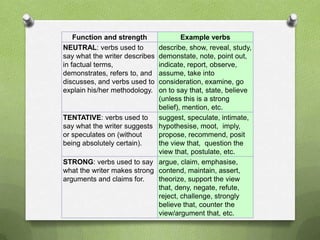
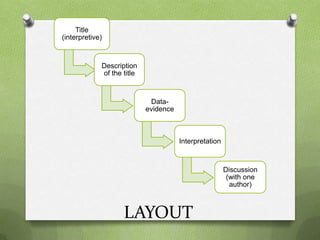
This document provides guidance for structuring findings from a research study. It recommends including 6 findings with at least 2 pieces of data to support each finding through triangulation of methods or participants. Findings and discussion should be in the same chapter. Data should be interpreted and evidence the intended revelation of each finding. The structure should have an interpretive title for each finding followed by a description, data evidence, and interpretation.







![What is this?
O Luisa: […] cuando estamos en los niveles más abajo […] a uno
siempre lo ponen es del libro, entonces cuando tú haces una
lectura es solamente sobre ese tema y tú te basas en tus
respuestas de lo que leíste del tema y se acabó o el profesor dice
lo correcto y se acabó, en cambio cuando hicimos la discusión tú
tienes que buscar la manera de hacerte entender ante los demás,
tú opinión, no solamente basado en lo que tú leíste, si no en tus
vivencias, en lo posible, entonces eso lo forza a uno más todavía
para expresarse con los demás.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/findingsdiscussion-120220145211-phpapp02/85/Findings-discussion-9-320.jpg)