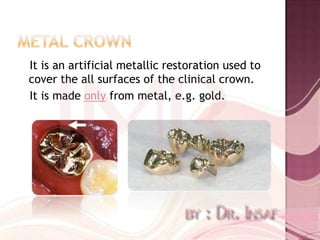
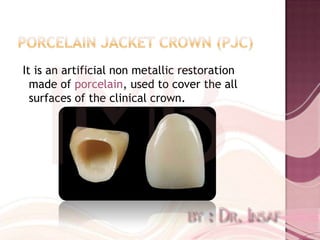
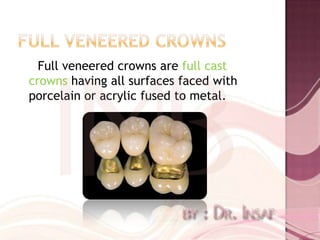
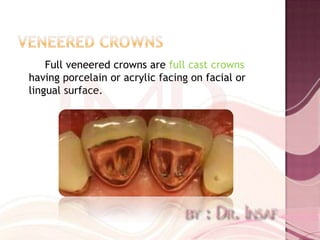
Full coverage restorations include metal crowns, porcelain jacket crowns, and metal-ceramic crowns. Metal crowns provide great strength but poor aesthetics, while porcelain jacket crowns have the best cosmetic results but risk of fracture. Metal-ceramic crowns combine the strength of metal with the aesthetics of porcelain, making them suitable for teeth requiring esthetics or with extensive destruction.