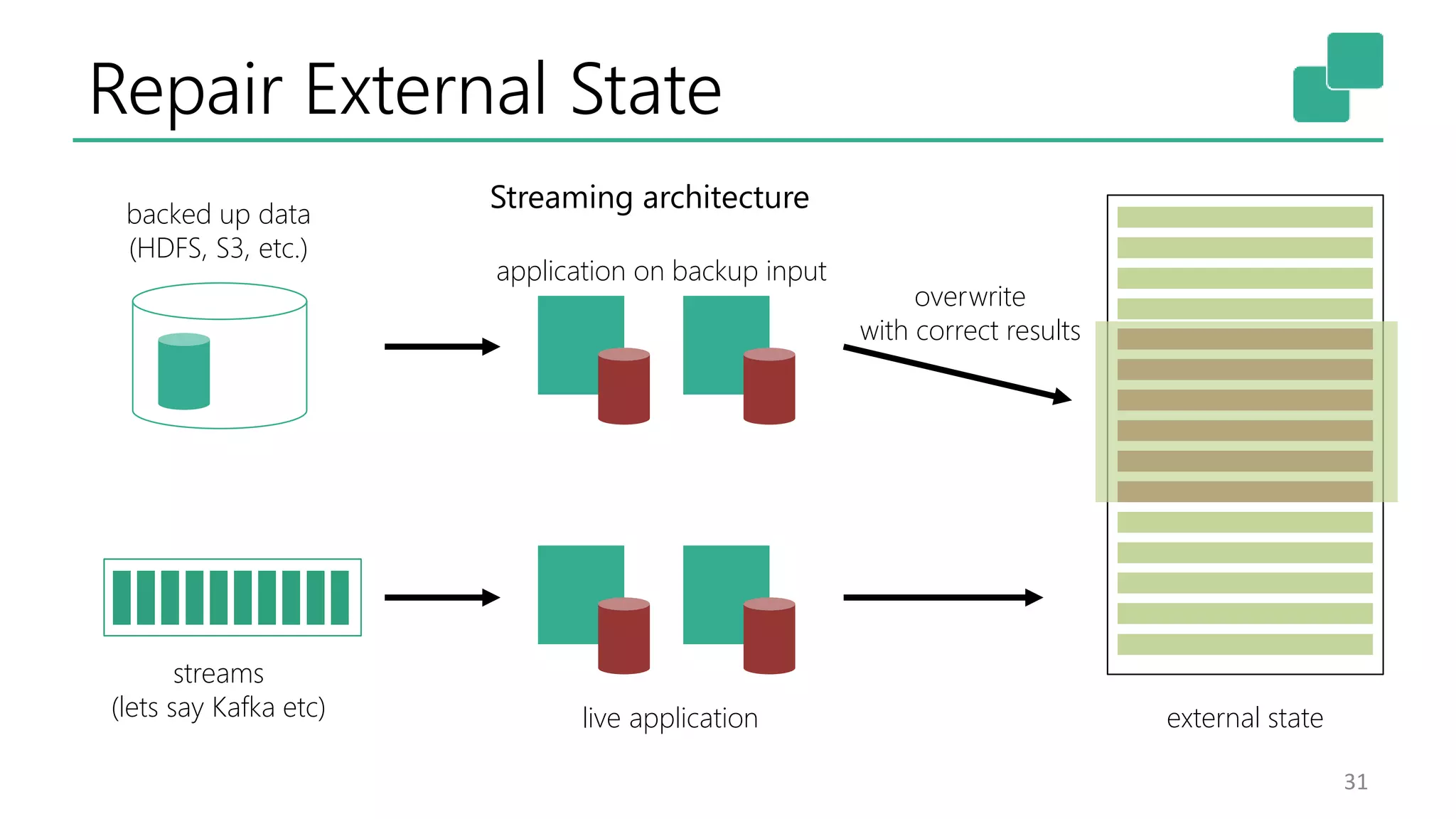
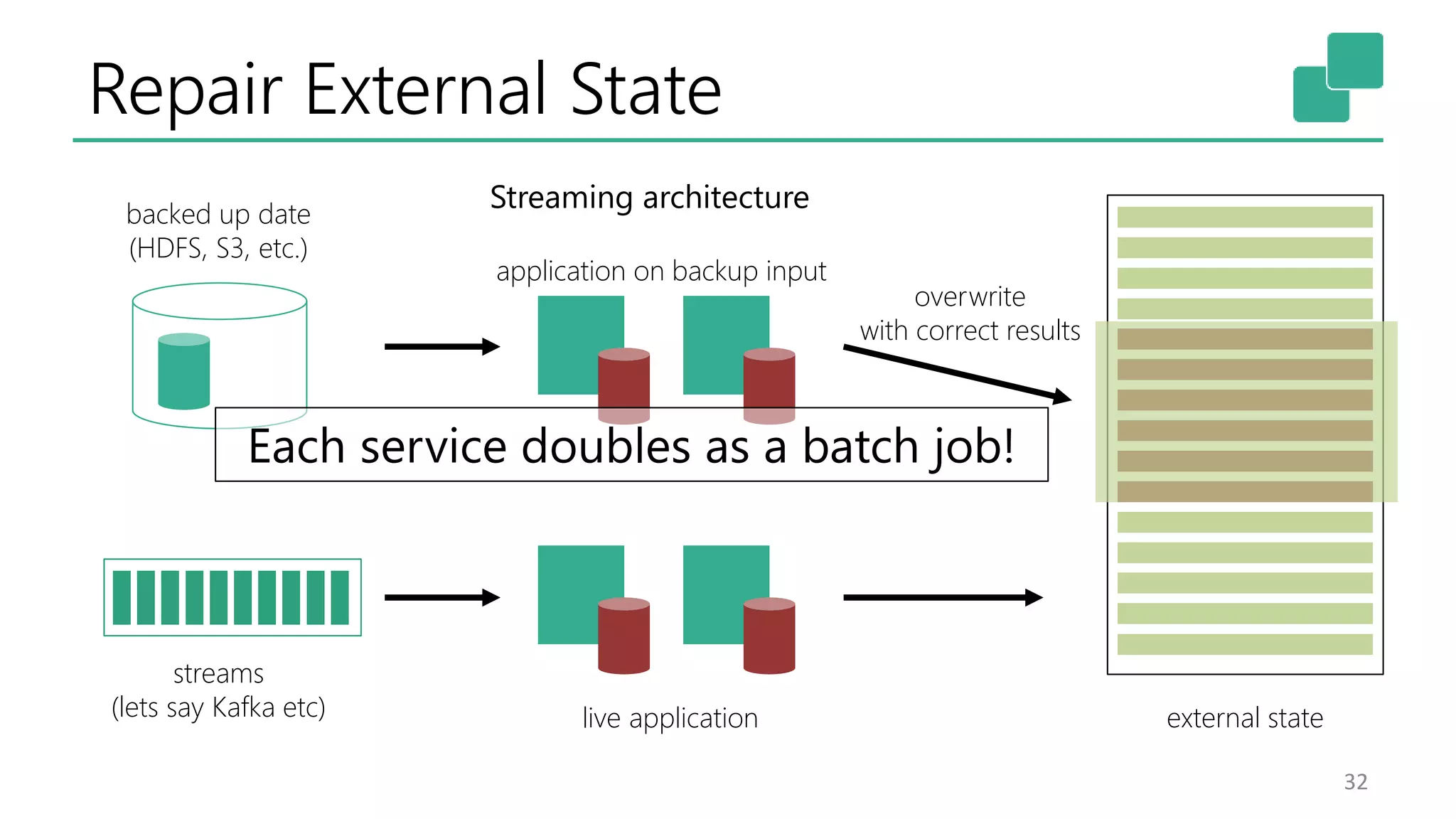
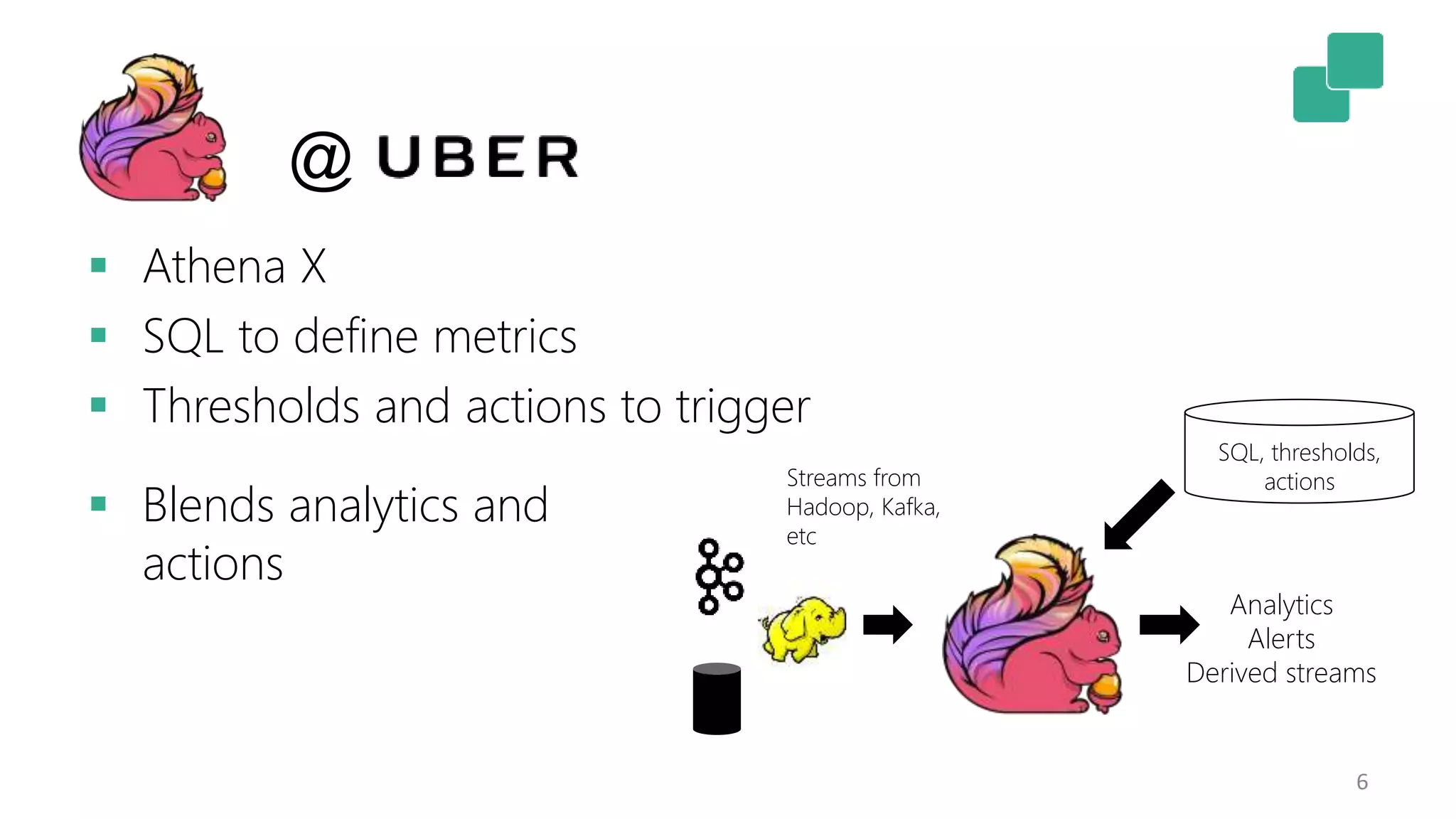
