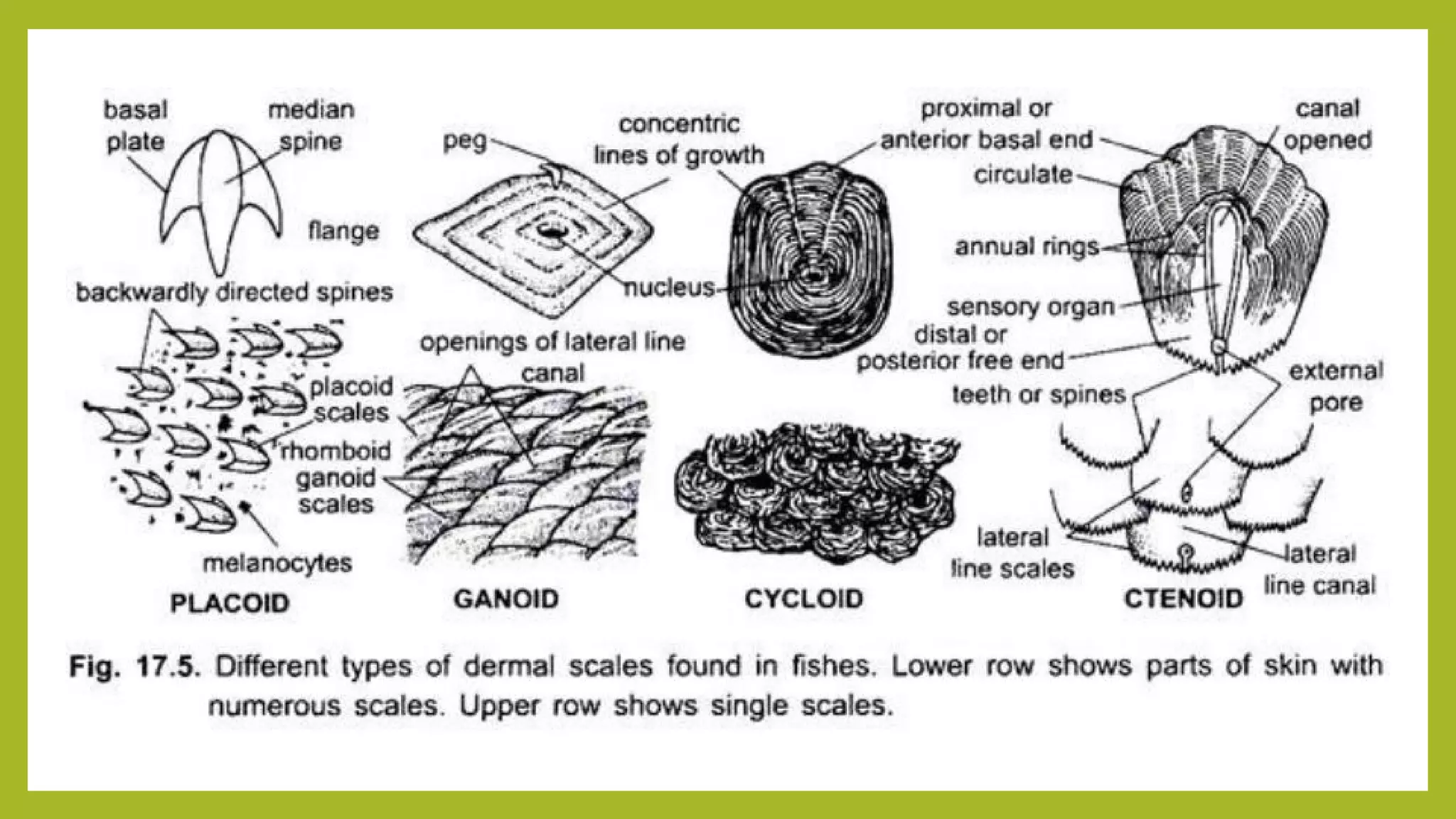
This document discusses the different types of scales found in fish. It defines fish scales as small, rigid plates that grow out of the skin. Scales come in various types depending on the fish, including cosmoid, ganoid, placoid, cycloid, and ctenoid scales. Each scale type has a distinct structure and provides different functions like protection from predators or parasites and aiding movement. Some fish lack scales and instead have alternatives like tough skin, bony plates, or prickles for protection. In summary, the document outlines the definition, functions, and major types of scales present in different groups of fish.