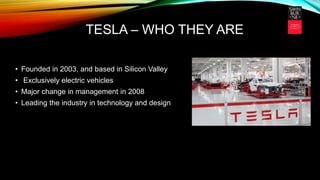
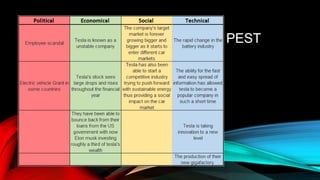
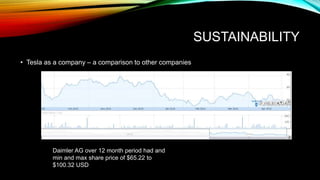
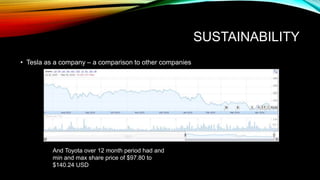
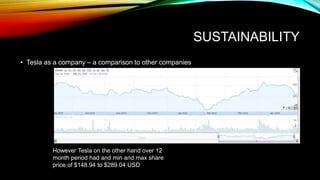
Tesla is an electric vehicle company founded in 2003 that is leading the industry in technology and design. It has strengths like Elon Musk's leadership and strategic alliances, but also faces weaknesses such as a limited global battery supply and low demand. Tesla aims to be sustainable by building a net-zero energy Gigafactory to double battery production and producing electric vehicles that are better for the environment, though their business model presents challenges and risks changing regulations.