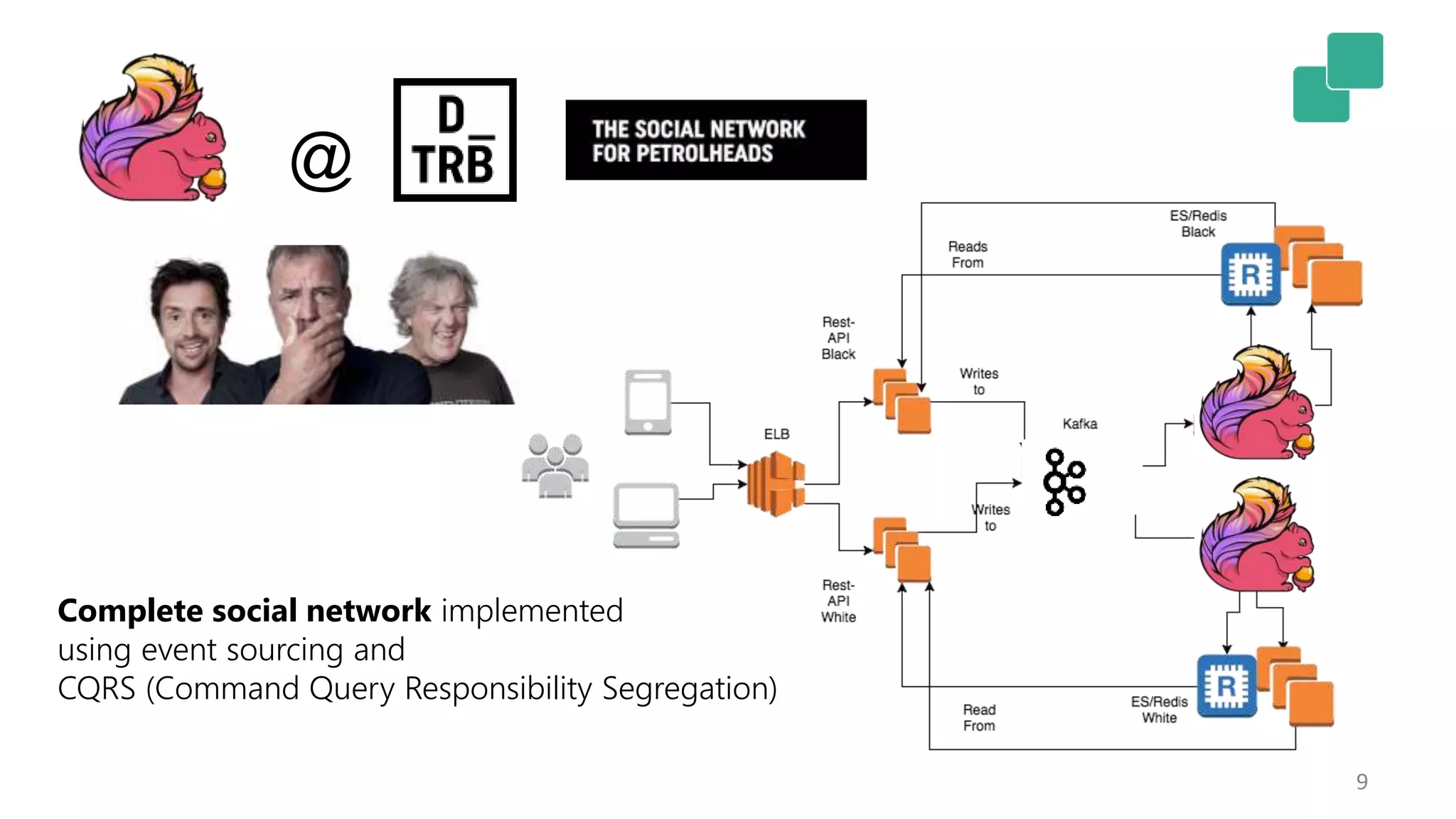
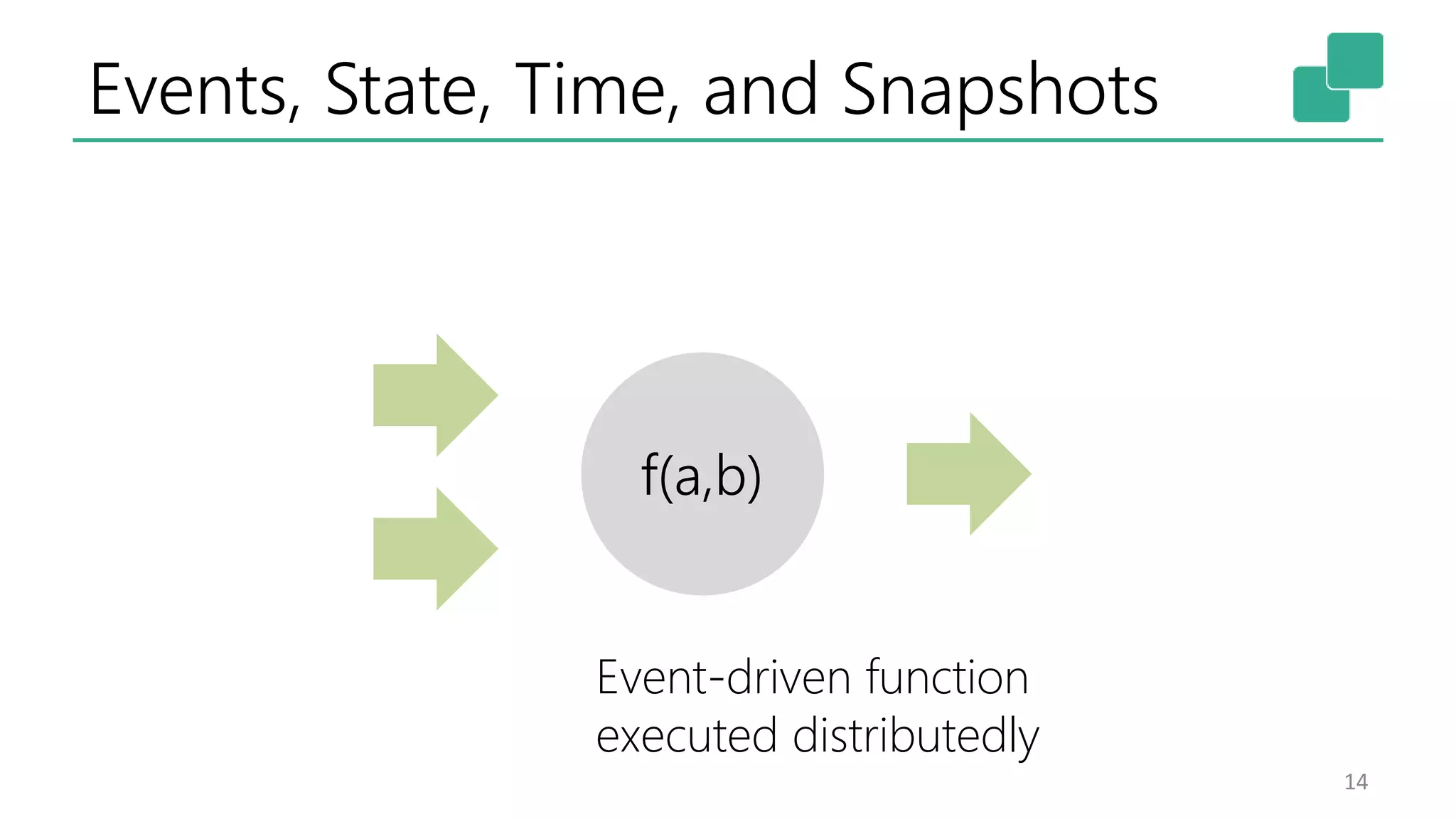
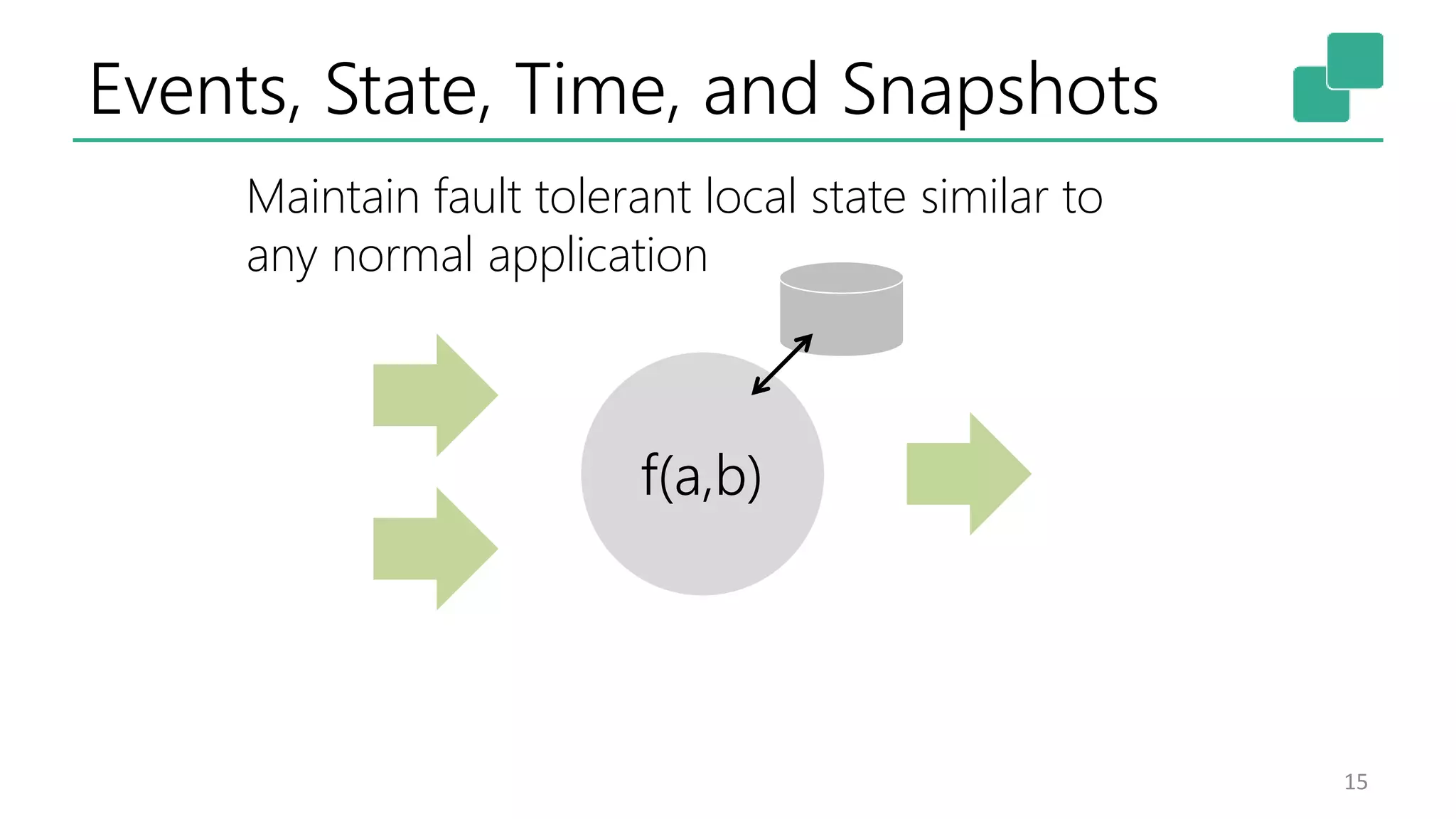
