Embed presentation
Downloaded 11 times









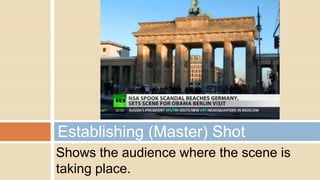















The document discusses different types of camera shots defined by how much of the subject or scene is included in the frame. Shots range from close-ups of just the face to long shots or extreme long shots that show the full body or more of the surrounding environment. It also covers different camera angles like eye-level, high-angle, and low-angle shots. Compositions can combine shots, like an establishing long shot followed by a close-up, or use techniques like over-the-shoulder shots or rule of thirds placement of the subject.























