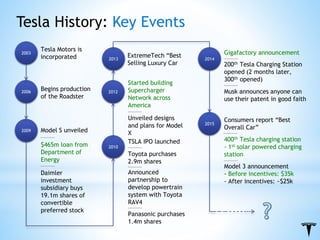
This document summarizes a consulting project report on Tesla. It identifies Tesla's strategic issues as the lack of charging infrastructure making long distance travel inconvenient and the high price of its vehicles limiting its market. Recommendations include cutting costs through economies of scale, creating state incentive programs, partnering to increase charging infrastructure, and increasing lobbying spending to allow direct sales.