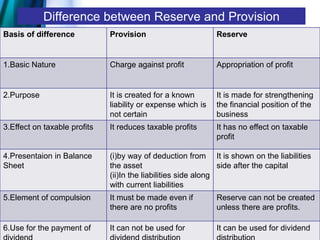
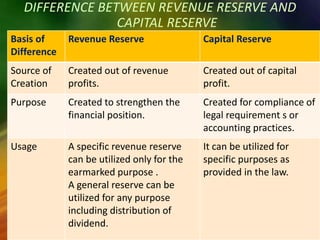
The document discusses accounting concepts related to provisions and reserves. It defines a provision as an amount written off to account for depreciation or known liabilities. Provisions for doubtful debts are created by debiting the profit and loss account and crediting the provision for doubtful debts account. Reserves are amounts appropriated from profits that are not meant to cover specific liabilities and help strengthen a company's financial position. The key differences between provisions and reserves are that provisions directly impact taxable profits while reserves do not, and provisions are for certain liabilities while reserves strengthen the balance sheet. Revenue and capital reserves are also discussed along with their uses.