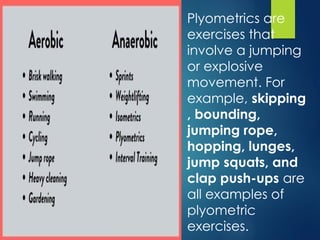
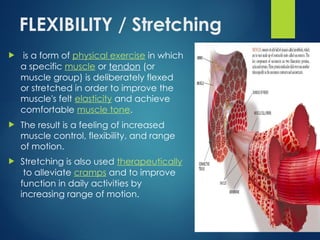
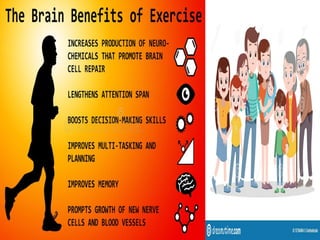
The document discusses the significance of physical education, physical fitness, and health, defining key terms and their interrelations. It emphasizes the benefits of regular physical activity in preventing diseases, improving mental health, and enhancing overall well-being, as well as outlining the components of physical fitness such as muscular strength, endurance, flexibility, and body composition. Additionally, it provides safety guidelines for physical education classes and details on various exercise types, nutritional needs, and their impact on health.