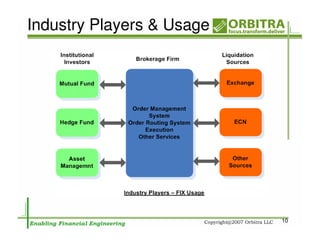
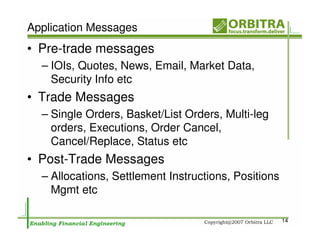
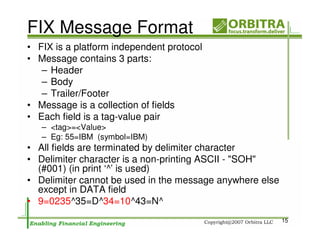
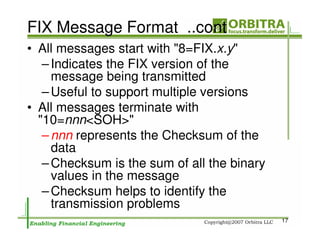
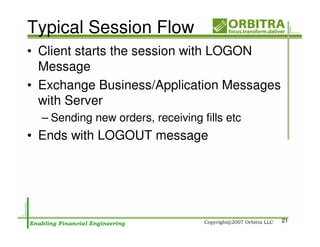
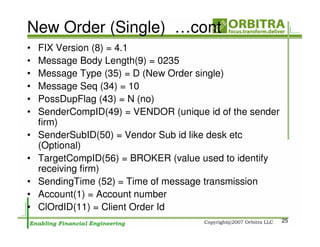
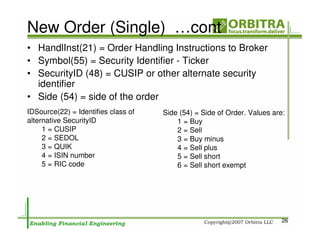
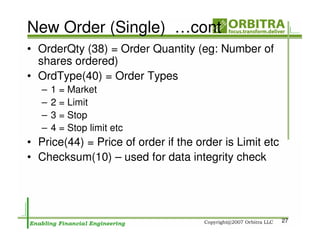
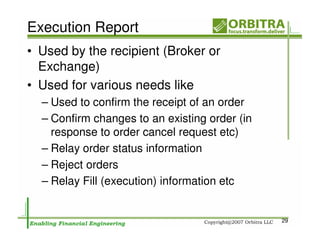
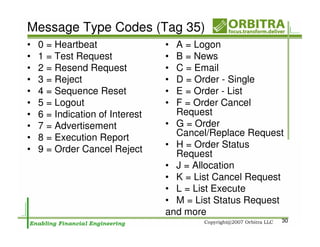
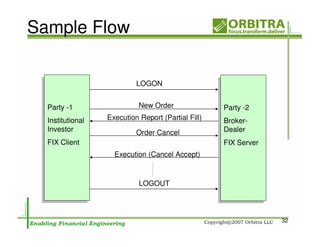
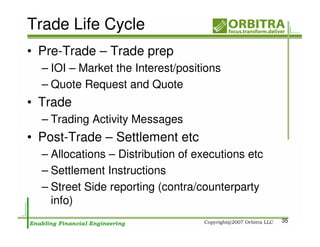
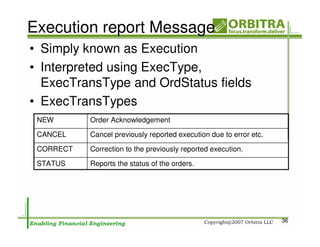
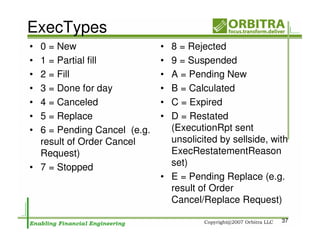
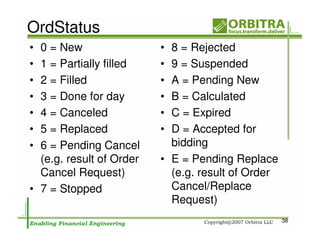
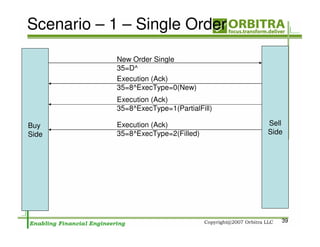
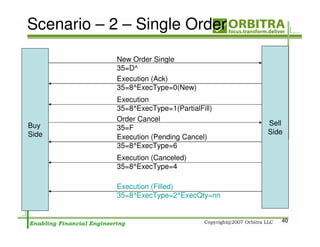
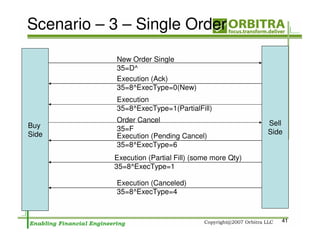
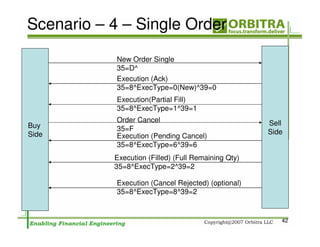
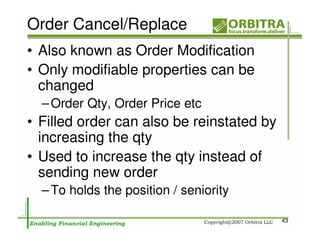
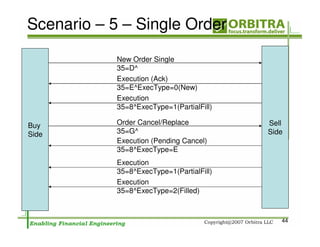
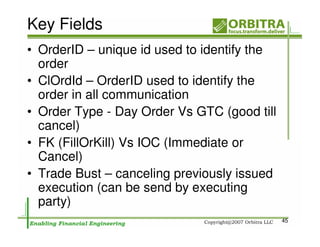
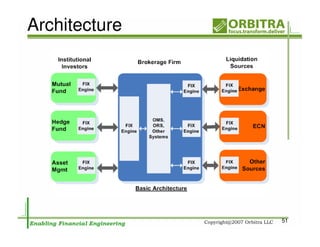
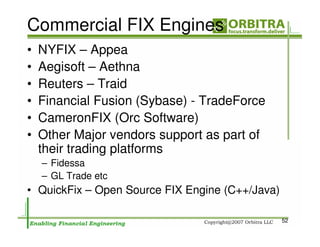
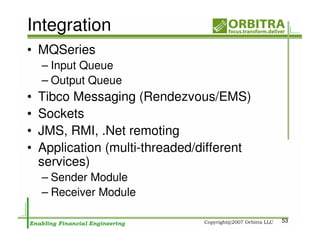
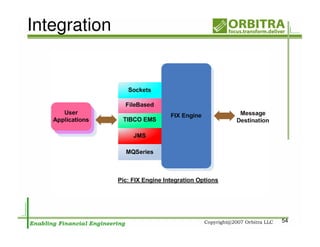
The document outlines an agenda for a one-day course on the FIX Protocol, covering an introduction to FIX including its history, components, and sample message flow, how FIX is used for electronic equity trading through order types and trading scenarios, and technical implementation considerations for FIX integration. FIX Protocol is an open, electronic messaging standard used widely in the financial industry for exchanging trading-related information.