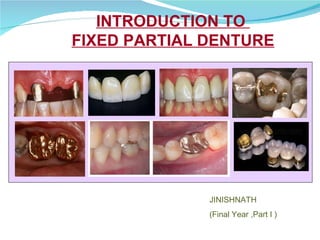
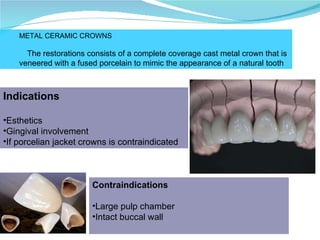
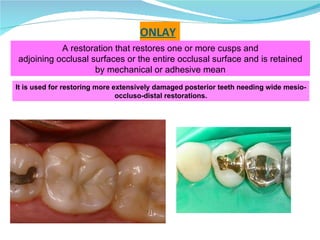
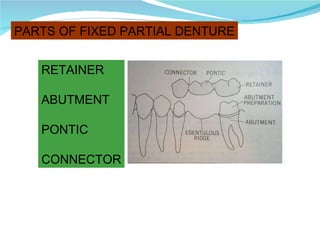
Prosthodontics is the dental specialty pertaining to the diagnosis, treatment planning, rehabilitation, and maintenance of patients with missing or deficient teeth using substitutes. It includes fixed and removable prostheses. A fixed partial denture is a partial denture that is securely attached to abutment teeth, roots, or implants to replace one or more missing teeth. Successful treatment requires attention to patient assessment, diagnosis, treatment planning, operative skills, and follow-up care.