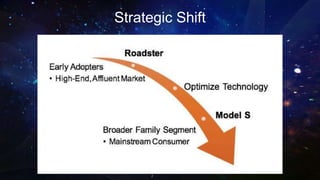
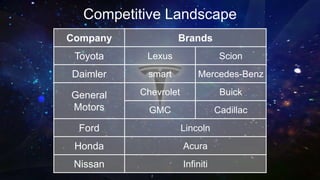
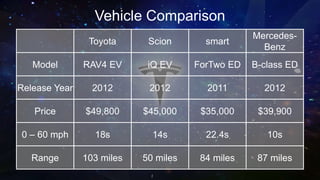
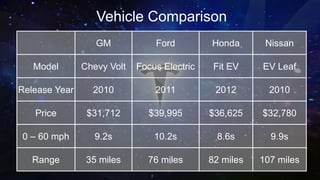
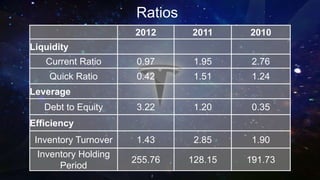
Tesla Motors aims to accelerate sustainable transportation by producing mass-market electric vehicles (EVs) and selling powertrain components. The company faces challenges such as negative net income, high debt leverage, and competition in the EV market while pursuing partnerships with firms like Panasonic and Toyota. Recommendations for Tesla include diversifying its product offerings through hybrid vehicles to mitigate risks and align with its sustainability mission.