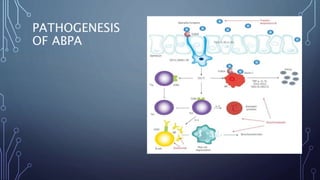
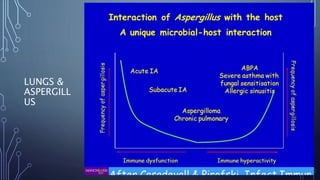
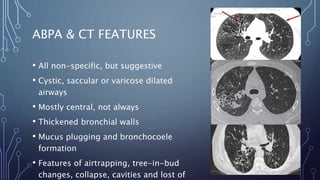
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) is a hypersensitivity reaction to the fungus Aspergillus fumigatus, affecting 1-2% of asthmatics and up to 8% of cystic fibrosis patients. Diagnosis involves evaluating specific IgE levels, CT imaging for bronchiectasis, and ruling out other conditions, while treatment encompasses inhalers, oral steroids, and antifungals like itraconazole. Routine follow-up is essential for monitoring, tapering corticosteroids, and managing potential disease progression through sputum surveillance.