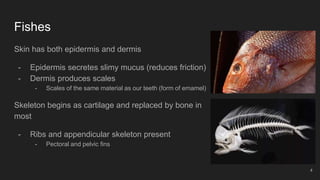
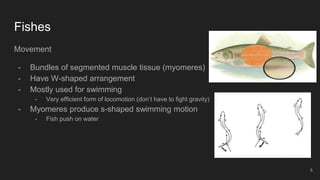
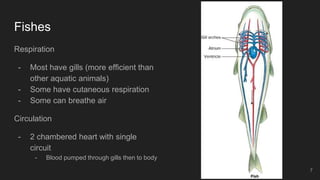
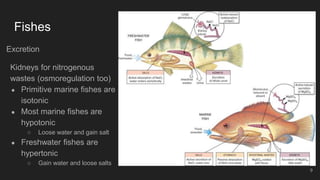
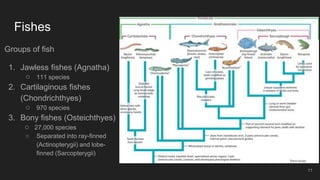
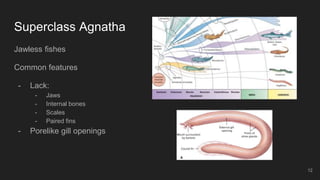
Fishes are the most ancient group of vertebrates, first appearing 530 million years ago. They are highly diverse with over 28,000 living species. Fishes are aquatic and have adapted various anatomical features for aquatic life including scales, fins, buoyancy control and efficient gill respiration. Major groups include jawless fishes, cartilaginous fishes like sharks, and bony fishes including the dominant ray-finned fishes and rare lobe-finned fishes like lungfishes and coelacanths.