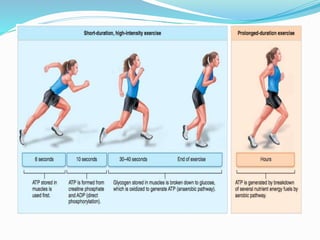
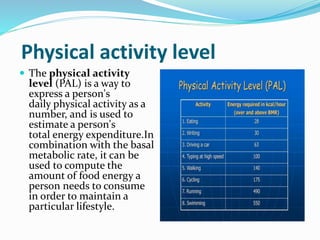
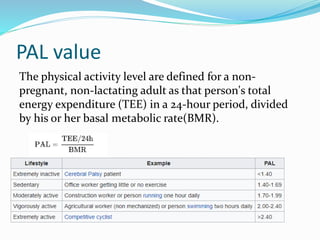
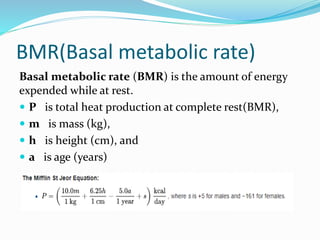
This document provides an overview of first aid, its aims, and specific disciplines related to it, along with items that should be included in a first aid kit. It also discusses physical therapy, the concept of physical exercise with its basic modes, and the importance of physical activity levels in calculating energy expenditure. Key health benefits of physical activity and its impact on lifestyle are highlighted.