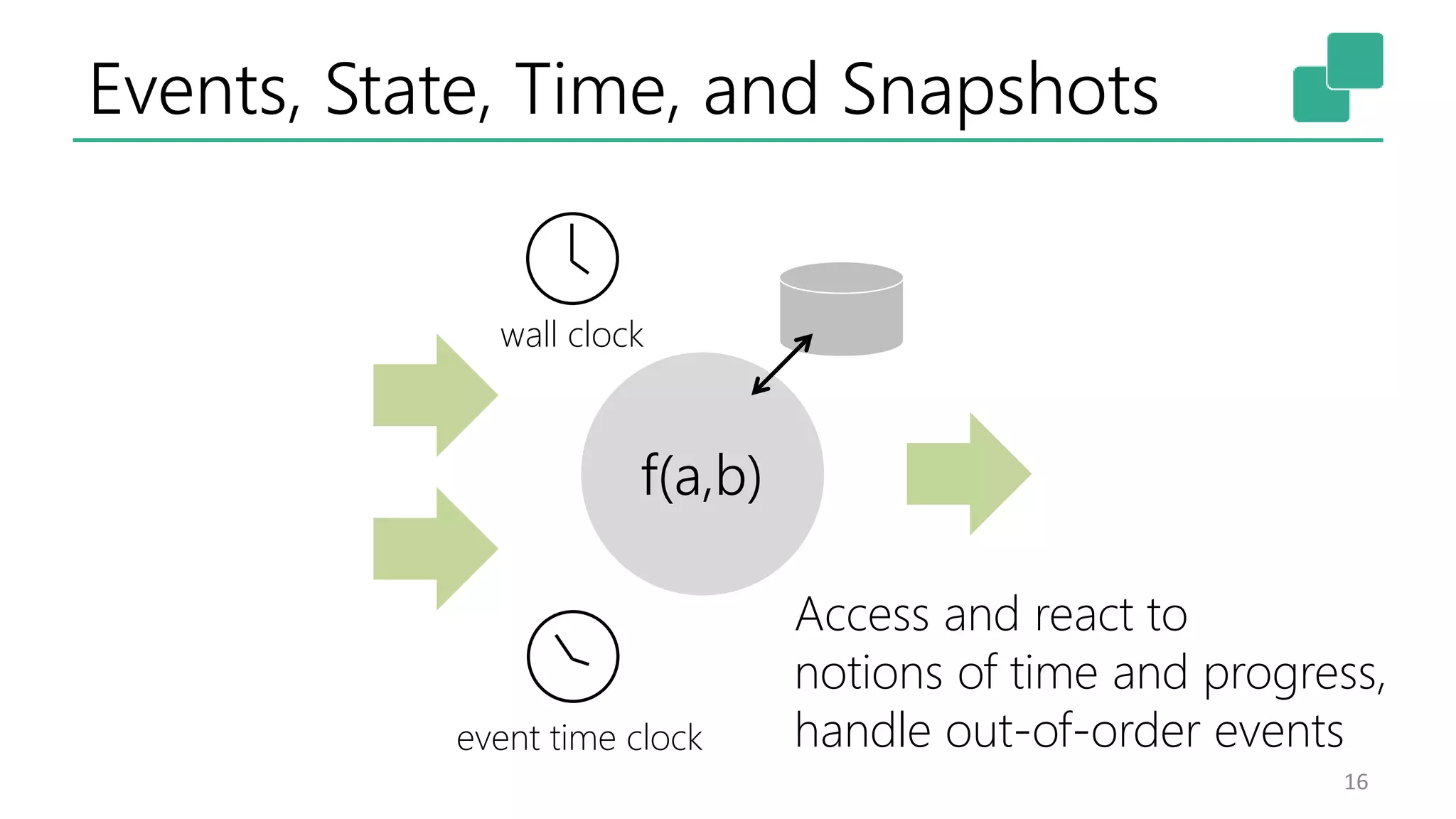
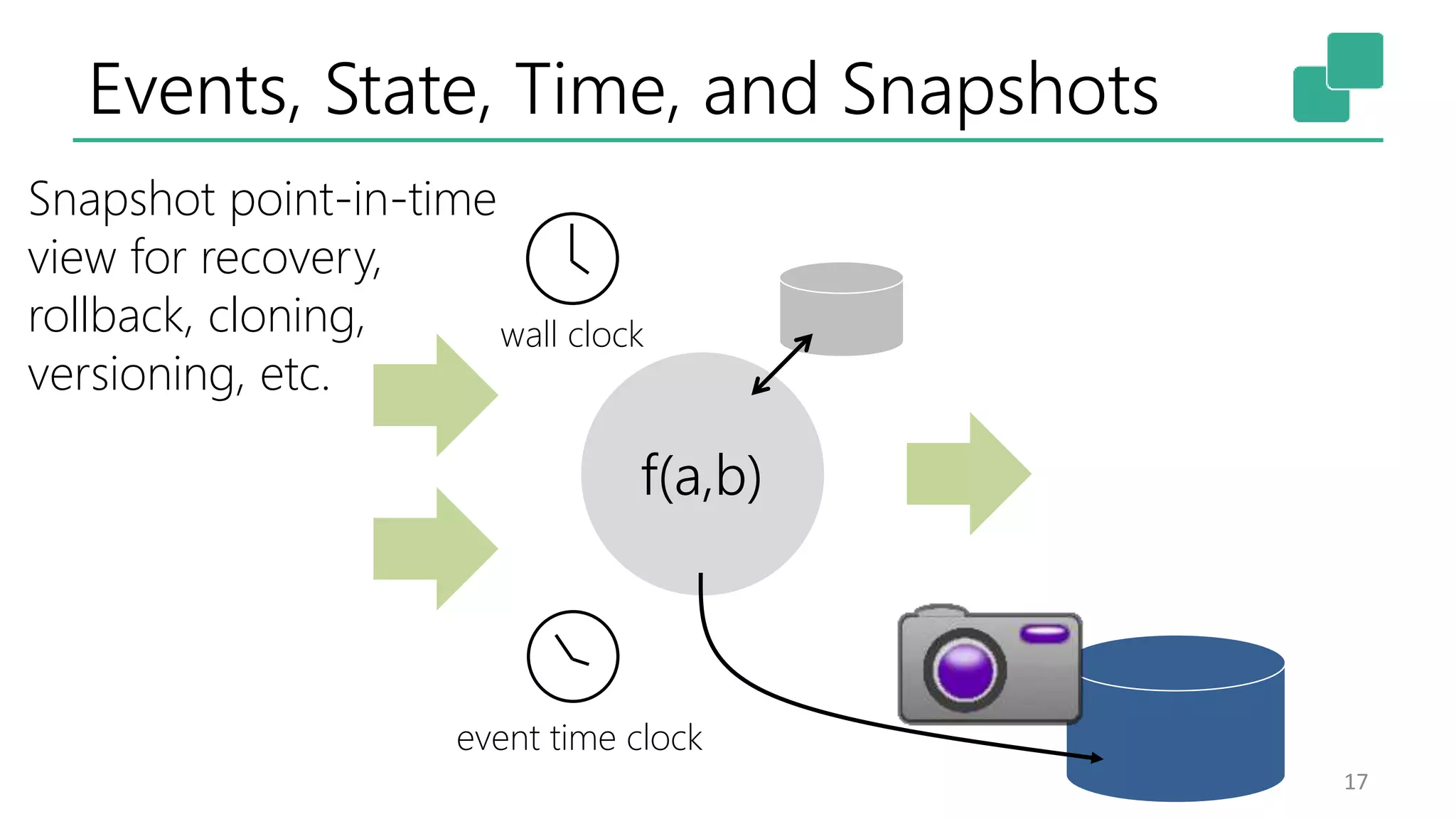
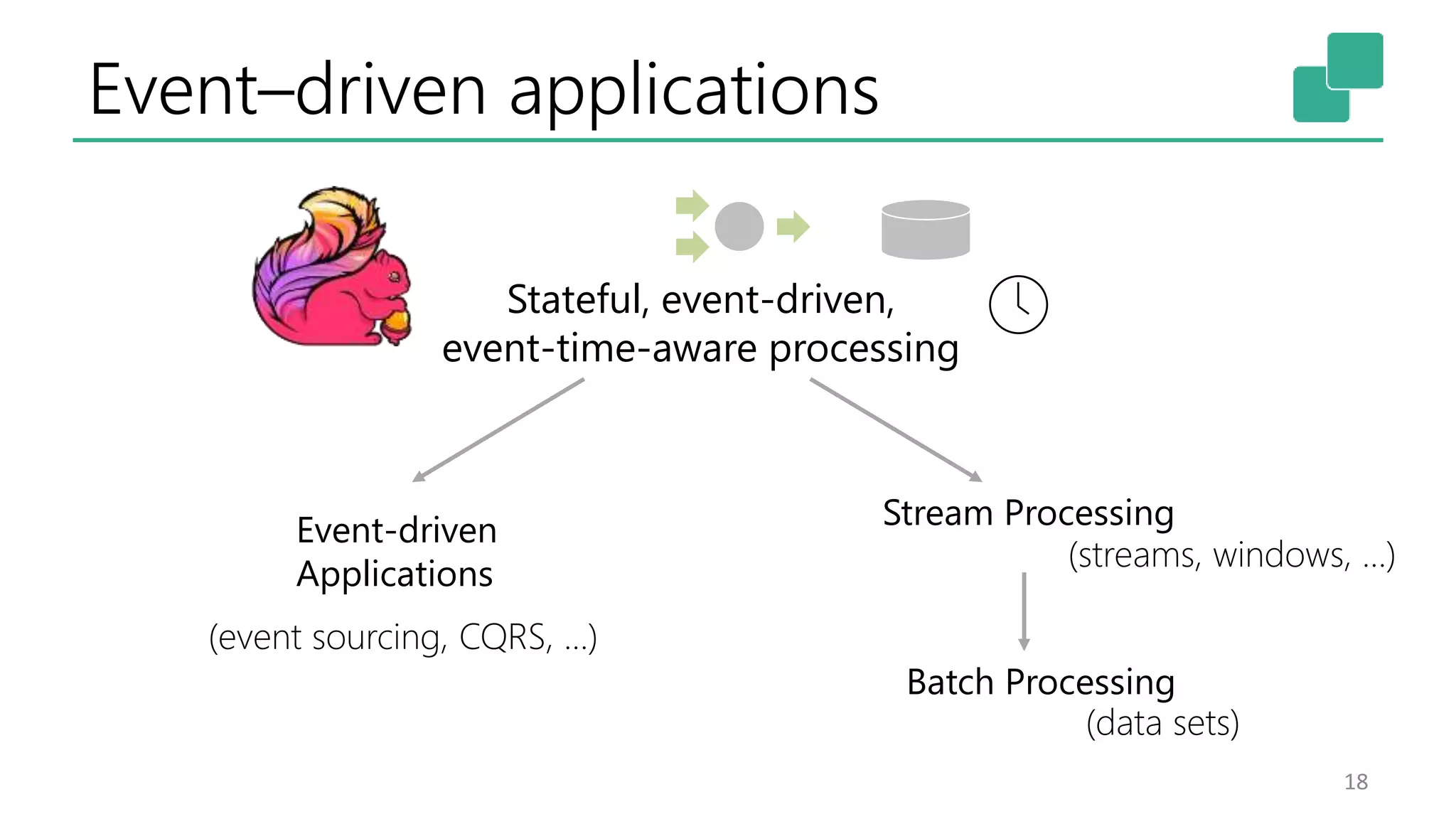
The document discusses the evolution and growing mainstream adoption of streaming technologies, particularly through event-driven applications using Apache Flink. It highlights the increasing need for real-time analytics, fraud detection, and services that operate 24/7 while utilizing complex data processing and storage systems. The document emphasizes a shift in architecture from traditional batch processing to a more dynamic, real-time architecture suitable for modern applications.









