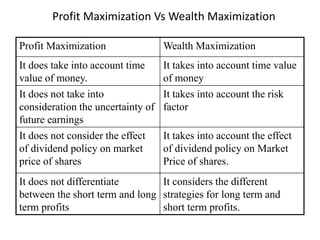
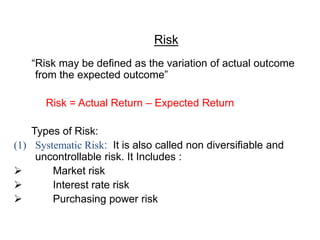
This document provides an overview of financial management. It defines financial management as dealing with the procurement and utilization of funds. The key aspects covered are procurement of funds through identifying sources and determining financing mixes, and effective utilization of funds through investment decisions. The traditional approach to financial management focused only on procurement, while the modern approach expanded the scope to include investment and dividend decisions. The objectives of financial management are discussed as profit maximization and wealth maximization of shareholders. Risk and return analysis and the time value of money are also covered.