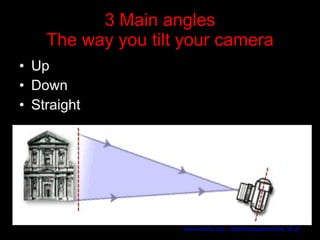
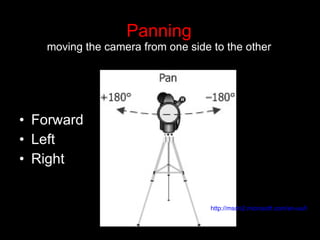
The document provides guidance on basic moviemaking techniques including necessary equipment, camera handling tips, types of shots, angles, distances, and shooting techniques. It discusses software, camera care, establishing shots, close-ups, panning, tilting, zooming, and capturing different levels and angles. Sound equipment options like lavalier and cardioid microphones are also mentioned. Proper camera operation and shot composition are emphasized to help teach students moviemaking skills.