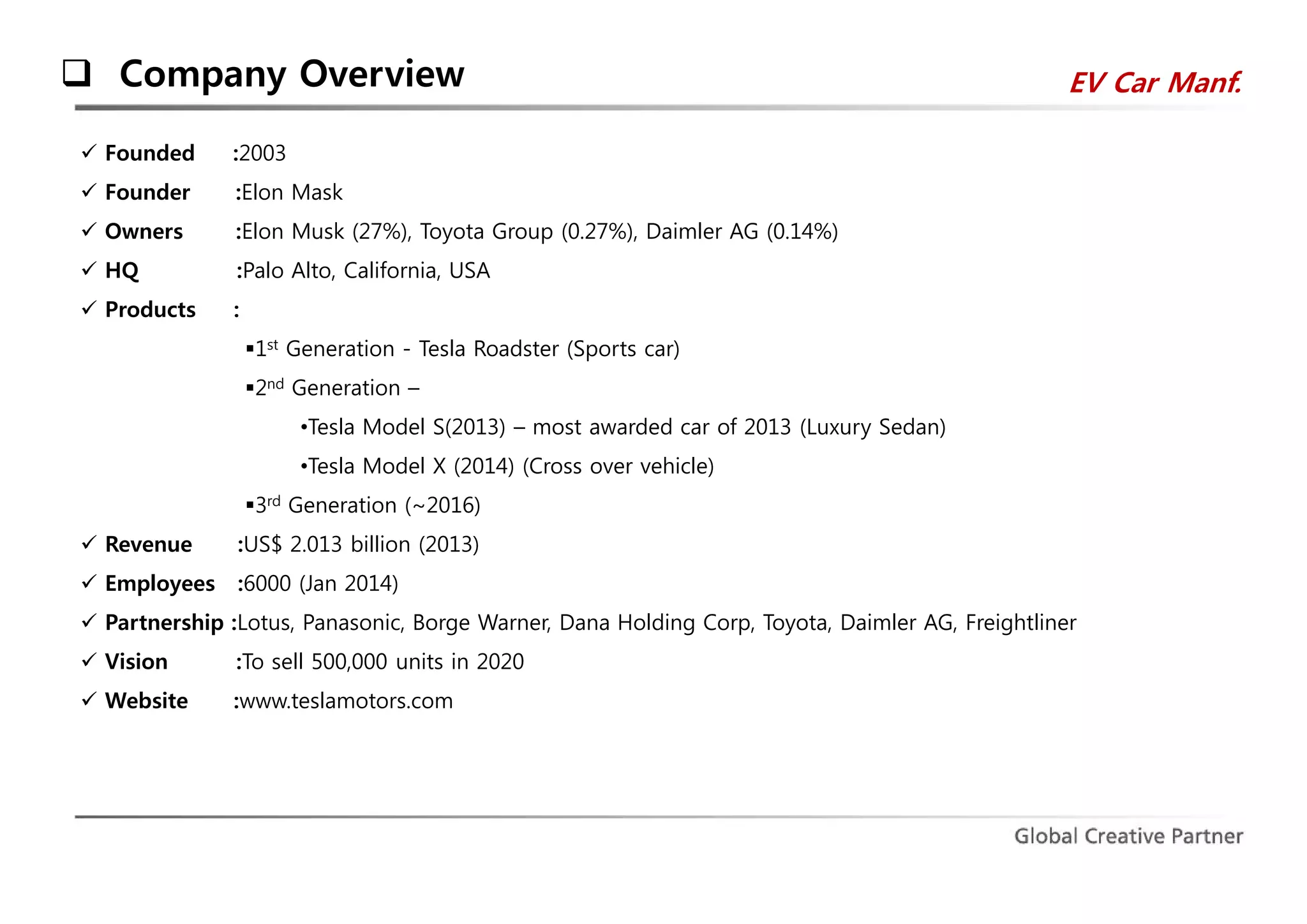
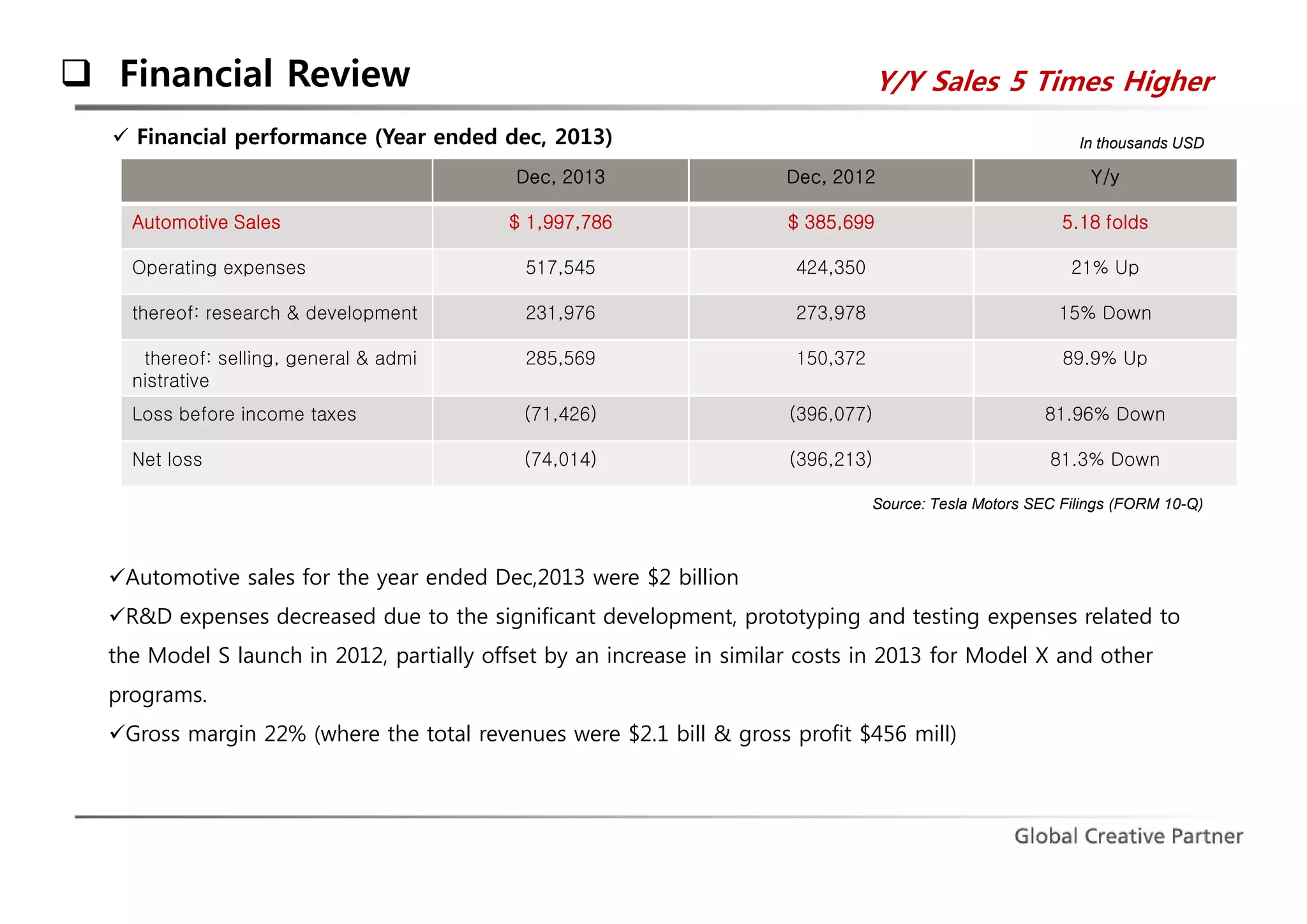
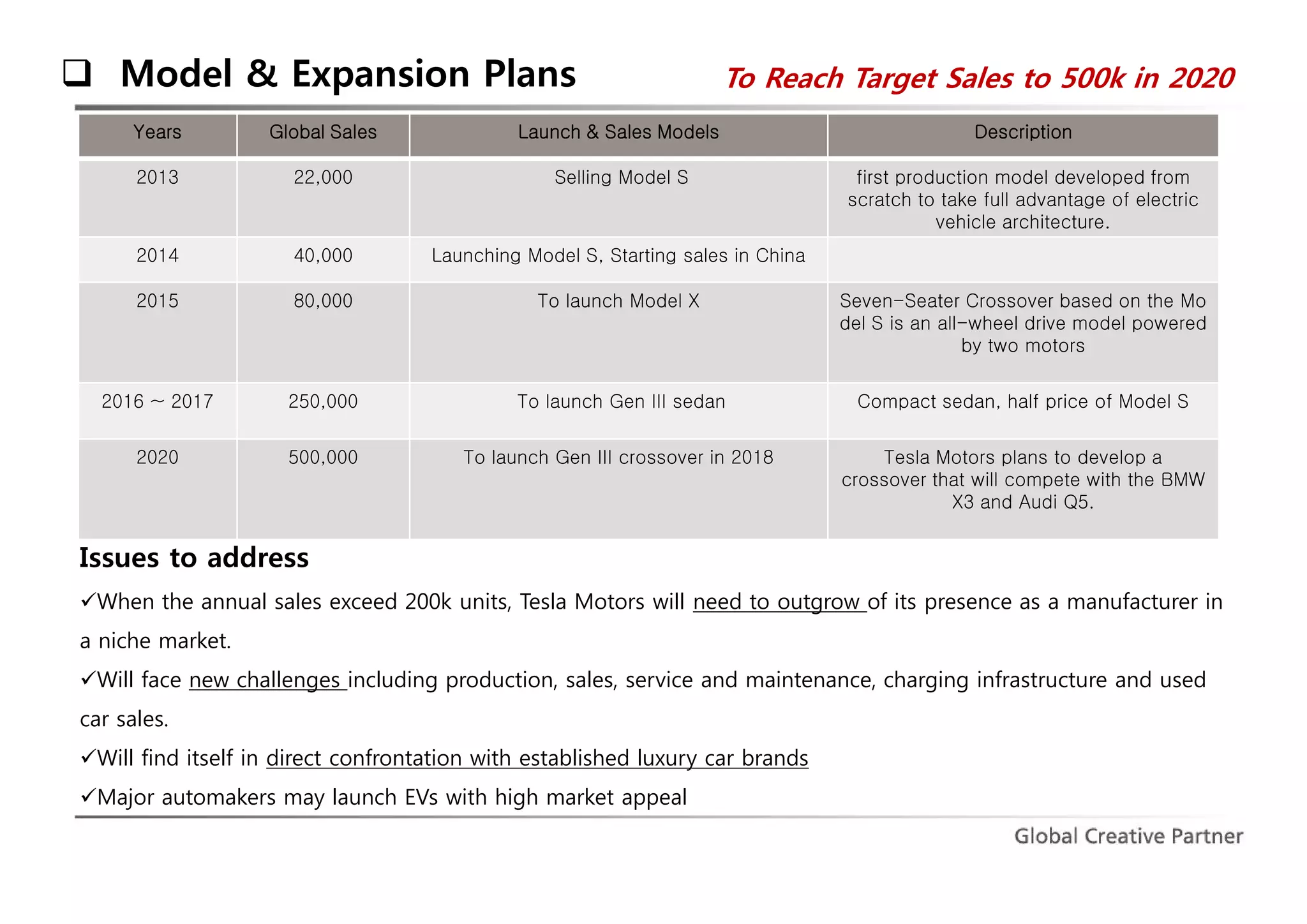