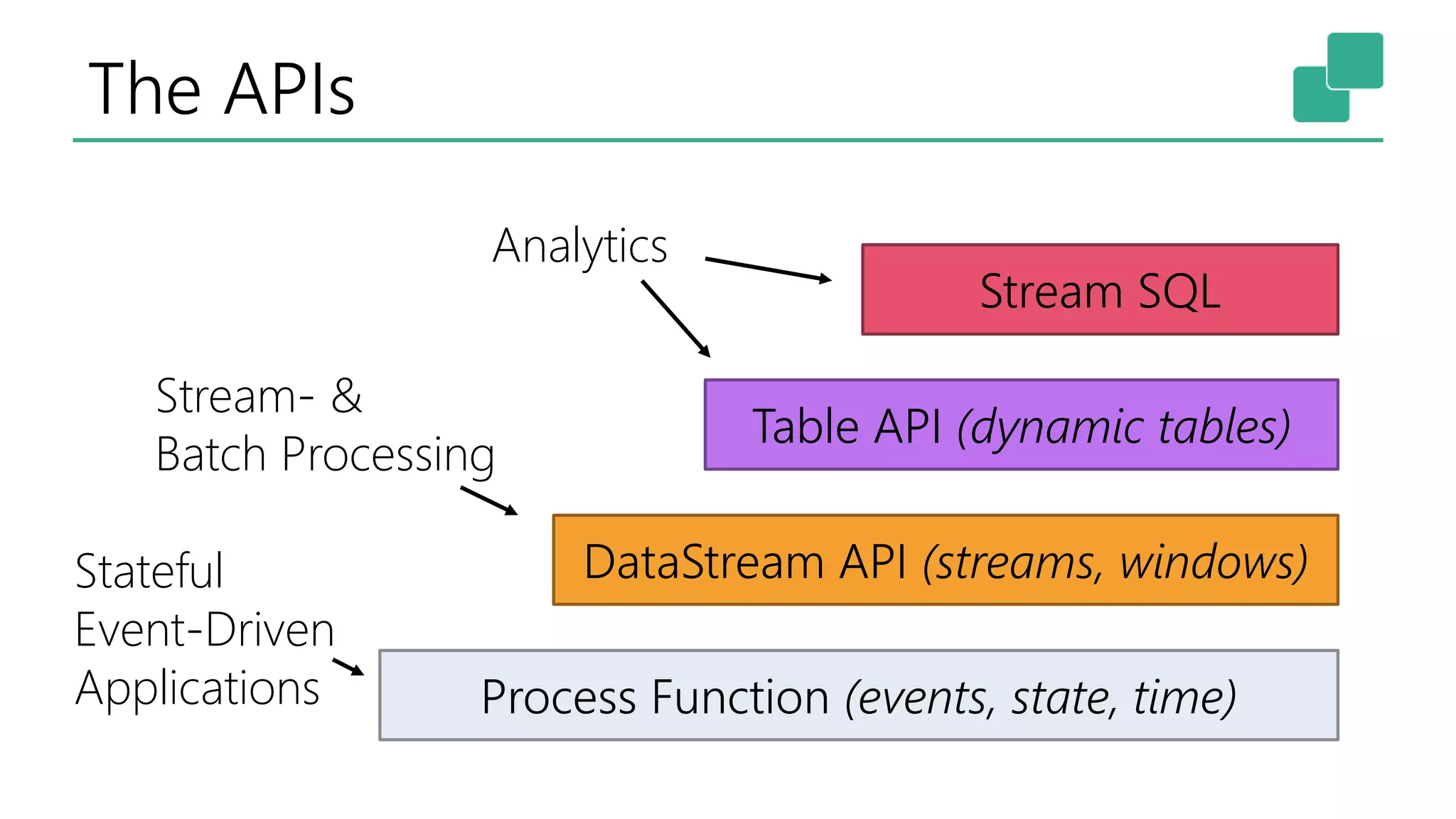
![Process Function
20
class MyFunction extends ProcessFunction[MyEvent, Result] {
// declare state to use in the program
lazy val state: ValueState[CountWithTimestamp] = getRuntimeContext().getState(…)
def processElement(event: MyEvent, ctx: Context, out: Collector[Result]): Unit = {
// work with event and state
(event, state.value) match { … }
out.collect(…) // emit events
state.update(…) // modify state
// schedule a timer callback
ctx.timerService.registerEventTimeTimer(event.timestamp + 500)
}
def onTimer(timestamp: Long, ctx: OnTimerContext, out: Collector[Result]): Unit = {
// handle callback when event-/processing- time instant is reached
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flinkforwardsf2017-stephanewen-convergenceofreal-timeanalyticsanddata-drivenapplications-170415221918/75/Flink-Forward-SF-2017-Stephan-Ewen-Convergence-of-real-time-analytics-and-data-driven-applications-19-2048.jpg)
![Data Stream API
21
val lines: DataStream[String] = env.addSource(
new FlinkKafkaConsumer09<>(…))
val events: DataStream[Event] = lines.map((line) => parse(line))
val stats: DataStream[Statistic] = stream
.keyBy("sensor")
.timeWindow(Time.seconds(5))
.sum(new MyAggregationFunction())
stats.addSink(new RollingSink(path))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flinkforwardsf2017-stephanewen-convergenceofreal-timeanalyticsanddata-drivenapplications-170415221918/75/Flink-Forward-SF-2017-Stephan-Ewen-Convergence-of-real-time-analytics-and-data-driven-applications-20-2048.jpg)