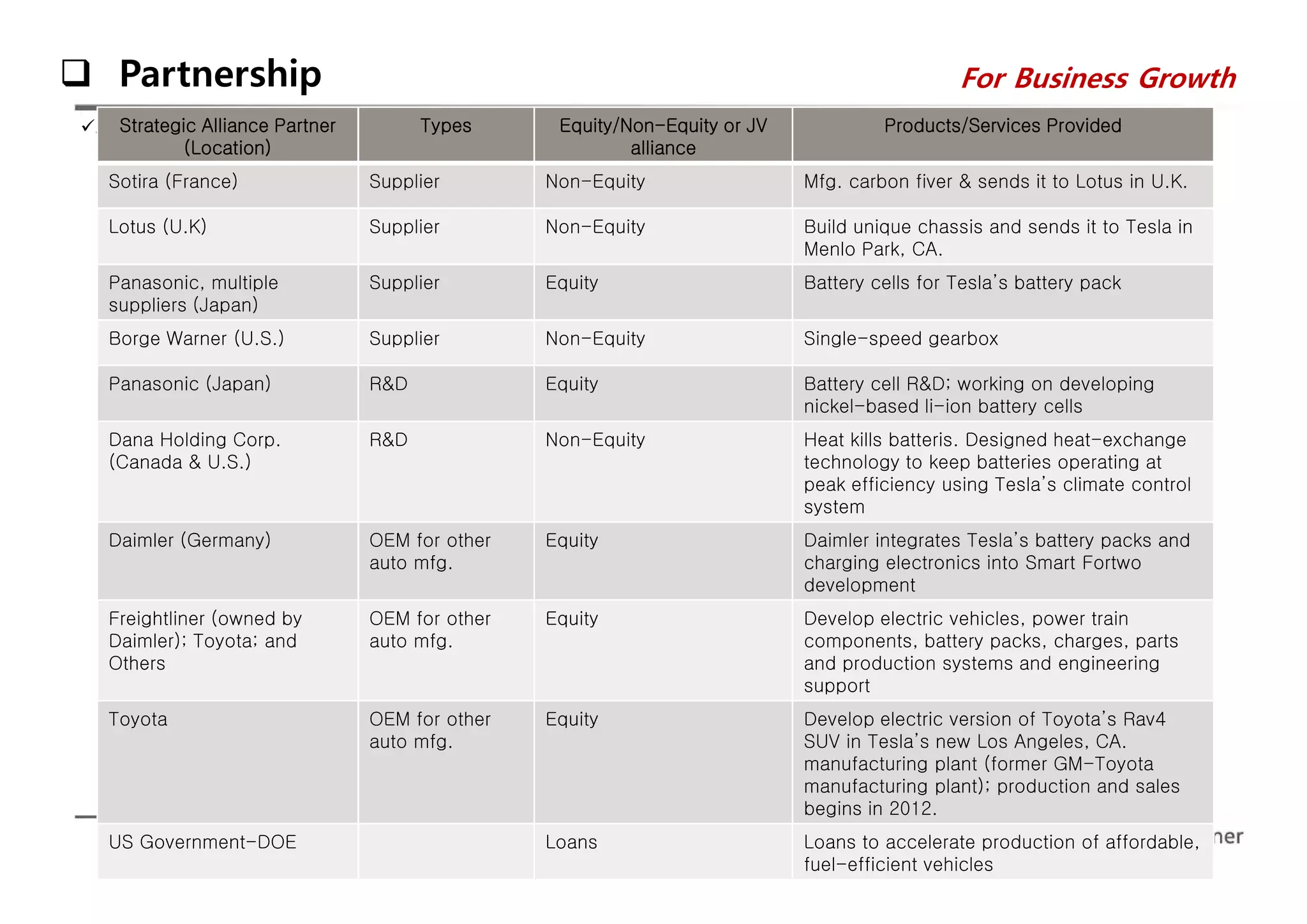
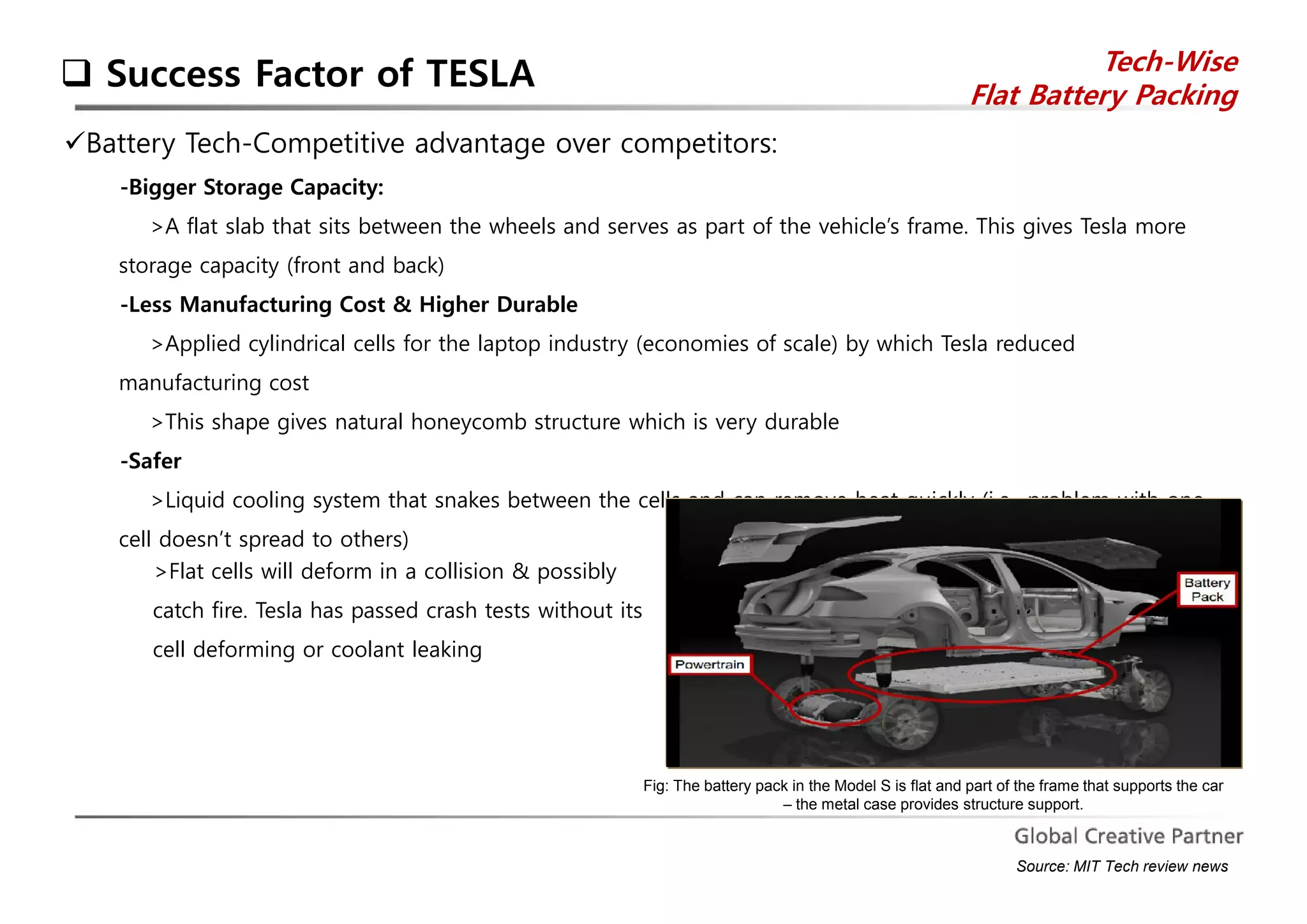
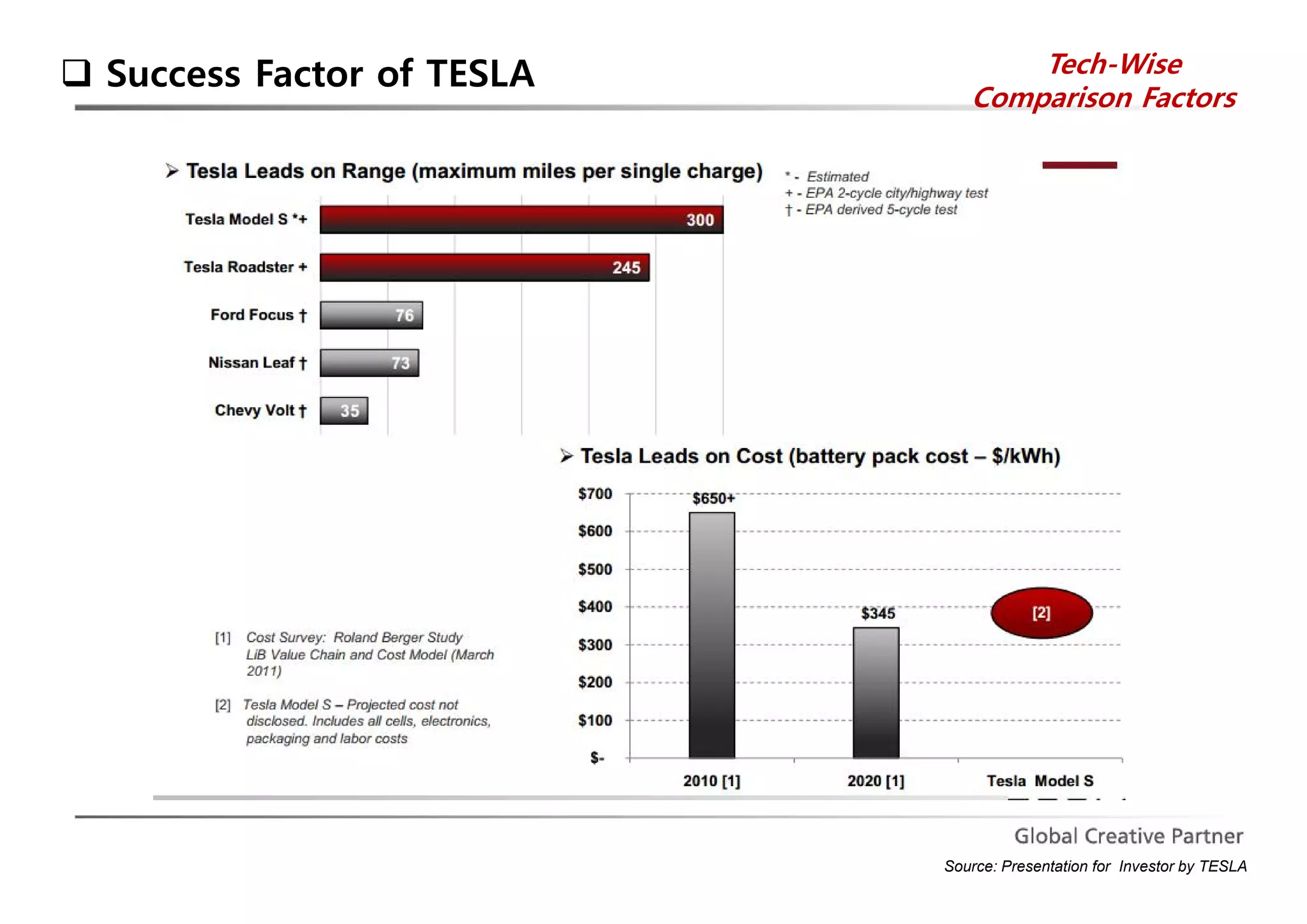
The document is a comprehensive analysis of Tesla's performance, corporate strategy, and growth plans as of 2014, highlighting its profitable operations, strategic partnerships, and innovative marketing approaches. While Tesla achieved significant sales growth and expanded its product offerings, challenges included customer dissatisfaction and regulatory hurdles regarding direct sales. The company aims to produce 500,000 vehicles by 2020 and seeks to strengthen its position through ongoing innovations and global expansion.